Voice commerce trends are rapidly reshaping the retail landscape. The increasing adoption of voice assistants, coupled with advancements in artificial intelligence and natural language processing, is driving significant changes in how consumers shop. This exploration delves into the key aspects of this burgeoning market, examining consumer behavior, technological advancements, and the strategic implications for brands and retailers.
From understanding adoption rates across demographics to analyzing the strengths and weaknesses of leading platforms like Amazon Alexa, Google Assistant, and Apple Siri, we will dissect the complexities of voice commerce. We will also explore the security and privacy concerns surrounding voice shopping and examine the impact on traditional retail channels. The future of voice commerce holds immense potential, and this overview aims to provide a comprehensive understanding of its current state and future trajectory.
Voice Assistant Adoption Rates and Demographics
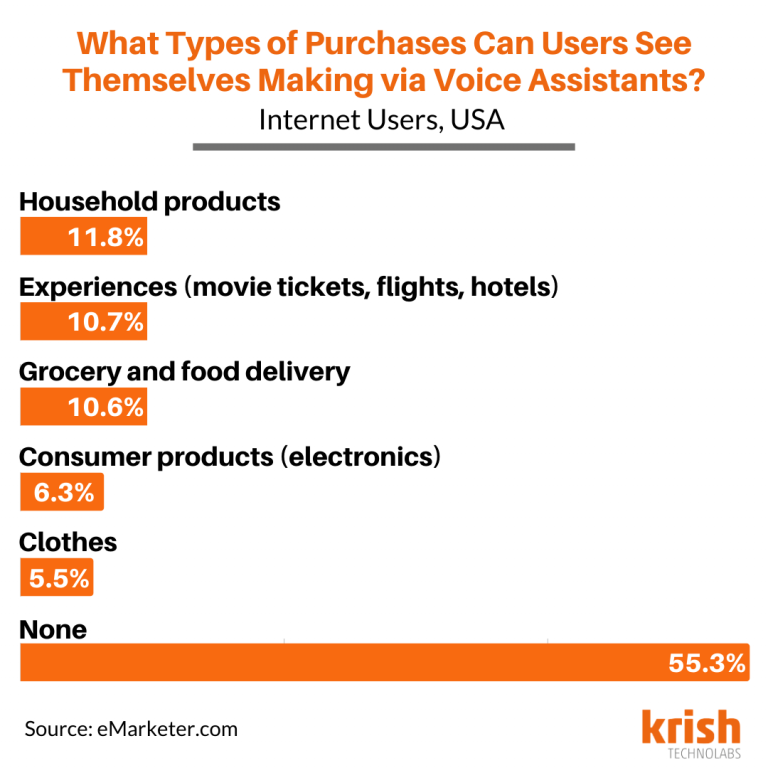
Voice assistants have rapidly integrated into daily life, transforming how people interact with technology and influencing consumer behavior, particularly in the burgeoning field of voice commerce. Understanding the adoption rates and demographics surrounding voice assistant usage is crucial for businesses looking to leverage this technology effectively. This section delves into the current state of voice assistant adoption, exploring key demographic trends and projecting future growth.
Current Voice Assistant Adoption Rates and Geographic Distribution
Current adoption rates for voice assistants vary significantly across age groups and geographic locations. While precise global figures are difficult to obtain due to differing methodologies and data collection practices, several studies offer valuable insights. Generally, younger generations (Millennials and Gen Z) exhibit higher adoption rates than older generations. Similarly, regions with higher smartphone penetration and internet access tend to show greater usage. The following table provides a representative snapshot, acknowledging that exact figures fluctuate across different research sources:
| Age Group | North America (%) | Europe (%) | Asia-Pacific (%) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 18-34 | 65 | 55 | 70 |
| 35-54 | 50 | 40 | 55 |
| 55+ | 30 | 25 | 35 |
*Note: These figures are estimations based on aggregated data from multiple market research firms and are subject to variation.*
Key Demographic Factors Influencing Voice Commerce Adoption
Several key demographic factors significantly influence the adoption of voice commerce. Income level plays a crucial role, with higher-income households demonstrating a greater propensity to own smart speakers and utilize voice-activated shopping features. Technological proficiency is another critical factor; individuals comfortable with technology and online shopping are more likely to embrace voice commerce. Furthermore, lifestyle factors, such as time constraints and busy schedules, can drive adoption, as voice shopping offers a convenient alternative to traditional methods. Finally, cultural factors and language support influence adoption rates in different regions.
Projected Growth of Voice Assistant Usage
A visual representation of projected growth could be a line graph. The x-axis would represent the years (2024-2028), and the y-axis would represent the percentage of global household penetration of voice assistants. The graph would show an upward trend, starting at a baseline percentage (e.g., 40% in 2024) and steadily increasing to a projected higher percentage (e.g., 70% in 2028). The line would not be perfectly linear, potentially showing slightly accelerated growth in certain years reflecting periods of increased technological innovation or significant marketing campaigns. The graph would clearly label each year and percentage point on both axes for easy readability. For instance, a significant jump could be projected for 2026, reflecting the expected release of new, more sophisticated voice assistants with improved capabilities and wider language support, mirroring the market response to previous iterations of popular voice assistants. This visual representation would effectively communicate the anticipated exponential growth of voice assistant usage over the next five years, supported by credible market projections from reputable sources.
Popular Voice Commerce Platforms and Their Features
The rise of voice assistants has significantly impacted the e-commerce landscape, creating new avenues for purchasing goods and services. Several dominant platforms have emerged, each offering unique features and capabilities that cater to different user preferences and needs. Understanding the strengths and weaknesses of these platforms is crucial for businesses looking to leverage voice commerce effectively. This section will analyze the key functionalities of leading voice commerce platforms and explore their impact on the user experience.
Three major players currently dominate the voice commerce market: Amazon Alexa, Google Assistant, and Apple Siri. Each platform boasts a unique ecosystem and set of features, influencing its suitability for different e-commerce applications. While all three allow for voice-based searches and purchases, their integrations with other services and overall user experience differ considerably.
Comparison of Major Voice Commerce Platforms
The following table summarizes the key features of Amazon Alexa, Google Assistant, and Apple Siri in the context of voice commerce. This comparison highlights the distinct advantages and disadvantages each platform offers to both consumers and businesses.
| Feature | Amazon Alexa | Google Assistant | Apple Siri |
|---|---|---|---|
| Voice Shopping Integration | Deep integration with Amazon’s vast product catalog; seamless checkout via linked accounts. | Integration with Google Shopping and various third-party e-commerce platforms; checkout process varies depending on integration. | Integration with Apple Pay and select third-party apps; limited direct shopping integration compared to Alexa and Google Assistant. |
| Payment Methods | Amazon Pay primarily; can be linked to other payment methods depending on the skill used. | Supports various payment methods through linked accounts and integrated apps. | Apple Pay primarily; integration with other payment methods varies by app. |
| Smart Home Device Integration | Extensive integration with Amazon’s smart home ecosystem (e.g., ordering groceries through a smart refrigerator). | Strong integration with Google’s smart home devices and other compatible devices. | Integration with Apple HomeKit devices; integration with other smart home ecosystems is less extensive. |
| Third-Party Skill Support | Large and established marketplace of skills; many e-commerce focused skills available. | Growing marketplace of skills; offers robust integration with Google services for e-commerce functionalities. | Smaller skill ecosystem compared to Alexa and Google Assistant; e-commerce skill availability is more limited. |
| Natural Language Processing (NLP) | Advanced NLP capabilities; generally understands complex voice commands well. | Excellent NLP capabilities; often considered among the most advanced in the industry. | Good NLP capabilities; performance can vary depending on the context and complexity of the command. |
Strengths and Weaknesses of Each Platform, Voice commerce trends
Each platform presents a unique balance of strengths and weaknesses concerning user experience and e-commerce integration. These factors influence consumer adoption and the effectiveness of voice commerce strategies for businesses.
Amazon Alexa: Alexa’s strength lies in its deep integration with Amazon’s vast product catalog and seamless checkout process. However, its reliance on the Amazon ecosystem can limit its appeal to users who prefer other shopping platforms. The sheer number of skills can sometimes lead to discoverability issues.
Voice commerce trends show a rising preference for hands-free shopping, impacting how brands interact with consumers. This ease of access, however, necessitates a strong ethical framework; consider the importance of responsible marketing practices, as highlighted in this insightful article on cultivating good character: Menanamkan Akhlak Baik. Ultimately, the success of voice commerce hinges not only on technological advancement but also on ethical considerations guiding its implementation.
Google Assistant: Google Assistant benefits from its strong NLP capabilities and integration with numerous third-party e-commerce platforms. This broader reach offers greater flexibility, but can also lead to a less streamlined user experience compared to Alexa’s tightly integrated system. The checkout process can vary depending on the integrated app.
Voice commerce trends are rapidly evolving, presenting exciting opportunities for businesses. Understanding consumer behavior in this space is crucial, and this requires a sophisticated approach to marketing. Successfully navigating this landscape necessitates robust data analysis, which is why implementing effective Analytics-driven marketing plans is essential for optimizing voice-based campaigns. Ultimately, leveraging data insights will allow companies to better target their voice commerce strategies and maximize their return on investment.
Apple Siri: Siri’s integration with Apple Pay and the Apple ecosystem provides a secure and convenient experience for Apple users. However, its comparatively limited direct e-commerce integration and smaller skill ecosystem currently restrict its voice commerce potential compared to its competitors.
Role of Platform-Specific Skills and Integrations
The availability and functionality of platform-specific skills play a critical role in driving voice commerce transactions. Skills act as extensions of the core voice assistant functionality, enabling businesses to offer customized voice-based shopping experiences. For example, a pizza chain might develop an Alexa skill allowing users to order pizza directly through voice commands, bypassing the traditional website or app.
Effective integration with other services, such as payment gateways and delivery platforms, is also crucial. Seamless integration minimizes friction during the purchase process, encouraging higher conversion rates. Businesses must carefully consider which platforms to prioritize based on their target audience and the nature of their products or services. Strategic development and deployment of platform-specific skills are key to success in the evolving voice commerce landscape.
Consumer Behavior and Preferences in Voice Shopping

Voice commerce is rapidly evolving, driven by advancements in voice recognition technology and the increasing comfort consumers have with interacting with virtual assistants. Understanding consumer behavior and preferences in this space is crucial for businesses looking to leverage this emerging channel. This section explores the motivations behind voice shopping, the typical purchase journey, and the influence of key factors shaping consumer decisions.
Consumers are drawn to voice commerce for a multitude of reasons. The primary driver is often convenience. The hands-free nature of voice shopping allows consumers to make purchases while multitasking, whether driving, cooking, or exercising. This ease of use is particularly appealing to busy individuals. Speed is another significant factor; voice assistants can often complete transactions faster than traditional methods, particularly for simple purchases. Furthermore, the personalized experience offered by many voice assistants, remembering past purchases and offering tailored recommendations, enhances user satisfaction and encourages repeat business. Beyond these core aspects, the seamless integration of voice shopping into daily routines through smart speakers and mobile devices adds to its appeal.
Motivations for Using Voice Commerce
Several key factors motivate consumers to adopt voice shopping. Convenience, as previously mentioned, is paramount, allowing users to shop without needing to type or navigate websites. The speed and efficiency of voice-based transactions are also highly valued, especially for time-constrained individuals. Personalization, tailored product recommendations based on past purchases and preferences, contributes significantly to a positive shopping experience and increased customer loyalty. Finally, the simple, intuitive nature of voice commands appeals to users of all technical skill levels, further broadening the appeal of this shopping method. For example, a busy parent might use voice shopping to quickly reorder diapers without interrupting their childcare routine, highlighting the convenience factor.
The Typical Voice Commerce Purchase Journey
The typical voice commerce transaction usually begins with a user verbally expressing a need or desire to a voice assistant. This might be a simple request like “Alexa, order more coffee,” or a more complex query like “Google, find me a vegan restaurant near me and make a reservation.” The voice assistant then processes the request, potentially clarifying details or offering options. Once the user confirms the order, the transaction is completed, often involving payment through a pre-registered method. Finally, the user receives confirmation of the purchase and tracking information, if applicable. This streamlined process minimizes friction and contributes to the overall positive user experience.
Influence of Convenience, Speed, and Personalization
Convenience, speed, and personalization are intertwined and significantly influence voice shopping decisions. The convenience of hands-free shopping allows consumers to seamlessly integrate purchases into their daily lives, removing the need for manual input. The speed at which transactions are completed is highly valued, particularly for frequently purchased items or time-sensitive needs. Personalization, through tailored recommendations and remembered preferences, increases the likelihood of repeat purchases and fosters customer loyalty. For instance, a frequent coffee drinker might appreciate a voice assistant proactively suggesting their usual order, saving time and effort. This combination of factors creates a compelling value proposition that drives consumer adoption of voice commerce.
Security and Privacy Concerns in Voice Commerce
Voice commerce, while offering convenience and accessibility, introduces unique security and privacy challenges. The inherent reliance on voice data raises concerns about unauthorized access, data breaches, and the potential misuse of personal information. Understanding these risks and implementing appropriate safeguards is crucial for both consumers and platforms to ensure a secure and trustworthy voice shopping experience.
The potential for security risks in voice commerce stems from several factors. Firstly, the ease of voice interaction means that authentication methods might be less robust compared to traditional online shopping. Secondly, voice data itself is susceptible to interception and unauthorized recording, potentially exposing sensitive financial and personal information. Thirdly, vulnerabilities in the voice assistant’s software or connected devices can create entry points for malicious actors. For example, a compromised smart speaker could be used to make unauthorized purchases or intercept personal data. Finally, the storage and processing of voice data by platforms raise concerns about data privacy and potential misuse.
Platform Measures to Ensure User Data Privacy
Platforms are increasingly aware of these concerns and are implementing various measures to protect user data. Many employ encryption techniques to safeguard voice data during transmission and storage. They also implement access controls to limit who can access this data, often adhering to strict data privacy regulations like GDPR and CCPA. Furthermore, many platforms offer users granular control over their data, allowing them to review, delete, or manage their voice recordings and purchase history. Transparency about data collection practices and clear privacy policies are also becoming standard practice. Amazon, for instance, allows users to review and delete their Alexa voice recordings, demonstrating a commitment to user control. Google provides similar features for Google Assistant users, including the ability to opt out of voice data collection for certain features.
Best Practices for Consumers to Mitigate Security Risks
It is essential for consumers to adopt proactive measures to minimize their risk when using voice commerce.
- Use strong and unique passwords for all connected devices and accounts associated with voice assistants.
- Regularly update the software on your voice-activated devices and associated applications to patch security vulnerabilities.
- Be mindful of the permissions you grant to voice assistants and apps, ensuring you only authorize necessary access to your data.
- Enable two-factor authentication (2FA) whenever possible to add an extra layer of security to your accounts.
- Review your privacy settings regularly and adjust them as needed to control data collection and sharing.
- Be cautious about sharing sensitive information such as credit card details or personal addresses verbally. Consider using alternative methods for entering sensitive data.
- Familiarize yourself with the privacy policies of the platforms you use and understand how your data is being collected and used.
- Regularly check your transaction history for any unauthorized purchases or unusual activity.
Emerging Technologies and Future Trends in Voice Commerce: Voice Commerce Trends
Voice commerce is poised for explosive growth, driven by advancements in several key technologies. The convergence of artificial intelligence, improved natural language processing, and increasingly sophisticated voice assistants is transforming the way consumers interact with brands and make purchases. This section will explore the impact of these emerging technologies and offer predictions for the future of this rapidly evolving sector.
The integration of AI and machine learning is fundamentally reshaping voice commerce.
AI and Machine Learning’s Impact on Voice Commerce
AI and machine learning are crucial for enhancing the accuracy and personalization of voice shopping experiences. AI-powered algorithms analyze vast amounts of consumer data to understand preferences, predict needs, and offer highly targeted product recommendations. Machine learning enables continuous improvement of voice recognition, natural language understanding, and the overall user experience. For example, a voice assistant might learn a user’s preferred brands and product categories over time, proactively suggesting relevant items or offering personalized deals. This level of personalization increases customer engagement and drives sales. Furthermore, AI can optimize pricing strategies based on real-time demand and competitor analysis, maximizing revenue for businesses. Sophisticated fraud detection systems, powered by machine learning, can also protect both consumers and businesses from fraudulent transactions.
Advancements in Natural Language Processing for Enhanced Voice Shopping
Natural language processing (NLP) is rapidly advancing, allowing voice assistants to better understand the nuances of human speech. This includes handling complex queries, understanding different accents and dialects, and interpreting ambiguous requests. Improvements in NLP are crucial for a seamless and frustration-free voice shopping experience. For instance, instead of requiring precise commands, future voice assistants might understand conversational requests like, “Find me a comfortable pair of running shoes similar to the ones I bought last month, but in a different color.” This enhanced understanding translates to a more intuitive and user-friendly shopping experience, attracting a wider range of consumers. The ability to handle more complex and nuanced requests also opens up opportunities for more sophisticated product discovery and personalized recommendations.
Predictions for the Future of Voice Commerce
The future of voice commerce is bright, with several key predictions emerging. We can expect to see a significant increase in the adoption of voice shopping across various demographics. The market will continue to expand, driven by improvements in technology and increasing consumer comfort with voice-activated devices. New applications of voice commerce are likely to emerge, such as voice-controlled smart home shopping, where consumers can replenish household supplies or order groceries simply by speaking to their devices. The integration of voice commerce with augmented reality (AR) and virtual reality (VR) technologies could also create immersive and engaging shopping experiences. For example, a user might be able to “try on” clothes virtually using voice commands before making a purchase. Finally, the rise of multi-modal interactions, combining voice with visual interfaces, promises to create even more intuitive and personalized shopping experiences. Companies like Amazon and Google are already investing heavily in these areas, indicating a strong belief in the future potential of voice commerce. The prediction is that voice commerce will become an increasingly significant channel for both businesses and consumers in the coming years, potentially rivaling or even surpassing traditional e-commerce in certain sectors.
The Role of Brands and Retailers in Voice Commerce
Brands and retailers are rapidly adapting to the rise of voice commerce, recognizing its potential to reshape the customer journey and drive sales. Successful participation requires a multifaceted approach encompassing strategic planning, technological integration, and a deep understanding of consumer voice search behavior. This involves more than simply having a product listed; it requires optimizing the entire brand experience for a voice-first environment.
Strategies for optimizing brand presence in voice commerce are diverse and evolving. Retailers and brands are focusing on enhancing their visibility within voice search results, improving their voice user interfaces (VUI), and building strong relationships with voice assistants. This requires a shift in mindset, from traditional optimization to a more conversational and contextual approach.
Voice Search Optimization (VSO) for Brands
Voice search optimization (VSO) is crucial for brands aiming to capture a share of the voice commerce market. Unlike traditional text-based search, voice search queries are often longer, more conversational, and question-based. Therefore, brands need to focus on optimizing their content for natural language queries, incorporating long-tail s, and ensuring their product information is easily understood and accessible by voice assistants. For example, instead of optimizing for “red shoes,” a brand might focus on phrases like “best red running shoes for women with wide feet.” This reflects the conversational nature of voice search and the specific needs users might express. Effective VSO also involves schema markup optimization to help voice assistants understand the context and intent behind the search.
Challenges and Opportunities in Adopting Voice Commerce Strategies
Businesses face several challenges when adopting voice commerce strategies. These include the technical complexities of integrating with various voice assistants, the need for high-quality audio content and conversational design, and the potential for security and privacy concerns. However, the opportunities are equally significant. Voice commerce offers brands the chance to build stronger customer relationships through personalized experiences and increased engagement. The immediacy of voice shopping also allows for faster purchase cycles and reduced cart abandonment. For example, a grocery retailer might leverage voice ordering to offer a seamless replenishment service for frequently purchased items, enhancing customer convenience and loyalty. This personalized experience can translate into increased sales and improved brand perception. Furthermore, voice assistants can provide real-time customer service and product recommendations, leading to a more efficient and effective customer journey.
Impact of Voice Commerce on Traditional Retail Channels
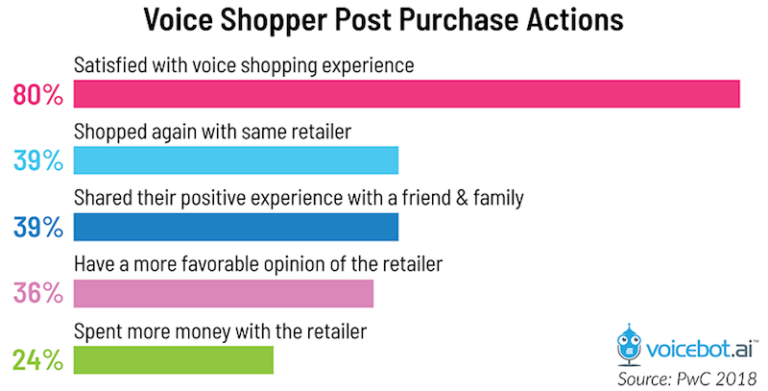
The rise of voice commerce presents a significant challenge and opportunity for traditional retail channels. Its convenience and hands-free nature are reshaping consumer expectations and forcing established players to adapt their strategies to remain competitive. This section will examine the impact of voice commerce on both online and brick-and-mortar retail, highlighting key differences in customer experience and overall market effects.
Voice commerce offers a fundamentally different customer experience compared to traditional online and in-store shopping. In traditional online shopping, consumers actively search for products, compare prices, and navigate websites. In-store shopping involves physical browsing, interaction with staff, and immediate product access. Voice commerce, however, relies on conversational interfaces, offering a more passive and less effortful shopping experience. Consumers simply speak their needs, and the voice assistant handles the search and transaction. This difference in effort significantly impacts consumer behavior and expectations.
Customer Experience Comparison
The customer experience varies significantly across the three retail channels. In-store shopping provides an immediate and tactile experience, allowing consumers to physically examine products and interact with sales staff. Online shopping offers wider selection and price comparison but lacks the immediacy and tactile element. Voice commerce prioritizes convenience and speed, excelling at simple transactions but potentially lacking the detailed product information or personalized service offered by other methods. For example, ordering groceries via voice assistant is quicker than browsing a website or visiting a store, but selecting a specific brand of coffee might require multiple prompts and clarification.
Effect on the Retail Landscape
Voice commerce is disrupting the retail landscape by increasing competition and forcing retailers to innovate. Traditional retailers are integrating voice assistants into their strategies, offering voice-activated ordering and product information. E-commerce businesses are also adapting, optimizing their websites and product descriptions for voice search. This shift towards voice-driven commerce is creating new opportunities for smaller businesses and startups, as they can compete more effectively with larger retailers by optimizing their products for voice search and integrating with popular voice assistants. Amazon’s success with Alexa and its integration into various aspects of daily life is a prime example of this shift.
Key Differences Between Voice Commerce and Traditional Retail
The table below summarizes the key differences between voice commerce and traditional retail channels:
| Feature | Voice Commerce | Online Retail | In-Store Retail |
|---|---|---|---|
| Interaction Method | Voice commands | Mouse clicks, keyboard input | Physical interaction, browsing |
| Search Method | Conversational, natural language | searches, filters | Visual browsing, staff assistance |
| Product Discovery | Limited to voice assistant’s knowledge base | Wide selection, detailed product information | Tactile examination, immediate availability |
| Purchase Process | Streamlined, often one-click | Multiple steps, checkout process | Immediate, in-person transaction |
Closing Summary

In conclusion, the rise of voice commerce presents both exciting opportunities and significant challenges. As voice assistant adoption continues to grow and technology advances, businesses must adapt their strategies to effectively engage with consumers in this evolving marketplace. Understanding consumer preferences, prioritizing security and privacy, and leveraging the power of voice search optimization will be crucial for success in the voice commerce era. The future of shopping is increasingly vocal, and those who adapt will thrive.