Analytics-driven marketing plans are revolutionizing how businesses approach marketing. By leveraging data-driven insights, companies can create more targeted, effective, and ultimately more profitable campaigns. This exploration delves into the core principles, methodologies, and ethical considerations of this transformative approach, showcasing real-world examples and practical strategies for implementation and optimization.
We will examine the crucial role of data collection and analysis, exploring various sources and techniques to extract meaningful information. We’ll then discuss how this data informs the development of targeted marketing strategies across different channels, from email and social media to paid advertising. Finally, we’ll address the importance of attribution modeling, ROI measurement, and ethical considerations to ensure responsible and effective marketing practices.
Defining Analytics-Driven Marketing
Analytics-driven marketing represents a fundamental shift in marketing strategy, moving away from intuition and guesswork towards a data-informed approach. It leverages data analysis to understand customer behavior, optimize campaigns, and ultimately drive better business results. This approach emphasizes measurable outcomes and continuous improvement based on real-time insights.
The core principles of analytics-driven marketing revolve around data collection, analysis, and action. It begins with the meticulous tracking of relevant data points across various marketing channels. This data is then analyzed to identify trends, patterns, and areas for improvement. Finally, these insights inform strategic decisions regarding campaign optimization, targeting, and resource allocation, creating a continuous feedback loop that constantly refines marketing efforts. The success of this methodology hinges on a strong understanding of both the business objectives and the capabilities of the analytical tools employed.
Key Performance Indicators (KPIs) in Analytics-Driven Marketing
Choosing the right KPIs is crucial for effectively measuring the success of an analytics-driven marketing strategy. These metrics provide quantifiable evidence of progress towards defined goals and allow for the identification of areas needing attention. Focusing on the wrong KPIs can lead to misdirected efforts and ultimately, a failure to achieve desired outcomes.
Examples of Successful Analytics-Driven Marketing Strategies, Analytics-driven marketing plans
Many businesses have successfully integrated analytics into their marketing strategies, resulting in significant improvements in efficiency and return on investment. The following table showcases a few examples, highlighting the KPIs they focused on and the positive results they achieved. It’s important to note that the specific KPIs and results will vary greatly depending on the industry, business goals, and the specific marketing campaigns undertaken.
| Company Name | Industry | KPI Focus | Results Achieved |
|---|---|---|---|
| Netflix | Streaming Entertainment | Customer churn rate, watch time, subscriber acquisition cost | Improved customer retention, increased subscriber base, optimized content recommendations. |
| Amazon | E-commerce | Conversion rate, average order value, customer lifetime value | Increased sales, improved website usability, personalized shopping experiences. |
| HubSpot | Marketing Software | Website traffic, lead generation, marketing qualified leads (MQLs) | Expanded market reach, increased lead generation efficiency, improved sales pipeline. |
| Nike | Apparel and Footwear | Website traffic, social media engagement, brand awareness | Enhanced brand image, increased customer loyalty, improved sales through targeted campaigns. |
Data Collection and Analysis Methods: Analytics-driven Marketing Plans

Effective analytics-driven marketing hinges on the ability to collect relevant data from diverse sources and apply appropriate analytical techniques to extract actionable insights. This section details the crucial data sources and analytical methods that form the bedrock of a successful analytics-driven marketing strategy. Understanding these elements is paramount to making data-informed decisions and optimizing marketing campaigns for maximum impact.
Data sources for analytics-driven marketing are numerous and varied, each offering a unique perspective on customer behavior and campaign performance. The selection of data sources depends heavily on the specific marketing objectives and the nature of the business.
Data Sources for Analytics-Driven Marketing
Website analytics, CRM data, and social media insights represent just a fraction of the available data sources. Website analytics platforms like Google Analytics provide detailed information on website traffic, user behavior, and conversion rates. This data reveals which marketing channels are driving the most valuable traffic and which website pages are most effective at converting visitors into customers. CRM systems, on the other hand, offer a comprehensive view of customer interactions, purchase history, and demographics. This allows marketers to segment their audience and tailor their messaging to specific customer groups. Finally, social media platforms provide insights into brand sentiment, audience engagement, and the effectiveness of social media marketing campaigns. Analyzing data from these platforms helps understand audience preferences and refine social media strategies. Other sources include email marketing platforms, market research reports, and even point-of-sale (POS) data from physical stores. The integration of these disparate data sources provides a holistic view of the customer journey and informs comprehensive marketing strategies.
Analytical Techniques for Interpreting Marketing Data
Several analytical techniques can be used to interpret the collected marketing data, each providing unique insights. A/B testing, a fundamental method, allows marketers to compare two versions of a marketing asset (e.g., website landing page, email subject line) to determine which performs better. Cohort analysis groups customers based on shared characteristics (e.g., acquisition date, demographics) to track their behavior over time and identify trends. Regression analysis, a more sophisticated statistical method, identifies relationships between different variables (e.g., advertising spend and sales) to predict future outcomes and optimize marketing investments. Other useful techniques include time series analysis for identifying trends and seasonality in marketing data, and cluster analysis for segmenting customers based on their similarities. The choice of analytical technique depends on the specific marketing question being addressed and the nature of the available data.
Data Collection, Analysis, and Interpretation Process Flowchart
The process of collecting, analyzing, and interpreting marketing data can be visualized as a flowchart.
The flowchart begins with *Data Collection*, encompassing various sources mentioned previously (website analytics, CRM, social media, etc.). This data is then *Cleansed and Prepared*, involving tasks like data validation, handling missing values, and data transformation. Next, *Data Analysis* is performed using appropriate techniques (A/B testing, cohort analysis, regression, etc.) to identify patterns and trends. The results of the analysis are then *Interpreted* to draw actionable insights. These insights then inform *Marketing Strategy Optimization*, leading to adjustments in campaigns and future data collection strategies. The process is iterative, with insights from each cycle feeding back into subsequent data collection and analysis. This cyclical nature ensures continuous improvement and optimization of marketing efforts. A visual representation would show these steps in a linear progression with feedback loops indicating the iterative nature of the process.
Developing Marketing Strategies Based on Data

Data-driven marketing transcends guesswork; it leverages insights gleaned from analyzing customer behavior, market trends, and campaign performance to craft highly effective strategies. By understanding the “why” behind customer actions, businesses can optimize their marketing efforts, maximizing ROI and fostering stronger customer relationships. This approach moves beyond broad strokes, allowing for precise targeting and personalized messaging that resonates deeply with individual customer segments.
Data insights are fundamental to crafting targeted marketing campaigns. For example, analyzing website analytics might reveal that a specific demographic segment frequently abandons their shopping carts. This data point suggests an opportunity to implement targeted retargeting campaigns, perhaps offering personalized discounts or highlighting frequently asked questions to alleviate concerns and encourage completion of purchases. Similarly, social media listening tools can identify trending topics relevant to the brand, allowing for timely and relevant content creation that capitalizes on current conversations.
Targeted Marketing Campaign Examples
Analyzing customer data allows for the creation of highly targeted marketing campaigns. For instance, a clothing retailer might segment its customer base by age, gender, purchasing history, and browsing behavior. This allows them to tailor their messaging and product recommendations. Younger customers might receive promotions highlighting trendy styles, while older customers might see advertisements for classic, timeless pieces. Email marketing becomes particularly powerful with segmentation, allowing for personalized subject lines and email content that increases open and click-through rates. A campaign promoting a new line of running shoes could target customers with a history of purchasing athletic wear, using location data to further refine targeting based on proximity to running trails or gyms.
Marketing Channels Benefiting from an Analytics-Driven Approach
Various marketing channels thrive when powered by data analysis. Email marketing, for example, benefits immensely from A/B testing subject lines, content, and call-to-actions. Analyzing open rates, click-through rates, and conversion rates provides invaluable insights into what resonates best with the target audience. Social media marketing similarly benefits from data analysis, enabling precise targeting based on demographics, interests, and behaviors. Paid advertising campaigns, whether on Google, social media, or other platforms, are highly dependent on data-driven optimization. Real-time performance tracking allows for continuous adjustments to bidding strategies, targeting parameters, and ad creatives to maximize ROI. Analyzing campaign performance data allows marketers to identify high-performing s, demographics, and ad copy variations, refining campaigns for better results.
Comparison of Marketing Strategy Effectiveness
The effectiveness of different marketing strategies is best evaluated through data analysis. Several key strategies and their respective advantages and disadvantages are listed below:
The following table compares different marketing strategies based on their advantages and disadvantages, highlighting the importance of data analysis in evaluating effectiveness:
| Marketing Strategy | Advantages | Disadvantages |
|---|---|---|
| Email Marketing | High personalization potential, cost-effective, measurable results | Requires a robust email list, potential for spam filters, declining open rates |
| Social Media Marketing | Large reach, engagement opportunities, targeted advertising | Algorithm changes, competitive landscape, requires consistent effort |
| Paid Advertising (PPC) | Fast results, precise targeting, measurable ROI | Can be expensive, requires ongoing optimization, competitive bidding |
| Content Marketing | Builds brand authority, attracts organic traffic, long-term value | Requires consistent effort, takes time to see results, difficult to measure direct ROI |
| Search Engine Optimization () | Drives organic traffic, long-term value, cost-effective | Takes time to see results, algorithm changes, competitive landscape |
Implementing and Monitoring Marketing Plans
Implementing an analytics-driven marketing plan requires a systematic approach that blends strategic planning with continuous monitoring and adaptation. Success hinges on effectively translating data insights into actionable strategies and then meticulously tracking the results to refine future campaigns. This iterative process ensures the marketing efforts remain aligned with achieving pre-defined objectives.
The process of implementing an analytics-driven marketing plan involves several key phases, from initial setup to ongoing optimization. It’s not a one-time action but a continuous cycle of refinement based on performance data. Effective implementation demands a clear understanding of the target audience, chosen channels, and key performance indicators (KPIs).
Campaign Implementation and Execution
Implementing the plan involves deploying the strategies across chosen marketing channels. This includes scheduling social media posts, launching email campaigns, managing paid advertising, and optimizing website content based on the data-driven insights gathered during the planning phase. For example, if data reveals a strong preference for video content among the target demographic, the implementation phase would prioritize creating and distributing high-quality video materials across relevant platforms. Similarly, if A/B testing indicated a higher click-through rate for a specific ad copy, that variation would be prioritized in subsequent ad campaigns. This ensures resources are allocated efficiently towards the most effective strategies.
Tracking Campaign Performance and Making Adjustments
Tracking campaign performance is crucial for determining the effectiveness of implemented strategies and making necessary adjustments. A step-by-step guide for this process is as follows:
- Define Key Performance Indicators (KPIs): Before launching any campaign, clearly define the KPIs that will measure success. These could include website traffic, conversion rates, customer acquisition cost (CAC), return on ad spend (ROAS), and brand awareness metrics. Selecting relevant KPIs depends on the campaign objectives.
- Establish a Monitoring System: Implement a system to track the defined KPIs in real-time. This may involve using analytics platforms like Google Analytics, social media analytics dashboards, and marketing automation tools. Regular monitoring allows for prompt identification of any deviations from the planned performance.
- Analyze Data and Identify Trends: Regularly analyze the collected data to identify trends and patterns. This involves comparing actual performance against projected targets and examining the data for any significant variations. For example, if the conversion rate is significantly lower than expected, a detailed analysis can pinpoint the potential causes.
- Make Necessary Adjustments: Based on the data analysis, make necessary adjustments to the marketing strategies. This could involve modifying ad creatives, adjusting targeting parameters, optimizing website content, or altering the messaging. Agility and responsiveness are key to maximizing campaign effectiveness.
- Document Findings and Iterate: Meticulously document all findings, adjustments made, and their impact on performance. This documentation serves as a valuable resource for future campaigns and helps refine the overall marketing strategy. The entire process is iterative; learnings from one campaign inform the next.
Sample Marketing Plan Integrating Data Analysis
This sample plan demonstrates the integration of data analysis throughout the marketing process. It focuses on a hypothetical company launching a new product: “SmartHome Hub.”
| Stage | Data Analysis Integration | Actionable Insights |
|---|---|---|
| Market Research | Analyzing demographic data, competitor analysis, and social media listening to understand target audience preferences and market trends. | Identify key customer segments (e.g., tech-savvy homeowners, families with young children) and their needs. Determine competitive advantages and areas for differentiation. |
| Strategy Development | Analyzing website analytics to identify high-performing content and channels. Examining customer journey maps to understand customer behavior and pain points. | Prioritize marketing channels based on past performance and potential ROI. Develop targeted messaging that resonates with specific customer segments and addresses their needs. |
| Campaign Execution | A/B testing different ad creatives and landing pages to optimize conversion rates. Tracking campaign performance in real-time using analytics dashboards. | Identify high-performing ad variations and landing page designs. Make real-time adjustments to maximize campaign effectiveness. |
| Performance Evaluation | Analyzing post-campaign data to evaluate ROI and identify areas for improvement. Comparing campaign performance against benchmarks and industry averages. | Identify successful strategies and areas needing refinement. Refine marketing strategies for future campaigns based on the lessons learned. |
Attribution Modeling and ROI Measurement
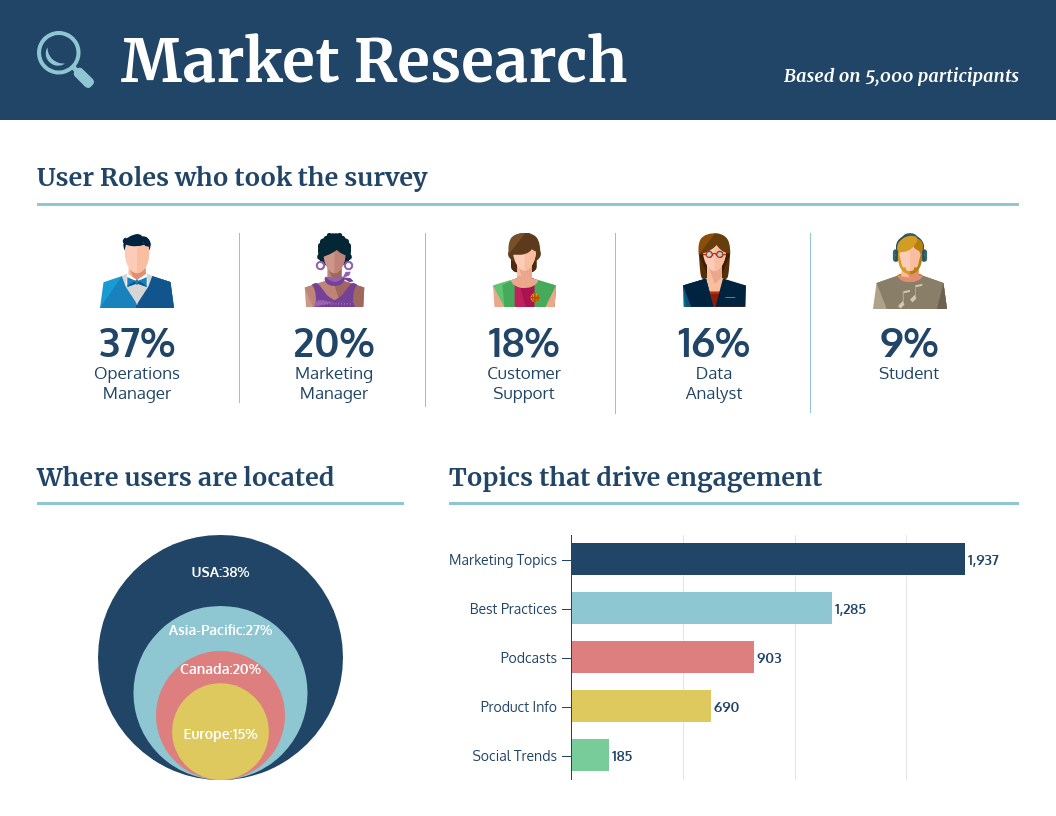
Understanding how different marketing touchpoints contribute to conversions and ultimately, return on investment (ROI), is crucial for optimizing marketing spend. Attribution modeling helps us assign credit for conversions across various channels, while ROI calculations quantify the effectiveness of our campaigns. This section will explore various attribution models and methods for calculating ROI, along with visualization techniques to effectively communicate these results.
Attribution Models
Different attribution models assign varying levels of credit to different touchpoints involved in a customer’s journey. Choosing the right model depends on the specific marketing goals and the nature of the customer journey. For instance, a last-click model assigns all credit to the final interaction before conversion, while a multi-touch model distributes credit across multiple touchpoints. The selection of an appropriate model significantly impacts the insights derived and subsequent marketing decisions.
Calculating Return on Investment (ROI)
Calculating ROI for marketing campaigns involves comparing the net profit generated from a campaign to the cost of the campaign. A simple formula is:
ROI = (Net Profit / Cost of Investment) x 100%
. Net profit is calculated by subtracting the cost of goods sold and marketing expenses from the revenue generated. More sophisticated ROI calculations might consider factors like customer lifetime value (CLTV) to provide a more holistic view of campaign profitability. For example, a campaign costing $10,000 that generates $25,000 in revenue (after accounting for costs) would have an ROI of 150%.
Dashboard Visualization of Key Metrics and ROI
Data visualization is key to effectively communicating the performance of marketing initiatives. Dashboards provide a consolidated view of key metrics and ROI, enabling quick identification of successful and underperforming campaigns. The following table illustrates how different metrics can be visualized:
| Metric | Data Source | Calculation Method | Visualization Type |
|---|---|---|---|
| Website Conversions | Google Analytics | Count of completed conversions (e.g., purchases, form submissions) | Bar chart showing conversions per campaign |
| Cost Per Acquisition (CPA) | Marketing Platform Data (e.g., Google Ads, Facebook Ads) | Total Campaign Cost / Number of Conversions | Line graph showing CPA over time |
| Customer Lifetime Value (CLTV) | CRM Data, Transactional Data | Sum of predicted future revenue from a customer minus the cost of acquiring and retaining that customer | Heatmap showing CLTV segments |
| Return on Ad Spend (ROAS) | Marketing Platform Data, Sales Data | Revenue Generated / Advertising Spend | Pie chart showing ROAS breakdown by campaign |
Ethical Considerations and Data Privacy

The ethical use of data in analytics-driven marketing is paramount. Building trust with customers requires transparency and respect for their privacy. Failing to prioritize these aspects can lead to reputational damage, legal repercussions, and ultimately, the erosion of customer loyalty. This section Artikels key ethical considerations and practical steps for responsible data handling.
Data privacy is not merely a compliance issue; it’s a fundamental ethical obligation. Regulations like the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) in Europe and the California Consumer Privacy Act (CCPA) in the US mandate specific requirements for data collection, storage, and usage. Compliance ensures that individuals retain control over their personal information and are protected from misuse. Ignoring these regulations can result in significant fines and legal action. Furthermore, ethical data handling fosters a culture of trust, strengthening the relationship between businesses and their customers.
Data Collection Transparency and Consent
Transparency is key to ethical data collection. Consumers should be clearly informed about what data is being collected, why it’s being collected, how it will be used, and who will have access to it. This information should be readily accessible and presented in a clear, concise, and understandable manner, avoiding technical jargon. Obtaining explicit consent before collecting and using personal data is crucial, ensuring individuals are aware and agree to the data processing activities. This consent must be freely given, specific, informed, and unambiguous. For example, a website might clearly state in its privacy policy that it collects IP addresses and cookie data for analytics purposes and that users can opt out of this data collection by disabling cookies in their browser settings.
Data Security and Protection
Robust security measures are essential to protect collected data from unauthorized access, use, disclosure, alteration, or destruction. This involves implementing appropriate technical and organizational safeguards, such as encryption, access controls, and regular security audits. Data breaches can have devastating consequences for both businesses and individuals, leading to financial losses, reputational damage, and legal liabilities. Companies should invest in comprehensive security systems and regularly update their security protocols to stay ahead of evolving threats. For example, implementing multi-factor authentication and regularly backing up data can significantly reduce the risk of data breaches.
Data Minimization and Purpose Limitation
Only collect the minimum amount of data necessary to achieve the specified marketing objectives. Avoid collecting unnecessary or excessive data. Data should only be used for the purposes explicitly stated at the time of collection, unless the individual provides consent for other uses. For example, if a company is collecting email addresses for newsletter subscriptions, they shouldn’t use that data for targeted advertising without obtaining explicit consent from subscribers.
Data Retention and Disposal
Establish clear data retention policies, specifying how long data will be stored and under what conditions it will be deleted. Data should be securely deleted or anonymized when it’s no longer needed for the specified purpose. This aligns with principles of data minimization and helps mitigate risks associated with data breaches and outdated information. For instance, a company might retain customer purchase history for a certain period for warranty claims but delete the data after that period.
Ethical Data Handling Checklist
Prior to any data collection or usage activity, review this checklist:
- Is the data collection transparent and have we obtained explicit consent?
- Are appropriate security measures in place to protect data from unauthorized access?
- Is the data being collected minimized and used only for its intended purpose?
- Do we have a clear data retention and disposal policy?
- Have we conducted a data protection impact assessment (DPIA) where required?
- Are we complying with all relevant data privacy regulations (e.g., GDPR, CCPA)?
- Do we have a process for handling data subject requests (e.g., access, correction, deletion)?
Future Trends in Analytics-Driven Marketing
The landscape of marketing is undergoing a rapid transformation, driven by the ever-increasing availability and sophistication of data analytics tools. Emerging technologies are not only enhancing our ability to understand customer behavior but are also reshaping the very strategies marketers employ to reach and engage their audiences. This section explores key future trends and their implications for effective marketing campaigns.
The convergence of artificial intelligence (AI), machine learning (ML), and predictive analytics is poised to revolutionize how marketers operate. These technologies offer unprecedented capabilities for personalization, automation, and predictive modeling, leading to more efficient and effective campaigns. The increased processing power and availability of large datasets are key drivers of this transformation.
Impact of AI, Machine Learning, and Predictive Analytics on Marketing Strategies
AI, ML, and predictive analytics are fundamentally altering marketing strategies by enabling hyper-personalization, automating repetitive tasks, and improving campaign effectiveness through predictive modeling. AI-powered chatbots, for example, provide instant customer support and personalized recommendations, significantly improving customer experience and engagement. Machine learning algorithms analyze vast amounts of data to identify patterns and predict future behavior, allowing marketers to optimize campaigns in real-time and personalize messaging at scale. Predictive analytics allows for proactive campaign adjustments based on anticipated customer responses, leading to higher conversion rates and improved ROI. For instance, a retailer might use predictive analytics to anticipate demand for specific products based on weather patterns, historical sales data, and social media trends, optimizing inventory and preventing stockouts.
Innovative Applications of Data Analytics in Marketing
The application of data analytics extends far beyond basic campaign tracking. Innovative applications are emerging across various marketing functions, enhancing efficiency and effectiveness.
- Real-time Personalization: Marketers can dynamically adjust website content, email messaging, and ad creatives based on individual customer behavior and preferences in real-time, leading to highly targeted and relevant experiences. For example, an e-commerce website might display product recommendations based on a customer’s browsing history and past purchases.
- Programmatic Advertising Optimization: AI-powered platforms automate the buying and placement of digital ads, optimizing campaigns based on real-time data and performance metrics. This ensures that ads are shown to the most relevant audiences, maximizing reach and minimizing wasted ad spend. A company launching a new product could use programmatic advertising to target specific demographics and interests based on their online behavior, ensuring efficient budget allocation.
- Sentiment Analysis and Social Listening: Analyzing social media conversations and customer reviews allows marketers to gauge public opinion, identify emerging trends, and proactively address negative feedback. This provides valuable insights into customer sentiment and brand perception, allowing for informed decision-making and proactive crisis management. For example, a brand might use sentiment analysis to monitor social media for mentions of their brand, identifying both positive and negative comments to better understand public perception and tailor their messaging accordingly.
Final Wrap-Up
In conclusion, the adoption of analytics-driven marketing plans represents a significant shift towards a more data-informed and efficient approach to marketing. By embracing data-driven strategies, businesses can optimize campaigns, improve ROI, and foster stronger customer relationships. The ongoing evolution of technology, particularly in AI and machine learning, promises to further enhance the power and precision of analytics-driven marketing, creating even greater opportunities for growth and success in the years to come. Mastering this approach is not merely an advantage; it’s a necessity for thriving in today’s competitive landscape.
Effective analytics-driven marketing plans rely on data-backed strategies to optimize campaigns. However, the ultimate success often hinges on ethical considerations, mirroring the importance of cultivating good character, as highlighted in this insightful article on Menanamkan Akhlak Baik. Similarly, responsible data usage and transparent marketing practices are crucial for building lasting customer trust and achieving long-term growth in analytics-driven marketing.
Effective analytics-driven marketing plans hinge on understanding customer behavior, and a key element of that is the checkout experience. Offering a variety of convenient payment methods is crucial for conversions, which is why thoroughly researching options like those detailed at E-commerce payment options is vital. Ultimately, optimizing payment options directly impacts your analytics and refines future marketing strategies.