Technology-driven growth represents a paradigm shift in global economic development. It’s not merely about faster computers or smarter phones; it’s a fundamental restructuring of industries, societies, and even our environment. This analysis explores the multifaceted nature of this growth, examining its drivers, measurement, challenges, and future trajectory. We’ll delve into specific case studies and explore how technological advancements are reshaping our world, both for better and for worse.
Understanding technology-driven growth requires a multidisciplinary approach. We must consider the interplay of technological innovation, infrastructure development, and strategic investments, as well as the crucial role of government policy and regulation. Equally important is a careful assessment of both the positive and negative consequences, including the potential for job displacement and the need for ethical considerations in technological deployment. By examining these aspects, we can gain a more nuanced perspective on the opportunities and challenges that lie ahead.
Defining Technology-Driven Growth
Technology-driven growth represents a significant paradigm shift in economic development, moving beyond traditional models reliant solely on capital accumulation and labor. It signifies a form of expansion fueled by technological innovation, impacting various aspects of society and the environment. This growth isn’t simply about increased production; it’s about transforming processes, creating new markets, and fundamentally altering how we live and interact.
Technology-driven growth is characterized by its multifaceted nature, encompassing economic, social, and environmental consequences. Economically, it leads to increased productivity, efficiency gains, and the creation of new industries and jobs. Socially, it can improve living standards, enhance communication, and foster greater access to information and services. Environmentally, however, the impact is more complex, with both positive (e.g., sustainable energy technologies) and negative (e.g., e-waste) consequences requiring careful consideration.
Key Characteristics of Technology-Driven Growth
Technology-driven growth differs from other forms of economic expansion primarily through its reliance on innovation as the central driver. Unlike growth fueled by increased resource extraction or population growth, technology-driven growth focuses on improving existing processes and creating entirely new ones. This leads to a higher rate of productivity growth and often involves the creation of entirely new industries and markets, unlike expansions based on exploiting existing resources. The process is also often characterized by rapid technological diffusion, leading to quick adoption and widespread impact across various sectors.
Industries Significantly Impacted by Technology-Driven Growth
The following table illustrates several industries profoundly impacted by technology-driven growth:
| Industry | Specific Technological Impact | Economic Effects | Social Effects |
|---|---|---|---|
| Healthcare | Telemedicine, AI-driven diagnostics, personalized medicine, robotic surgery | Increased efficiency, reduced costs, new treatment options, expansion of healthcare access | Improved patient outcomes, increased life expectancy, greater convenience for patients |
| Finance | Fintech, blockchain technology, algorithmic trading, mobile banking | Increased financial inclusion, improved efficiency in transactions, new financial products and services | Greater access to financial services, faster and more secure transactions, enhanced financial literacy |
| Manufacturing | Automation, robotics, 3D printing, IoT-enabled production | Increased productivity, reduced labor costs, improved quality control, customized production | Job displacement in some areas, creation of new jobs in technology-related fields, potential for reskilling initiatives |
| Transportation | Autonomous vehicles, ride-sharing apps, electric vehicles, drone delivery | Increased efficiency in logistics, reduced transportation costs, new transportation options | Improved traffic flow, reduced emissions, increased accessibility for some populations |
Drivers of Technology-Driven Growth
Technology-driven growth is not a monolithic phenomenon; rather, it’s a complex interplay of several key drivers. Understanding these drivers is crucial for policymakers, businesses, and individuals seeking to navigate and benefit from the ongoing technological revolution. This section will examine the primary technological advancements propelling current growth trajectories, analyzing the roles of innovation, infrastructure, and investment, and exploring the impact of government policies and regulations.
Technological advancements are fundamentally reshaping industries and economies. Artificial intelligence (AI), machine learning (ML), the Internet of Things (IoT), and advanced data analytics are prominent examples. AI, for instance, is automating tasks, improving decision-making, and creating entirely new products and services across sectors from healthcare to finance. The proliferation of IoT devices generates vast amounts of data, fueling the development of more sophisticated analytics capabilities. These technologies, in conjunction with others like blockchain and quantum computing (still in its early stages but with immense potential), are collectively driving significant productivity gains and fostering innovation.
The Interplay of Innovation, Infrastructure, and Investment, Technology-driven growth
Innovation, infrastructure, and investment are intrinsically linked in driving technological progress. Innovation provides the ideas and solutions; infrastructure provides the necessary physical and digital platforms for implementation and scaling; and investment provides the financial resources needed to fund research, development, and deployment. Consider the development of 5G networks: innovation in wireless communication technologies was essential, but it required massive infrastructure investments in new towers, equipment, and network architecture. Furthermore, significant private and public investment was crucial to make 5G a reality, demonstrating the synergistic relationship between these three factors. A lack of any one element significantly hampers progress. For example, groundbreaking innovations in renewable energy technologies might remain largely theoretical without sufficient infrastructure to support their widespread adoption and the necessary investment to bring them to market at scale.
Government Policies and Regulations
Government policies and regulations play a crucial role in shaping the landscape of technology-driven growth. Supportive policies can foster innovation by providing incentives for research and development (R&D), such as tax breaks for technology companies or grants for university research projects. Furthermore, regulations can ensure fair competition, protect consumer interests, and address potential negative externalities of technological advancements, such as data privacy concerns. For example, the European Union’s General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) has significantly influenced how companies collect, store, and process personal data, prompting a global shift towards more responsible data practices. Conversely, overly restrictive regulations or a lack of clear regulatory frameworks can stifle innovation and hinder technological progress. Finding the right balance between fostering innovation and ensuring responsible development is a continuous challenge for governments worldwide. The success of technology hubs like Silicon Valley often points to a supportive regulatory environment that allows for experimentation and risk-taking while also addressing potential downsides.
Measuring Technology-Driven Growth
Accurately measuring the impact of technology on economic growth and societal well-being is crucial for informed policymaking and strategic investment. A comprehensive framework must consider not only the direct economic contributions but also the broader social and environmental consequences. This requires a multi-faceted approach, utilizing a range of quantitative and qualitative metrics to capture the complex interplay between technology and development.
Successfully measuring technology-driven growth necessitates a nuanced understanding of its multifaceted nature. It’s not simply about calculating the GDP contribution of the tech sector; instead, it requires analyzing how technology permeates various industries, boosting productivity, creating new markets, and reshaping existing economic structures. Furthermore, assessing the social and environmental implications requires careful consideration of factors like job displacement, inequality, and resource consumption.
Economic Contribution Measurement Framework
A robust framework for measuring the economic contribution of technology should encompass several key aspects. First, it should differentiate between the direct and indirect economic impacts. Direct impacts include the revenue generated by the technology sector itself, while indirect impacts encompass the increased productivity and efficiency in other sectors due to technological adoption. Second, it should account for the multiplier effect, where the initial investment in technology generates further economic activity through job creation and supply chain expansion. Third, it needs to consider the long-term effects of technological innovation, including its impact on future economic growth and competitiveness. For example, the development of the internet spurred the growth of e-commerce and countless other digital services, leading to a significant boost in global GDP. Similarly, advancements in manufacturing technology have led to increased efficiency and reduced production costs across many industries. Finally, a geographical breakdown, assessing regional variations in technological impact, is essential for targeted policy interventions.
Quantifying Social and Environmental Consequences
Quantifying the social and environmental consequences of technology-driven growth requires a multi-dimensional approach. Social metrics might include changes in employment rates (both job creation and displacement), income inequality, access to education and healthcare, and social inclusion. For instance, automation technologies can lead to job losses in certain sectors, while creating new opportunities in others. Careful analysis is required to understand the net impact and develop strategies to mitigate negative consequences, such as retraining programs for displaced workers. Environmental metrics would include greenhouse gas emissions, resource depletion, waste generation, and biodiversity loss. For example, the manufacturing of electronic devices often involves the extraction of rare earth minerals, which can have significant environmental impacts. Life cycle assessments (LCAs) can be used to quantify the environmental footprint of different technologies across their entire lifespan. Further, a metric focusing on digital equity – access to and usage of technology – is crucial for ensuring inclusive growth.
Metrics for Assessing Sustainability of Technology-Driven Development
Assessing the sustainability of technology-driven development requires a set of metrics that integrate economic, social, and environmental considerations. These metrics should measure not only current performance but also the long-term viability and resilience of the system. Examples include the carbon footprint of technological innovations, the circularity of technological systems (e.g., the recyclability of electronic devices), and the resilience of technological infrastructure to climate change. A widely used metric is the Environmental Performance Index (EPI), which ranks countries based on their environmental performance. Another important consideration is the societal impact of AI development, particularly concerning issues of bias and fairness. The development of ethical guidelines and responsible AI frameworks are crucial for ensuring that technological advancements contribute to a more equitable and sustainable future. Furthermore, indicators measuring the durability and repairability of technological products, promoting a shift away from planned obsolescence, are critical for long-term sustainability.
Challenges and Risks of Technology-Driven Growth
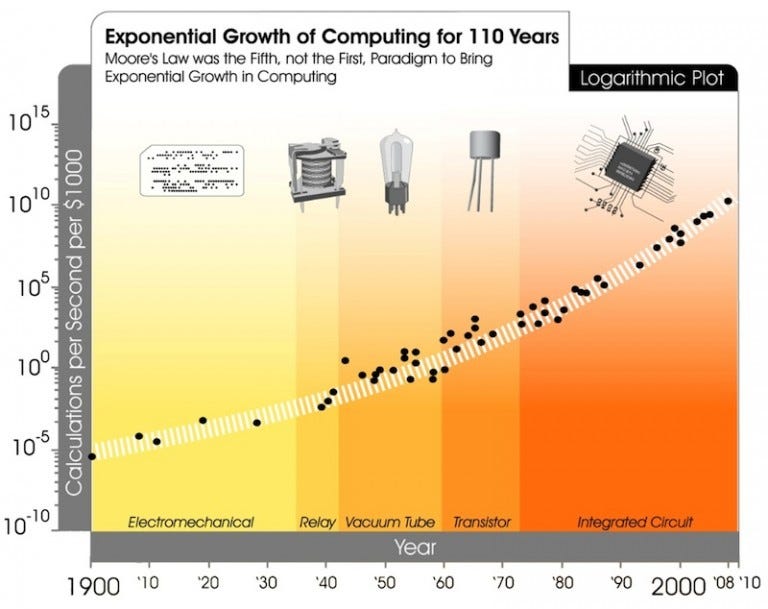
The relentless pursuit of technological advancement, while offering immense potential for progress, also presents a complex array of challenges and risks. Rapid technological change disrupts established industries and societal structures, leading to unforeseen consequences that require careful consideration and proactive mitigation strategies. Ignoring these risks could exacerbate existing inequalities and create new societal problems.
Technological advancements, while beneficial, often come with significant downsides. The rapid pace of innovation can outstrip our ability to adapt, creating social and economic disruptions.
Job Displacement and Inequality
Automation and artificial intelligence are rapidly transforming the job market, leading to significant job displacement in certain sectors. While new jobs are created, they often require different skills and educational levels, leaving many workers behind. This widening skills gap contributes to increased income inequality, potentially exacerbating social unrest and hindering overall economic growth. For example, the rise of automation in manufacturing has led to significant job losses in developed countries, while the creation of new jobs in the technology sector often requires specialized skills that many displaced workers lack. This necessitates reskilling and upskilling initiatives to bridge this gap and ensure a more equitable distribution of opportunities.
Ethical Considerations in Technology Development and Deployment
The development and deployment of new technologies raise profound ethical questions. Issues such as data privacy, algorithmic bias, and the potential for autonomous weapons systems require careful consideration. Algorithmic bias, for instance, can perpetuate and amplify existing societal biases, leading to unfair or discriminatory outcomes in areas like loan applications, hiring processes, and even criminal justice. The lack of transparency in many AI systems further complicates the problem, making it difficult to identify and address these biases. Similarly, the increasing use of surveillance technologies raises concerns about individual privacy and the potential for misuse by governments or corporations.
Strategies for Mitigating Risks
Addressing the challenges of technology-driven growth requires a multi-faceted approach. A proactive strategy is crucial to ensure that technological advancements benefit society as a whole.
- Invest in education and reskilling programs: Equipping workers with the skills needed for the jobs of the future is crucial to mitigating job displacement. This includes fostering STEM education and providing opportunities for lifelong learning and retraining.
- Promote responsible innovation: Developing ethical guidelines and regulations for the development and deployment of new technologies is essential. This includes establishing standards for data privacy, algorithmic transparency, and the responsible use of AI.
- Implement social safety nets: Strengthening social safety nets, such as unemployment benefits and universal basic income, can help cushion the impact of job displacement and reduce income inequality.
- Foster collaboration between stakeholders: Open dialogue and collaboration between governments, businesses, academia, and civil society are crucial for developing effective strategies to manage the risks associated with technology-driven growth. This includes involving diverse voices in the development and implementation of policies related to technology.
- Encourage equitable access to technology: Ensuring that the benefits of technological advancements are shared broadly across society is essential. This includes addressing the digital divide and promoting access to technology and digital literacy for all.
Case Studies of Technology-Driven Growth
Technology has fundamentally reshaped numerous industries, propelling some companies to unprecedented heights while leaving others struggling to adapt. Examining specific case studies allows us to understand the multifaceted nature of technology-driven growth, identifying common success factors and pitfalls. These examples illuminate the strategic choices, challenges overcome, and broader trends that define this era of rapid technological advancement.
Amazon’s E-commerce Dominance
Amazon’s transformation from an online bookstore to a global e-commerce giant exemplifies technology’s power to disrupt and redefine industries. Its relentless focus on technology, from its proprietary recommendation algorithms to its highly efficient logistics network (including robotics and AI-powered fulfillment centers), has fueled explosive growth. Amazon Web Services (AWS), its cloud computing arm, further diversified its revenue streams and cemented its technological leadership. However, Amazon has faced criticism regarding labor practices and its impact on smaller businesses, highlighting the ethical considerations inherent in rapid technological expansion. The company’s consistent investment in R&D, its data-driven approach to decision-making, and its ability to adapt to changing consumer preferences have been crucial to its success.
Netflix’s Streaming Revolution
Netflix’s shift from DVD rentals to streaming video on demand is another compelling example of technology-driven growth. By leveraging advancements in internet infrastructure and streaming technology, Netflix bypassed the limitations of physical media and redefined how consumers access entertainment. Its sophisticated recommendation system, personalized user experiences, and original content production have solidified its position as a leading global streaming platform. Challenges included navigating copyright issues, managing content costs, and competing with other streaming services, illustrating the competitive pressures within rapidly evolving digital markets. Netflix’s success showcases the importance of understanding consumer behavior and adapting to changing technological landscapes.
Tesla’s Disruption of the Automotive Industry
Tesla’s impact on the automotive industry is a testament to the transformative power of technological innovation in a traditionally conservative sector. Tesla’s focus on electric vehicles (EVs), coupled with its advancements in battery technology, autonomous driving features, and over-the-air software updates, has disrupted established automakers. However, challenges include scaling production, managing supply chains, and overcoming regulatory hurdles. Tesla’s success highlights the potential for technology to disrupt established industries by offering superior products and services, even in the face of significant initial challenges. Their vertical integration, from battery production to vehicle sales and service, provides a strong competitive advantage.
The Rise of Mobile Payment Systems
The rapid adoption of mobile payment systems, such as Apple Pay and Alipay, showcases the potential for technology to fundamentally alter everyday transactions. These systems leverage smartphones and near-field communication (NFC) technology to provide a convenient and secure alternative to traditional payment methods. Challenges included overcoming consumer concerns about security and privacy, integrating with existing financial infrastructure, and competing with established payment processors. The success of these systems demonstrates the importance of user experience, security features, and strategic partnerships in fostering widespread adoption of new technologies. The global reach of these systems further underscores the potential for technology to transcend geographical boundaries.
Future Trends in Technology-Driven Growth

Technology-driven growth will continue to accelerate, shaped by converging advancements across multiple domains. The next decade promises transformative changes driven by the synergistic effects of artificial intelligence, blockchain technology, and biotechnology, impacting various sectors in profound ways. Understanding these trends is crucial for businesses and policymakers to navigate the future effectively.
Predicting the precise trajectory of technology-driven growth is inherently complex, yet identifying key technological advancements and their likely impacts allows for informed strategic planning. The interplay between these technologies will create novel opportunities and challenges, requiring adaptive strategies to harness their potential while mitigating risks.
Key Technological Advancements Shaping Future Growth
Several technological advancements will significantly influence future growth patterns. Artificial intelligence (AI), particularly in its machine learning and deep learning forms, will automate tasks, improve decision-making, and unlock new levels of efficiency across industries. Blockchain technology will enhance transparency, security, and trust in various transactions and data management systems. Biotechnology, encompassing gene editing and personalized medicine, will revolutionize healthcare and potentially address some of humanity’s most pressing challenges. Quantum computing, while still in its nascent stages, holds the potential to solve complex problems currently intractable for classical computers, leading to breakthroughs in materials science, drug discovery, and financial modeling. The convergence of these technologies will further accelerate innovation and growth.
Impact of Emerging Technologies on Various Sectors
The impact of AI, blockchain, and biotechnology will be felt across diverse sectors. In healthcare, AI-powered diagnostics and personalized medicine will improve patient outcomes and reduce costs. Blockchain will enhance supply chain transparency and traceability in pharmaceuticals and medical devices. Biotechnology will lead to the development of novel therapies and diagnostics. In finance, AI will optimize trading strategies and risk management, while blockchain will enhance security and efficiency in payments and settlements. In manufacturing, AI-powered robotics and automation will increase productivity and reduce operational costs. Blockchain will enable secure and transparent supply chain management. The convergence of these technologies will foster innovation and efficiency across various industries.
Projected Trajectory of Technology-Driven Growth
Imagine a graph depicting the projected trajectory of technology-driven growth over the next decade. The x-axis represents time (years), from the present to 2033. The y-axis represents a composite index of technology-driven growth, encompassing factors like GDP growth attributed to technology, innovation rates, and technological adoption across various sectors. The graph would show a generally upward trend, reflecting the accelerating pace of technological advancement. However, the curve would not be linear. We might see periods of steeper growth, corresponding to major technological breakthroughs or widespread adoption of new technologies (e.g., a surge in AI adoption across multiple sectors), interspersed with periods of slightly slower growth, reflecting periods of integration and adaptation. For instance, a significant increase in the curve might be observed around 2025-2027, coinciding with the predicted wider adoption of AI and quantum computing solutions in various industries. A slight plateau could be seen around 2030 as the industry adjusts to new technologies before a renewed upward trend. The overall trajectory would depict an exponential increase, reflecting the compounding effects of technological progress. The graph would also show the potential for variability and uncertainty, with potential dips representing temporary setbacks or economic fluctuations, illustrating the inherent unpredictability of technological advancement and its impact on overall growth. This visual representation would highlight the transformative power of technology while acknowledging the complexities and uncertainties inherent in predicting future trends.
Outcome Summary
In conclusion, technology-driven growth presents a complex tapestry of opportunities and challenges. While technological advancements offer immense potential for economic prosperity and societal progress, careful consideration must be given to mitigating the risks associated with rapid technological change. A proactive approach that emphasizes ethical development, sustainable practices, and inclusive growth strategies is crucial to harnessing the full potential of technology while safeguarding against potential downsides. Continued research and adaptation will be essential to navigating this dynamic landscape and ensuring a future where technological progress benefits all of humanity.
Technology-driven growth is significantly impacting modern businesses. To capitalize on this, companies need a robust plan to boost their income streams. A well-defined Revenue acceleration strategy is crucial for achieving this, ensuring that technological advancements translate directly into increased revenue and sustainable growth for the future. Ultimately, leveraging technology effectively is key to unlocking substantial financial success.
Technology-driven growth hinges on understanding your market’s nuances. Successfully navigating this requires a robust strategy, which is why understanding effective Strategic market positioning is crucial. By aligning technological advancements with a well-defined market position, companies can maximize their potential for sustainable growth in the ever-evolving digital landscape. This strategic approach is key to leveraging technology for lasting competitive advantage.