Strategic market positioning sets the stage for sustainable business success. Understanding how to effectively position your product or service within a competitive landscape is crucial. This involves a deep dive into analyzing your target market, crafting a compelling unique value proposition, and developing a marketing message that resonates with your ideal customer. This guide will explore these key elements and provide practical strategies for achieving a strong and defensible market position.
We will examine various methods for market segmentation, including demographic, geographic, psychographic, and behavioral approaches. The importance of a unique value proposition (UVP) will be highlighted, along with techniques for creating a memorable and effective marketing message. Furthermore, we will delve into the implementation and monitoring of a strategic market positioning plan, using key performance indicators (KPIs) to track progress and adapt the strategy as needed. A case study will illustrate the successful application of these principles.
Defining Strategic Market Positioning
Strategic market positioning is the act of establishing a unique and desirable place for a product or service in the minds of consumers relative to its competitors. It’s not simply about what you offer, but how you are perceived in the marketplace. A strong position allows a business to command premium prices, build brand loyalty, and achieve sustainable competitive advantage. Essentially, it’s about crafting a compelling narrative that resonates with your target audience and differentiates you from the crowd.
Effective strategic market positioning requires a deep understanding of the target market, the competitive landscape, and the company’s unique strengths and weaknesses. It’s a process of careful analysis, strategic decision-making, and consistent execution. Without a clear position, a business risks getting lost in the noise, failing to attract customers, and ultimately, failing to thrive.
Examples of Strong and Weak Market Positioning
Strong market positioning is exemplified by companies that have cultivated a distinct and highly valued brand identity. Apple, for example, consistently positions itself as a premium brand synonymous with design, innovation, and user experience. This allows them to command premium prices and maintain high customer loyalty despite competition from numerous Android-based smartphone manufacturers. In contrast, a company with weak positioning might struggle to define its unique selling proposition, resulting in a lack of brand recognition and diluted customer appeal. Imagine a generic clothing retailer trying to compete directly with established brands like Nike or Zara without a clear differentiator – they might struggle to attract customers due to a lack of distinctive identity.
Key Elements of Effective Strategic Market Positioning
Several key elements contribute to effective strategic market positioning. Firstly, a thorough understanding of the target market is crucial. This involves identifying the needs, wants, and preferences of the intended customer base. Secondly, a compelling value proposition is essential. This is a clear statement of the benefits that a product or service offers to the customer, highlighting its unique advantages over competitors. Thirdly, consistent brand messaging is paramount. The brand’s message should be communicated consistently across all platforms and touchpoints to reinforce the desired perception. Finally, continuous monitoring and adaptation are necessary to ensure the positioning remains relevant and effective in a dynamic market. Market trends and competitor actions require ongoing evaluation and adjustments to maintain a strong position.
Analyzing the Competitive Landscape: Strategic Market Positioning

Understanding the competitive landscape is crucial for effective strategic market positioning. A thorough analysis allows businesses to identify opportunities, mitigate threats, and ultimately, gain a sustainable competitive advantage. This involves not only recognizing direct competitors but also considering indirect competitors and potential future entrants. A robust analysis considers the market share, strengths, and weaknesses of each competitor, enabling informed strategic decision-making.
Analyzing competitor market positions requires a multi-faceted approach. It involves identifying key players, assessing their market share, understanding their strategies, and evaluating their resources and capabilities. This information can be gathered through various methods including market research reports, competitor websites, news articles, and industry publications. By systematically analyzing this data, businesses can build a comprehensive understanding of the competitive dynamics within their market.
Competitive Positioning Strategies
Different businesses adopt varying competitive positioning strategies to achieve their objectives. Some may focus on cost leadership, aiming to offer the lowest prices. Others may pursue differentiation, emphasizing unique product features or superior customer service. Still others might concentrate on niche market specialization, targeting a specific segment with tailored offerings. Each strategy has its own set of strengths and weaknesses, and the optimal choice depends heavily on the specific market context and the company’s resources.
For example, a cost leadership strategy might be highly effective in a price-sensitive market, allowing a business to capture significant market share. However, it may also lead to lower profit margins and require significant economies of scale to remain competitive. In contrast, a differentiation strategy can command premium prices, but requires substantial investment in research and development, marketing, and brand building. A niche strategy offers a focused approach, reducing competition but limiting the overall market potential.
Competitive Analysis Matrix
A competitive analysis matrix provides a visual representation of the competitive landscape. It allows for a concise comparison of key competitors based on several crucial factors. The following table illustrates a sample competitive analysis matrix for a hypothetical coffee market. Note that the market share data presented is purely illustrative and should be replaced with actual market data for a real-world analysis.
| Competitor | Market Share | Strengths | Weaknesses |
|---|---|---|---|
| Starbucks | 35% | Strong brand recognition, wide distribution network, loyal customer base, diverse product offerings | Premium pricing, potential for brand saturation |
| Dunkin’ | 25% | Extensive franchise network, value pricing, strong coffee and donut offerings | Less premium image compared to Starbucks, potentially less diverse menu |
| Local Coffee Shop (Example) | 5% | Strong community ties, unique coffee blends, personalized customer service | Limited distribution, smaller scale operations, potentially higher prices |
| Independent Roasters (Aggregate) | 10% | High-quality beans, specialty coffee options, strong online presence | Inconsistent brand image across different roasters, potential for logistical challenges |
| Other (Aggregate) | 25% | Variety of options, convenience | Lack of brand loyalty, inconsistent quality |
Understanding Target Market Segmentation
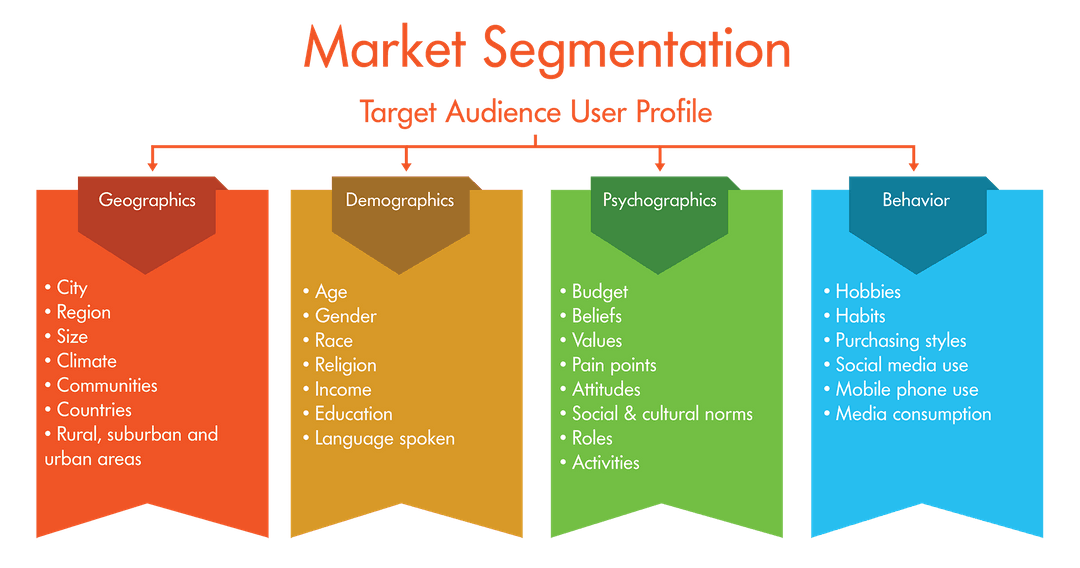
Effective market segmentation is crucial for successful strategic market positioning. By dividing a broad market into smaller, more manageable groups, businesses can tailor their marketing efforts to resonate more effectively with specific customer needs and preferences, ultimately increasing efficiency and profitability. This process involves identifying shared characteristics within groups to create targeted strategies.
Understanding the different methods for segmenting a target market allows businesses to pinpoint their ideal customer profiles and develop focused marketing campaigns. This targeted approach ensures resources are allocated effectively and maximizes the return on investment.
Demographic Segmentation, Strategic market positioning
Demographic segmentation uses readily available data to categorize consumers based on measurable characteristics like age, gender, income, education, occupation, family size, and ethnicity. This is a straightforward method, often used as a starting point for more detailed segmentation. For example, a company selling luxury cars might focus on high-income individuals aged 35-55 with advanced degrees, while a company selling children’s toys would target families with young children. The effectiveness hinges on the accuracy of the data and its relevance to the product or service.
Geographic Segmentation
Geographic segmentation involves dividing the market based on location. This could include countries, regions, states, cities, or even neighborhoods. Factors like climate, population density, and cultural nuances can significantly influence consumer behavior. A company selling snow shovels would naturally focus its marketing efforts on regions with heavy snowfall, while a business selling beachwear would target warmer climates. Understanding regional variations is vital for effective geographic segmentation.
Psychographic Segmentation
Psychographic segmentation delves into the psychological aspects of consumers, including their lifestyles, values, interests, attitudes, and personality traits. This provides a deeper understanding of consumer motivations and preferences beyond demographic data. For example, a company selling organic food products might target consumers who value health and sustainability, while a company selling adventure travel packages would focus on thrill-seeking individuals. Psychographic segmentation requires more in-depth research methods, such as surveys and focus groups.
Behavioral Segmentation
Behavioral segmentation categorizes consumers based on their past behavior, such as purchasing habits, brand loyalty, usage rate, and response to marketing campaigns. This approach provides valuable insights into actual consumer actions, offering a more concrete understanding of market dynamics. A company selling coffee might segment its market based on the frequency of coffee consumption (daily, weekly, occasional), while a company offering subscription boxes might target consumers based on their past purchase history and subscription preferences. Analyzing past behavior allows for highly targeted and personalized marketing efforts.
Target Market Segment Profile: Health-Conscious Millennials
This segment comprises millennials (generally defined as individuals born between 1981 and 1996) who prioritize health and wellness. They are typically digitally savvy, environmentally conscious, and value experiences over material possessions. Their needs include healthy food options, fitness apparel and equipment, and access to wellness information. Their wants encompass a sense of community, social responsibility, and convenience. Their preferences lean towards sustainable and ethically sourced products, personalized experiences, and brands that align with their values. They are active on social media and are influenced by online reviews and influencer marketing. This segment is a prime target for businesses offering organic foods, fitness classes, mindfulness apps, and sustainable lifestyle products.
Implications of Choosing Different Target Market Segments
Selecting a specific target market segment directly influences a business’s strategic market positioning. Focusing on a niche segment allows for specialized marketing efforts and a strong brand identity, but may limit market reach. Targeting a broader segment increases market potential but requires a more generalized marketing strategy and may dilute brand messaging. The optimal approach depends on the business’s resources, competitive landscape, and overall strategic goals. A startup with limited resources might initially focus on a niche segment, while a larger established company might adopt a multi-segment approach.
Developing a Unique Value Proposition
A unique value proposition (UVP) is the core reason why a customer should choose your product or service over a competitor’s. It’s a concise statement that highlights the specific benefits your offering provides and how it solves a customer’s problem better than the alternatives. Crafting a compelling UVP is crucial for differentiating your brand and attracting your target audience.
A strong UVP goes beyond simply listing features; it focuses on the tangible value those features deliver to the customer. It addresses the customer’s needs and desires, showcasing how your product or service improves their lives or businesses. This requires a deep understanding of your target market and their pain points.
Examples of Compelling Unique Value Propositions
Several successful companies have built their brands around powerful UVPs. Consider these examples:
- Dollar Shave Club: Their UVP wasn’t about the quality of their razors (though it was good), but about the convenience and affordability. They famously communicated this with a humorous video emphasizing the ridiculous markup of traditional razor brands. Their UVP was essentially: “High-quality razors delivered to your door at a fraction of the cost.”
- Netflix: Netflix disrupted the movie rental industry with its UVP focused on convenience and choice. Instead of trips to the video store, customers could stream unlimited movies and TV shows on demand. Their UVP boiled down to: “Watch what you want, when you want, without the hassle.”
- Airbnb: Airbnb redefined the travel industry by offering unique and affordable lodging options. Their UVP is centered around the experience of staying in a local’s home, often at a lower cost than hotels, and getting a more authentic experience. This translates to a UVP like: “Unique and affordable accommodations, connecting you with local experiences.”
Designing a UVP for a Hypothetical Product
Let’s imagine a new service called “MealPrepPro,” a meal-kit delivery service tailored for busy professionals. Its differentiation lies in its focus on healthy, customizable meals prepared with locally sourced ingredients and delivered on a flexible schedule.
The UVP for MealPrepPro could be: “Reclaim your evenings. Enjoy healthy, customizable meals delivered on your schedule, made with fresh, locally sourced ingredients.”
Key Features and Benefits of MealPrepPro’s UVP
The success of MealPrepPro’s UVP hinges on clearly communicating its key features and benefits. This can be effectively done through bullet points:
- Healthy & Nutritious Meals: Meals are designed by registered dietitians, emphasizing whole foods and portion control.
- Customization Options: Customers can select meals based on dietary restrictions and preferences (vegetarian, vegan, gluten-free, etc.).
- Locally Sourced Ingredients: Commitment to using fresh, high-quality ingredients from local farmers and suppliers.
- Flexible Delivery Schedule: Choose your delivery frequency and adjust as needed to accommodate your busy lifestyle.
- Time Savings: Eliminates the need for grocery shopping, meal planning, and cooking, freeing up valuable time.
Crafting a Marketing Message
Crafting a compelling marketing message is crucial for translating your unique value proposition (UVP) into tangible results. This message needs to resonate with your target market, clearly communicating the benefits of your product or service and differentiating you from the competition. A well-crafted message will not only attract potential customers but also reinforce your brand identity and strategic market positioning.
The marketing message should directly reflect the core elements of your strategic market positioning. This means it should accurately represent your target audience, the problem your product solves, and the unique way you solve it better than the competition. In essence, it’s the concise summary of your entire strategic plan, tailored for communication with your customers. Inconsistency between your message and your overall strategy will lead to confusion and diluted marketing efforts.
Marketing Message Examples and Alignment
Let’s consider a hypothetical company, “EcoClean,” offering eco-friendly cleaning products. Their strategic market positioning targets environmentally conscious consumers who value both effectiveness and sustainability. Their UVP is “Powerful cleaning, guilt-free conscience.” A marketing message reflecting this could be: “EcoClean: Get sparkling clean results without harming the planet.” This message directly addresses the target audience’s values (environmental consciousness) and highlights the key benefit (powerful cleaning) while subtly mentioning the UVP (“guilt-free conscience”). The message’s simplicity and clarity ensure it effectively communicates the brand’s core proposition. Another option could be: “EcoClean: Sustainable cleaning solutions for a healthier home and planet.” This emphasizes both the sustainability and the health benefits, aligning with the broader market positioning.
Marketing Channel Selection and Effectiveness
Choosing the right marketing channels is essential for reaching your target audience effectively. The effectiveness of each channel depends on the target audience’s media consumption habits and the nature of your message.
For EcoClean, targeting environmentally conscious consumers, several channels could be effective:
- Social Media (Instagram, Facebook): Visually appealing content showcasing the product’s eco-friendly packaging and highlighting user-generated content emphasizing cleaning results. Instagram’s visual nature aligns well with showcasing the product’s aesthetic appeal and eco-friendly packaging. Facebook allows for targeted advertising based on demographics and interests, reaching environmentally conscious consumers directly.
- Influencer Marketing: Partnering with environmental advocates or sustainable living influencers to promote the product to their engaged audience. This leverages the trust and credibility of influencers to build brand awareness and drive sales.
- Print Advertising (Magazines, Newspapers): Advertising in publications targeting environmentally conscious readers can effectively reach a specific demographic. However, the cost-effectiveness needs careful consideration.
- Website and Email Marketing: A well-designed website with clear information about the product’s sustainability features and email marketing campaigns to nurture leads and announce promotions.
The choice of channels should be strategic, considering the budget, target audience, and the overall marketing objectives. A multi-channel approach, combining several methods, is often the most effective strategy to maximize reach and impact. For instance, a campaign might use social media for brand building and influencer marketing to generate awareness, while email marketing focuses on converting leads into sales. This integrated approach ensures that the marketing message is consistently delivered across multiple platforms, reinforcing the brand’s identity and driving engagement.
Implementing and Monitoring the Strategy

Successfully implementing a strategic market positioning strategy requires a well-defined plan and consistent monitoring. This involves translating the carefully crafted positioning statement into tangible actions across all marketing and operational areas. Continuous monitoring ensures the strategy remains effective and adaptable to market changes.
The implementation process involves several key steps, each requiring careful planning and execution. Effective monitoring then allows for adjustments based on performance data, ensuring the strategy remains aligned with market realities and business goals.
Implementation Steps
Implementing a strategic market positioning strategy is a multi-faceted process. It requires coordinated efforts across various departments and a clear understanding of roles and responsibilities. A phased approach is often beneficial, allowing for iterative improvements and adjustments along the way.
- Resource Allocation: This involves assigning budget, personnel, and other resources necessary to execute the marketing plan. For example, a company launching a new product might allocate a larger portion of its marketing budget to digital advertising and influencer outreach, aligning with its target audience’s online behavior.
- Marketing Plan Development: A detailed marketing plan outlining specific tactics and timelines is crucial. This plan should integrate all marketing channels and activities, ensuring a cohesive and consistent brand message. For example, a plan might detail specific social media campaigns, email marketing strategies, and public relations initiatives.
- Team Training and Communication: Ensuring all team members understand and are aligned with the new positioning is vital. This involves training sessions, internal communications, and clear guidelines on how to represent the brand consistently. A company launching a new brand image, for example, might hold workshops to train its sales staff on the new brand messaging and visual identity.
- Launch and Execution: The actual implementation of the marketing plan. This involves executing marketing campaigns, launching new products or services, and actively engaging with the target market. For instance, a company launching a new eco-friendly product line might simultaneously launch a social media campaign highlighting its sustainable practices.
- Ongoing Monitoring and Reporting: Regularly tracking key performance indicators (KPIs) to assess progress and identify areas for improvement is crucial. This includes analyzing sales data, website traffic, social media engagement, and customer feedback. A detailed reporting system will allow for effective tracking of progress and facilitate necessary adjustments.
Key Performance Indicators (KPIs)
Tracking the success of a strategic market positioning strategy requires a set of carefully chosen KPIs. These metrics should directly reflect the goals and objectives of the positioning strategy. Regular monitoring of these KPIs allows for timely identification of areas needing improvement and facilitates data-driven decision-making.
- Brand Awareness: Measured through surveys, social media mentions, and website traffic. A significant increase in brand awareness indicates successful positioning.
- Market Share: Tracks the percentage of the market controlled by the company. Growth in market share suggests effective positioning and competitive advantage.
- Customer Acquisition Cost (CAC): Measures the cost of acquiring a new customer. A decrease in CAC indicates improved efficiency in reaching the target market.
- Customer Lifetime Value (CLTV): Represents the total revenue generated by a customer over their relationship with the company. An increase in CLTV indicates improved customer loyalty and retention, often a direct result of successful positioning.
- Customer Satisfaction (CSAT): Measured through surveys and feedback mechanisms. High CSAT scores indicate that the positioning resonates with the target market and meets their needs.
Adapting and Refining the Strategy
Market dynamics are constantly evolving, necessitating regular review and adaptation of the market positioning strategy. Performance data provides valuable insights for identifying areas for improvement and making informed adjustments. A flexible and iterative approach is key to long-term success.
- Regular Performance Reviews: Conducting regular reviews of the KPIs allows for timely identification of any deviations from the planned trajectory. This provides opportunities to adjust the strategy before significant setbacks occur.
- Competitive Analysis: Continuously monitoring competitors’ actions and strategies allows for proactive adjustments to maintain a competitive edge. This might involve adapting the value proposition or refining the marketing message.
- Customer Feedback Analysis: Actively soliciting and analyzing customer feedback helps identify areas where the positioning strategy might be falling short or where improvements can be made. This feedback can be used to refine the value proposition and enhance customer experience.
- Market Trend Analysis: Staying abreast of emerging market trends allows for proactive adjustments to the strategy, ensuring it remains relevant and effective. This might involve adapting the marketing channels used or shifting the focus of the value proposition.
- A/B Testing: Conducting A/B tests on marketing materials and campaigns allows for data-driven optimization. This ensures that the marketing message and approach are resonating effectively with the target audience.
Case Study: Apple’s Strategic Market Positioning

Apple’s enduring success stems from a meticulously crafted and consistently executed strategic market positioning. This case study examines their approach, highlighting key contributing factors and potential future challenges. Their strategy transcends mere product development; it’s a carefully constructed ecosystem designed to foster brand loyalty and premium pricing.
Apple’s Core Positioning Strategy
Apple’s market positioning centers around a premium brand image associated with design, user experience, and a carefully curated ecosystem of products and services. This contrasts sharply with competitors focusing on specifications or price points. They consistently target a specific demographic – tech-savvy individuals and professionals who value seamless integration and a polished user experience, willing to pay a premium for it. This focused approach allows them to command higher prices and maintain strong profit margins.
Key Factors Contributing to Apple’s Success
Several interconnected factors underpin Apple’s sustained market dominance. First, their relentless focus on user experience creates a strong emotional connection with customers. This is reinforced by their retail strategy, fostering a premium and personalized shopping experience. Secondly, their vertically integrated business model, controlling hardware, software, and services, enables tighter control over the entire user experience and ecosystem. This allows for seamless integration and consistent brand messaging. Finally, their effective marketing consistently communicates their brand values – innovation, simplicity, and elegance – resonating deeply with their target audience.
Apple’s success isn’t just about technology; it’s about crafting a desirable lifestyle.
Challenges and Risks in Maintaining Market Position
While Apple’s position is strong, maintaining it presents significant challenges. Increasing competition from Android manufacturers offering comparable features at lower prices poses a constant threat. Furthermore, the company’s reliance on a premium pricing strategy makes it vulnerable to economic downturns affecting consumer spending. Another risk is the potential for innovation to stagnate, leading to a decline in brand appeal. Maintaining its innovative edge and continuing to deliver exceptional user experiences are crucial for Apple to navigate these challenges.
The challenge for Apple is to balance innovation with the maintenance of its existing ecosystem and brand image.
Last Recap
Successfully establishing a strong strategic market position requires a comprehensive understanding of the competitive landscape, a clear articulation of your target market, and a compelling unique value proposition. By meticulously analyzing these elements and crafting a cohesive marketing message, businesses can differentiate themselves, build brand loyalty, and achieve sustainable growth. Regular monitoring and adaptation of the strategy, based on performance data, are essential for long-term success in a dynamic marketplace. This strategic approach ensures that your business not only survives but thrives.
Strategic market positioning requires understanding your target audience and their needs. For instance, in the burgeoning EdTech sector, a key consideration is the accessibility of learning resources. Many platforms offer solutions, such as the comprehensive coding education available through this application: Aplikasi belajar kode pemrograman. Ultimately, successful positioning hinges on effectively communicating your unique value proposition within a competitive landscape.
Strategic market positioning requires understanding your target audience and their needs. For example, a game developer might analyze the popularity of adventure games, specifically those set in mysterious forests, like the engaging title found at Permainan petualangan hutan misteri. By identifying such trends, they can effectively position their product to capture a significant market share, ensuring its success through strategic planning and execution.