Cross-border e-commerce presents a dynamic and rapidly expanding market, connecting businesses and consumers across geographical boundaries. This intricate landscape blends technological advancements, logistical complexities, and diverse cultural nuances, creating both exciting opportunities and significant challenges. Understanding the intricacies of international shipping, diverse payment methods, and varying legal frameworks is crucial for success in this global arena.
This exploration delves into the key aspects of cross-border e-commerce, from defining its core characteristics and analyzing market trends to navigating the complexities of logistics, payments, and legal compliance. We will examine consumer behavior, effective marketing strategies, and the potential risks and rewards associated with this increasingly important sector of the global economy.
Defining Cross-Border E-commerce
Cross-border e-commerce represents the buying and selling of goods and services across international borders through electronic channels like websites and online marketplaces. It’s a rapidly growing sector fueled by increased internet penetration, improved logistics, and the globalization of consumer preferences. This expansion presents both significant opportunities and unique challenges for businesses.
Cross-border e-commerce transactions are characterized by several key aspects. Firstly, they involve buyers and sellers located in different countries, necessitating international shipping and potentially different currencies and languages. Secondly, these transactions are facilitated by digital platforms, ranging from dedicated cross-border marketplaces to individual company websites. Thirdly, they often involve navigating diverse legal and regulatory frameworks, including customs regulations, import duties, and tax laws. Finally, successful cross-border e-commerce relies on effective international logistics and payment processing solutions.
Differences Between Domestic and Cross-Border E-commerce
Domestic e-commerce, in contrast, involves transactions within a single country’s borders. This simplifies logistics, payment processing, and regulatory compliance considerably. For instance, shipping times are generally shorter, and there are no customs duties or import taxes to consider. Cross-border e-commerce introduces complexities related to international shipping, currency conversion, language barriers, and varying consumer preferences and expectations across different cultures. Furthermore, legal and regulatory differences necessitate careful planning and compliance.
Business Models in Cross-border E-commerce
Several distinct business models drive cross-border e-commerce. The most prevalent include the direct-to-consumer (D2C) model, where businesses sell directly to international customers through their own websites; the marketplace model, where businesses leverage established platforms like Amazon or eBay to reach global audiences; and the third-party logistics (3PL) model, where businesses outsource their fulfillment and shipping operations to specialized providers. Hybrid models, combining elements of these approaches, are also common. For example, a company might use a marketplace for initial expansion and then transition to a D2C model with its own website once it establishes a stronger international presence.
Comparison of Cross-Border E-commerce Platforms
The choice of platform significantly impacts a business’s success in cross-border e-commerce. Different platforms offer varying levels of functionality, reach, and support. The following table provides a comparison of some popular options:
| Platform | Global Reach | Integration Capabilities | Pricing Model |
|---|---|---|---|
| Amazon Global Selling | Extensive, across many countries | Integrates with various shipping and payment providers | Commission-based, with varying fees |
| eBay | Wide global reach, particularly strong in certain regions | Offers integration options, but requires more manual management | Listing fees and commission-based |
| Shopify | Global reach through app integrations and localized settings | Highly customizable, integrates with a vast ecosystem of apps | Subscription-based, with transaction fees |
| AliExpress | Predominantly focused on Asia, but expanding globally | Integrates with various payment and logistics providers | Commission-based, with varying fees |
Market Trends and Growth
The global cross-border e-commerce market is experiencing explosive growth, driven by increased internet penetration, rising disposable incomes in emerging markets, and the ever-improving logistics infrastructure. This expansion presents significant opportunities for businesses of all sizes, but also necessitates a deep understanding of the prevailing market trends to effectively capitalize on them.
The global cross-border e-commerce market is a dynamic and rapidly evolving landscape. Understanding its key trends is crucial for businesses aiming to participate successfully. Several factors contribute to its continuous expansion, including advancements in technology, shifting consumer preferences, and the globalization of supply chains.
Global Market Size and Growth Projections
Estimates suggest the global cross-border e-commerce market reached trillions of dollars in value in recent years, and is projected to continue its robust growth trajectory throughout the next decade. While precise figures vary depending on the source and methodology, the consistent trend points to a significant expansion, fueled by factors like increasing smartphone adoption in developing nations and the rising popularity of online marketplaces. For example, a report by eMarketer projected substantial growth in specific regions, highlighting the market’s potential. These projections, while estimates, are supported by observed growth patterns in various sectors and regions.
Fastest-Growing Regions and Sectors
Asia-Pacific, particularly China and Southeast Asia, consistently demonstrates the fastest growth in cross-border e-commerce. This is attributed to a burgeoning middle class, increasing internet and mobile penetration, and a preference for online shopping. Within specific sectors, electronics, fashion, and beauty products show exceptionally strong growth, driven by factors such as competitive pricing and wider product availability online compared to traditional retail channels. The North American and European markets, while mature, also exhibit continued growth, albeit at a slower pace than the Asia-Pacific region. This suggests a diverse and geographically dispersed market with significant potential across different regions.
Technological Advancements and Their Impact
Technological advancements significantly impact cross-border e-commerce growth. Improvements in logistics, such as automated warehousing and sophisticated delivery networks, enable faster and more efficient shipping. The rise of mobile commerce (m-commerce) and the increasing sophistication of e-commerce platforms enhance the customer experience and accessibility. Furthermore, advancements in payment gateways and secure online transaction processing are crucial in building consumer trust and facilitating seamless cross-border transactions. Artificial intelligence (AI) is also playing an increasingly important role in areas like personalized recommendations and fraud detection. For instance, the use of AI-powered chatbots for customer service is improving responsiveness and efficiency.
Examples of Successful Cross-Border E-commerce Businesses
Companies like ASOS (fashion), SHEIN (fast fashion), and Alibaba (general merchandise) exemplify successful cross-border e-commerce strategies. ASOS leverages its global reach and strong brand recognition to cater to diverse international markets. SHEIN focuses on fast fashion and competitive pricing to appeal to a younger, global audience. Alibaba utilizes its massive online marketplace to connect international buyers and sellers, facilitating cross-border trade on a large scale. These examples highlight the diverse approaches to successful cross-border e-commerce, emphasizing the importance of understanding target markets and adapting strategies accordingly. Each company’s success is tied to its ability to navigate the complexities of international shipping, logistics, payment processing, and cultural nuances.
Logistics and Shipping
Successfully navigating the complexities of international shipping is paramount to the success of any cross-border e-commerce venture. The process involves a multitude of variables that can significantly impact both cost and delivery times, demanding careful planning and execution. Understanding these intricacies is crucial for businesses aiming to provide a seamless and efficient customer experience.
International shipping presents unique challenges compared to domestic shipping. Factors such as varying customs regulations, longer transit times, increased transportation costs, and potential language barriers contribute to a more intricate logistical landscape. Furthermore, managing inventory across multiple international locations, handling potential returns and exchanges, and ensuring timely delivery all add layers of complexity. Effective management of these challenges requires a robust logistics strategy that anticipates potential issues and proactively mitigates risks.
Shipping Methods and Associated Costs and Timelines
The choice of shipping method significantly influences both the cost and speed of delivery in cross-border e-commerce. Several options exist, each with its own set of advantages and disadvantages. The optimal method depends on factors such as the size and weight of the shipment, the destination country, the desired delivery speed, and the overall budget.
- Express Shipping: This offers the fastest delivery times, typically within 2-5 business days, but comes at a premium cost. Services like FedEx International Priority and DHL Express are examples of express shipping providers. This is ideal for high-value or time-sensitive goods.
- Standard Shipping: This provides a more economical option with longer delivery times, ranging from 7-21 business days or more, depending on the destination and chosen carrier. This method is suitable for less time-sensitive products with lower value.
- Freight Forwarding: For larger shipments, freight forwarding services consolidate goods from multiple sellers and handle the logistics of transporting them internationally. This can offer cost savings for bulk shipments but requires more planning and coordination.
Customs and Import/Export Regulations
Customs regulations and import/export procedures are critical aspects of cross-border e-commerce. Each country has its own set of rules and regulations governing the import and export of goods, including tariffs, duties, taxes, and documentation requirements. Non-compliance can lead to delays, penalties, and even the seizure of goods. Understanding these regulations is vital for ensuring smooth and compliant cross-border shipments.
Businesses need to be aware of the specific documentation required for each shipment, including commercial invoices, packing lists, certificates of origin, and any other necessary permits or licenses. They must also accurately classify their products according to the Harmonized System (HS) code to determine the applicable tariffs and duties. Furthermore, understanding the customs clearance process in the destination country is essential for minimizing delays and ensuring timely delivery. Many businesses utilize customs brokers to navigate these complexities.
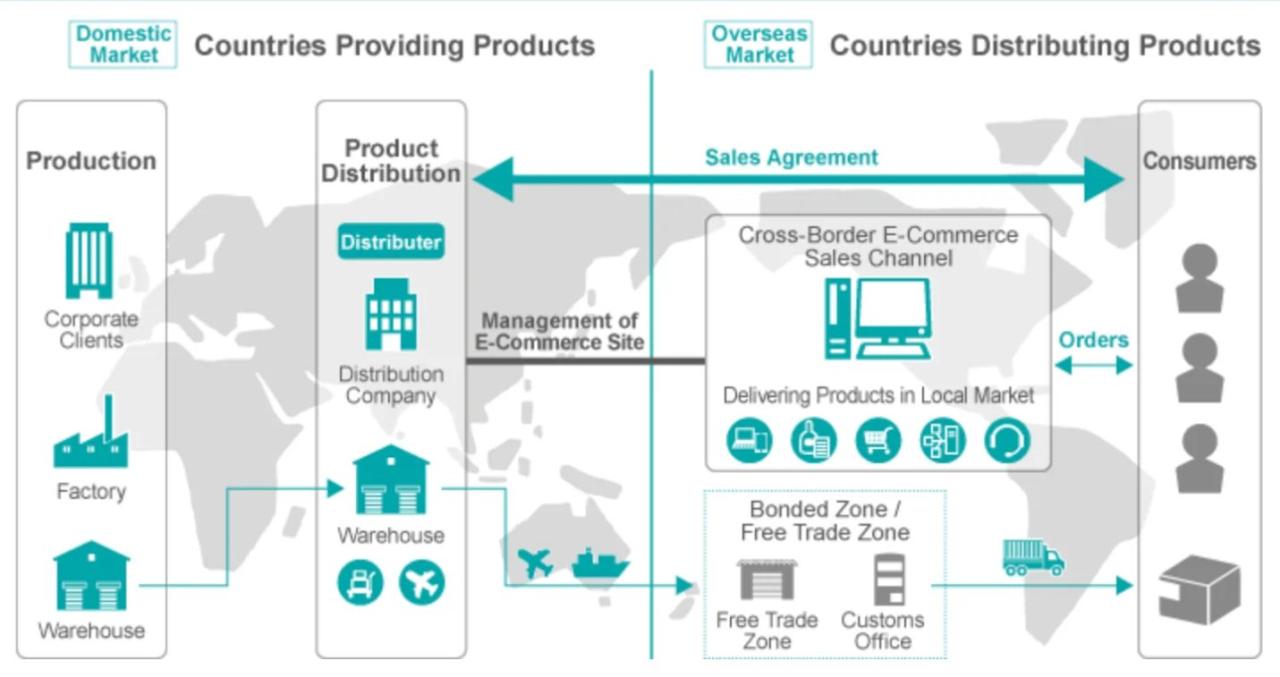
Cross-Border E-commerce Order Fulfillment Process
The following flowchart illustrates a typical cross-border e-commerce order fulfillment process:
[Diagram description: The flowchart begins with “Customer Places Order.” This leads to “Order Received and Processed.” Next, “Inventory Check” determines if the item is in stock. If yes, it proceeds to “Packaging and Labeling,” followed by “Shipping (selection of appropriate method).” If the inventory check shows the item is out of stock, it leads to a “Backorder Notification” to the customer. The next step is “Customs Clearance and Documentation,” followed by “International Shipping.” Finally, “Delivery to Customer” completes the process. If issues arise during any stage, a feedback loop is shown leading to “Problem Resolution.”]
Payment and Currency
Cross-border e-commerce necessitates a robust and secure payment infrastructure capable of handling diverse currencies and payment preferences across geographical boundaries. The complexities involved in facilitating these transactions extend beyond simply processing payments; they encompass currency conversion, managing exchange rate fluctuations, and ensuring the security of sensitive financial data.
Payment methods in cross-border e-commerce are varied and depend on both the buyer’s and seller’s locations, as well as the platform used. Consumers expect a seamless and familiar payment experience, regardless of location. The ability to offer multiple payment options significantly impacts conversion rates and overall customer satisfaction.
Payment Methods in Cross-Border E-commerce
A wide array of payment methods cater to the international e-commerce market. These options range from traditional methods to newer, technology-driven solutions, each presenting its own set of advantages and disadvantages. Commonly used methods include credit and debit cards (Visa, Mastercard, American Express), digital wallets (PayPal, Alipay, Apple Pay, Google Pay), bank transfers, and alternative payment methods specific to certain regions (e.g., Boleto in Brazil, iDEAL in the Netherlands). The optimal choice often depends on factors like transaction volume, target market demographics, and processing fees. For instance, while credit cards offer broad acceptance, they may incur higher processing fees compared to digital wallets. Conversely, digital wallets often have limitations in certain regions.
Challenges of Currency Conversion and Exchange Rates
Fluctuating exchange rates pose a significant challenge to cross-border e-commerce businesses. The cost of goods and services changes constantly depending on the prevailing exchange rate between the buyer’s and seller’s currencies. This volatility can lead to unpredictable pricing for consumers and profitability concerns for businesses. Accurate real-time conversion is crucial, and any delay or discrepancy can negatively affect customer trust and satisfaction. Furthermore, currency conversion fees add to the overall transaction cost, which can significantly influence the final price for the consumer. For example, a business selling products in USD to a customer in EUR faces the risk of reduced profit margins if the EUR depreciates against the USD between the time of order and payment processing.
Comparison of Payment Gateways and Security Features
Various payment gateways facilitate cross-border transactions, each offering unique features and security measures. Popular gateways include PayPal, Stripe, Shopify Payments, and Worldpay. Security is paramount; gateways employ various techniques to protect against fraud, such as encryption (SSL/TLS), fraud detection systems, and two-factor authentication. The choice of gateway depends on factors such as transaction fees, supported currencies, integration with existing e-commerce platforms, and the level of security offered. For example, PayPal offers a robust buyer and seller protection system, while Stripe provides extensive customization options for businesses. A comparison table highlighting key features would be beneficial in making an informed decision.
Best Practices for Secure Cross-Border Online Payments
Prioritizing security in cross-border payments is critical to maintain customer trust and avoid financial losses. Implementing robust security measures is essential. This includes using strong encryption protocols (like SSL/TLS) to protect sensitive data during transmission, employing fraud detection systems to identify and prevent fraudulent transactions, and offering multiple secure payment options to cater to diverse customer preferences. Regular security audits and compliance with relevant industry standards (e.g., PCI DSS) are vital. Additionally, clear and transparent communication with customers regarding payment processing and security measures helps build trust and reduces potential concerns. For example, clearly displaying security badges and providing detailed information about data protection policies can significantly enhance customer confidence.
Consumer Behavior and Preferences
Understanding consumer behavior is paramount to success in cross-border e-commerce. Global consumers exhibit diverse purchasing habits shaped by cultural nuances, economic factors, and technological access. Analyzing these differences allows businesses to tailor their strategies for maximum impact.
Several key factors influence consumer purchasing decisions in the cross-border e-commerce landscape. Price competitiveness remains a significant driver, especially considering potential savings on imported goods. However, trust and reliability are equally important, particularly when dealing with unfamiliar brands and international shipping. Product quality, availability of customer service in the consumer’s native language, and convenient payment options all play crucial roles. Furthermore, positive online reviews and social proof significantly impact purchasing decisions, particularly in markets where brand recognition may be lower.
Cross-border e-commerce presents unique challenges and opportunities. Reaching a global audience requires careful consideration of logistics and cultural nuances. For example, the increasing popularity of digital games, such as the engaging virtual table tennis game found at Permainan tenis meja virtual , highlights the potential for growth in niche markets. This underscores the importance of understanding consumer preferences across borders for successful cross-border e-commerce ventures.
Shopping Habits Across Regions
Consumer shopping habits vary considerably across different regions. For instance, consumers in North America often prioritize convenience and speed of delivery, exhibiting a preference for large online marketplaces with extensive product selections. In contrast, consumers in Asia, particularly in countries like China and South Korea, often show a strong preference for mobile commerce and social commerce platforms, often influenced by social media trends and recommendations. European consumers, on the other hand, may place greater emphasis on sustainable and ethical sourcing, leading to a higher demand for eco-friendly products and transparent supply chains. These differences highlight the need for tailored marketing strategies and localized approaches to meet diverse regional preferences.
The Importance of Localization and Cultural Adaptation
Localization and cultural adaptation are critical for success in cross-border e-commerce. Simply translating website content is insufficient; a truly localized experience requires understanding and adapting to cultural nuances in various aspects of the online shopping experience. This includes adapting website design to reflect local aesthetic preferences, offering customer support in local languages, using culturally relevant imagery and messaging, and adjusting payment methods to suit local banking practices. For example, a website selling clothing might feature models reflecting the ethnic diversity of the target market. Ignoring these cultural factors can lead to misinterpretations, alienate potential customers, and ultimately hinder sales.
Profile of the Typical Cross-Border E-commerce Consumer
The typical cross-border e-commerce consumer is increasingly tech-savvy, comfortable navigating international websites and utilizing various online payment methods. They are often motivated by seeking products unavailable domestically, accessing better prices, or experiencing a wider range of choices. They are also more likely to be digitally fluent, researching products extensively before making a purchase, and relying heavily on online reviews and social media recommendations. However, concerns about shipping costs, customs duties, and potential return complications remain significant factors influencing their purchasing decisions. This profile is, of course, a generalization; the specific characteristics will vary significantly based on the region, demographics, and product category.
Legal and Regulatory Frameworks
Navigating the complex legal landscape is crucial for success in cross-border e-commerce. Businesses face a multitude of regulations impacting various aspects of their operations, from data privacy to product safety and customs procedures. Understanding and adhering to these frameworks is not merely a matter of compliance; it’s essential for maintaining a positive brand reputation, avoiding costly penalties, and fostering trust with international customers.
Key Legal and Regulatory Challenges in Cross-Border E-commerce present significant hurdles for businesses. These challenges stem from the diverse legal systems and regulatory environments across different countries. For instance, differing product safety standards, labeling requirements, and consumer protection laws necessitate careful consideration and adaptation of business practices. Furthermore, intellectual property rights protection varies significantly across jurisdictions, requiring businesses to implement robust strategies to safeguard their brands and innovations. Taxation, including VAT and import duties, also poses a complex challenge, demanding accurate calculation and timely remittance to avoid penalties. Finally, contract law and dispute resolution mechanisms vary across countries, making it essential to have well-drafted contracts that address potential conflicts effectively.
Data Privacy Regulations
Compliance with data privacy regulations is paramount in cross-border e-commerce. The General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) in Europe, the California Consumer Privacy Act (CCPA) in the US, and similar laws in other jurisdictions impose strict requirements on how businesses collect, process, and store personal data of their customers. Failure to comply can result in significant fines and reputational damage. Businesses must implement robust data protection measures, obtain explicit consent for data processing, and ensure data security throughout the entire customer journey. This includes transparent data handling policies, readily available mechanisms for data access and correction, and secure data storage and transfer practices. For example, a company operating in the EU must comply with GDPR, regardless of its location. This includes ensuring data is processed lawfully, fairly, and transparently, and that appropriate technical and organizational measures are in place to ensure the security of personal data.
The Role of International Trade Agreements
International trade agreements play a vital role in facilitating cross-border e-commerce by reducing tariffs, simplifying customs procedures, and harmonizing regulations. Agreements like the World Trade Organization (WTO) agreements and regional trade agreements, such as the Comprehensive and Progressive Agreement for Trans-Pacific Partnership (CPTPP), aim to create a more predictable and transparent environment for businesses. These agreements often include provisions related to electronic commerce, addressing issues such as digital signatures, electronic contracts, and data flows. However, the extent of their impact varies depending on the specific provisions of each agreement and the level of implementation by participating countries. For example, the CPTPP includes provisions that aim to reduce tariffs and eliminate barriers to digital trade, facilitating easier cross-border e-commerce among its member countries.
Best Practices for Legal Compliance
Implementing best practices is essential for legal compliance in cross-border e-commerce. This involves conducting thorough due diligence to understand the relevant legal and regulatory requirements in each target market. Businesses should seek legal counsel specializing in international trade and e-commerce to ensure compliance. Developing clear and comprehensive terms and conditions, privacy policies, and shipping policies that address relevant legal requirements in all target markets is also crucial. Moreover, businesses should proactively monitor changes in legislation and adapt their practices accordingly. Regular audits of compliance procedures and investing in appropriate technology to facilitate compliance, such as data encryption and secure payment gateways, are also essential elements of a robust compliance program. For instance, a company selling goods online should ensure its website complies with all applicable advertising standards and consumer protection laws in each country it operates in. This might involve adapting website content, providing translated versions, and ensuring compliance with specific labeling and product safety requirements.
Marketing and Customer Acquisition
Successfully marketing and acquiring customers in the cross-border e-commerce landscape requires a nuanced understanding of international markets and consumer behavior. Effective strategies must overcome geographical barriers, language differences, and cultural nuances to resonate with diverse audiences. This involves targeted marketing campaigns, localized content, and a strong emphasis on building trust and brand reputation.
Effective marketing strategies for reaching international customers leverage a multi-faceted approach, combining digital marketing with traditional methods where appropriate. It’s crucial to adapt messaging and visuals to resonate with the specific cultural contexts of target markets. For example, a campaign that works well in North America might need significant adjustments to be successful in Asia.
Social Media and Digital Marketing in Cross-Border E-commerce
Social media platforms present powerful opportunities for reaching international customers. Targeted advertising campaigns on platforms like Facebook, Instagram, and TikTok allow businesses to reach specific demographics and interests across geographical boundaries. Utilizing multilingual content and culturally relevant visuals is essential for engagement. For instance, a company selling clothing might use influencer marketing on Instagram in different countries, partnering with local influencers who understand the nuances of the local fashion scene and can authentically represent the brand to their followers. Search engine optimization () tailored to different languages and regions is also crucial for driving organic traffic to the e-commerce website. A well-structured strategy should include research in multiple languages and adaptation of website content to suit local search engine algorithms.
Building Trust and Brand Reputation in International Markets
Trust is paramount in cross-border e-commerce, especially when consumers are purchasing from unfamiliar brands across international borders. Building trust requires transparency, clear communication, and a commitment to customer satisfaction. This can be achieved through: showcasing positive customer reviews and testimonials from international customers; providing multiple secure payment options; offering multilingual customer support; and displaying clear shipping information and return policies. A strong brand reputation is built over time through consistent quality, reliable service, and positive customer experiences. For example, a company might actively participate in relevant international industry events to build relationships and credibility within the global community. They might also seek out partnerships with established local businesses to enhance their credibility in the target market.
Customer Service for International Customers, Cross-border e-commerce
Providing exceptional customer service is vital for success in cross-border e-commerce. This requires a multilingual customer support team capable of addressing inquiries and resolving issues in the customer’s native language. Multiple communication channels, such as email, live chat, and phone support, should be available to cater to diverse customer preferences. Utilizing a customer relationship management (CRM) system to track interactions and personalize communications can significantly enhance the customer experience. Proactive communication regarding order updates and shipping information is also essential to keep customers informed and engaged throughout the purchasing process. For instance, automated email updates in the customer’s language can inform them about order status and estimated delivery times. Furthermore, a readily accessible FAQ section on the website, translated into multiple languages, can address common customer inquiries efficiently.
Risks and Challenges
Cross-border e-commerce, while offering immense opportunities, presents a unique set of risks and challenges that businesses must navigate carefully to ensure success. These challenges span logistical complexities, regulatory hurdles, and inherent security vulnerabilities, demanding proactive risk management strategies. Failure to address these adequately can lead to significant financial losses, reputational damage, and ultimately, business failure.
Fraud and Security Breaches
The expansion of cross-border e-commerce increases the risk of fraudulent activities and security breaches. The global nature of transactions exposes businesses to a wider range of potential threats, including credit card fraud, identity theft, and data breaches. Furthermore, navigating diverse legal jurisdictions and differing data protection regulations adds complexity to security management.
Mitigating Fraud and Security Risks
Effective mitigation strategies involve implementing robust security protocols, including multi-factor authentication, encryption of sensitive data, and regular security audits. Employing fraud detection systems that leverage artificial intelligence and machine learning to identify suspicious transactions is crucial. Furthermore, adhering to international data protection standards like GDPR and CCPA is essential to build consumer trust and avoid hefty fines. Regular employee training on cybersecurity best practices is also vital in minimizing human error, a common entry point for many security breaches. For instance, a company might implement a system that flags orders from unusual IP addresses or those with mismatched billing and shipping addresses.
Geopolitical Factors
Geopolitical instability, trade wars, and changes in international regulations can significantly impact cross-border e-commerce. Trade tariffs, sanctions, and political tensions can disrupt supply chains, increase shipping costs, and create uncertainty for businesses. Currency fluctuations also present a significant risk, impacting profitability and pricing strategies. For example, the ongoing trade tensions between the US and China have led to increased tariffs on various goods, affecting the pricing and competitiveness of businesses involved in cross-border e-commerce between the two countries. Brexit also serves as a prime example, creating significant uncertainty and logistical challenges for businesses trading between the UK and the EU.
Overcoming Cross-Border E-commerce Challenges: Successful Strategies
Successful businesses leverage a combination of strategies to overcome these challenges. This includes building strong relationships with reliable logistics providers experienced in international shipping, implementing robust payment gateways that support multiple currencies and secure transactions, and proactively adapting to changes in regulations and geopolitical landscapes. Investing in localized marketing campaigns tailored to specific target markets is also crucial for effective customer acquisition. For example, a company might choose to partner with a local fulfillment center in a key market to reduce shipping times and costs, enhancing customer satisfaction. Another strategy could involve utilizing a global payment gateway that simplifies currency conversions and reduces transaction fees, making the purchasing process smoother for international customers.
Future Trends and Opportunities: Cross-border E-commerce

The cross-border e-commerce landscape is constantly evolving, driven by technological advancements, shifting consumer preferences, and global economic factors. Understanding these future trends is crucial for businesses seeking to thrive in this dynamic market. This section will explore key trends, emerging technologies, innovative approaches, and the resulting opportunities.
Several powerful forces are reshaping the future of cross-border e-commerce. These include the increasing adoption of mobile commerce, the rise of social commerce, the expansion of marketplaces, and the growing importance of personalized shopping experiences. Simultaneously, technological advancements like artificial intelligence and blockchain are creating new possibilities for efficiency, security, and customer engagement.
Emerging Technologies and Their Impact
The integration of artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning (ML) is revolutionizing various aspects of cross-border e-commerce. AI-powered chatbots provide 24/7 customer support in multiple languages, improving customer satisfaction and reducing operational costs. ML algorithms personalize product recommendations, enhancing conversion rates. Furthermore, AI-driven fraud detection systems mitigate financial risks associated with cross-border transactions. Blockchain technology offers enhanced security and transparency in supply chain management and payment processing, building trust between buyers and sellers across international borders. For example, companies like Walmart are using blockchain to track the origin and movement of products, ensuring product authenticity and improving supply chain efficiency.
Innovative Approaches to Cross-Border E-commerce
Several innovative approaches are emerging to address the unique challenges and opportunities of cross-border e-commerce. One such approach is the use of localized websites and marketing materials. This allows businesses to cater to the specific cultural preferences and language requirements of different markets. Another innovative strategy is the implementation of global fulfillment networks, which reduce shipping times and costs by strategically positioning inventory closer to consumers. Companies like Amazon are pioneers in this area, utilizing a vast network of fulfillment centers worldwide. Finally, the growth of cross-border marketplaces, such as AliExpress and eBay, provides smaller businesses with access to a global customer base, simplifying the complexities of international trade.
Visual Representation of Future Opportunities
Imagine a dynamic, interconnected network map. At the center is a large node representing a global e-commerce platform. Radiating outwards are numerous smaller nodes, each representing a different country or region. Lines connecting these nodes represent the seamless flow of goods, information, and payments across borders. The thickness of these lines varies, reflecting the volume of trade between different regions. Within each regional node, smaller sub-nodes represent individual businesses, consumers, and logistics providers. The entire network is vibrant and ever-expanding, reflecting the growth and interconnectedness of the cross-border e-commerce ecosystem. This network is further enhanced by embedded technologies, represented by glowing lines and symbols denoting AI, ML, and blockchain integration, all contributing to a more efficient, secure, and personalized shopping experience. This visual representation highlights the increasing interconnectedness of global markets and the significant opportunities for businesses that can effectively navigate this complex landscape.
Conclusive Thoughts
Successfully navigating the world of cross-border e-commerce requires a strategic approach that considers the interplay of technology, logistics, cultural understanding, and legal compliance. By leveraging technological advancements, optimizing logistics, and understanding diverse consumer preferences, businesses can unlock significant growth opportunities in this global marketplace. However, proactive risk management and a commitment to ethical practices remain paramount for sustained success.
Cross-border e-commerce presents unique challenges and opportunities for businesses. Understanding current market dynamics is crucial for success, and staying informed on the latest strategies is essential. For insightful analysis on effective approaches, you should check out resources like Marketing trend reports , which offer valuable data on consumer behavior and emerging trends. This knowledge directly informs successful cross-border e-commerce strategies, leading to improved market penetration and higher ROI.