Workforce growth planning is crucial for organizations aiming for sustainable success. It’s not just about hiring more people; it’s a proactive strategy encompassing forecasting future needs, developing talent, and ensuring the right skills are in place at the right time. This involves careful analysis of current capabilities, identification of skill gaps, and the creation of robust training and development programs to bridge those gaps. Ultimately, effective workforce growth planning fosters a high-performing, engaged workforce capable of driving organizational growth and achieving strategic objectives.
This guide delves into the key components of a comprehensive workforce growth plan, from defining future workforce needs and developing a strategic talent acquisition plan to implementing effective training programs and establishing robust succession planning processes. We’ll explore various forecasting techniques, budgeting models, and methods for measuring the return on investment of workforce initiatives. Furthermore, we’ll address potential challenges and provide mitigation strategies to ensure the plan’s successful implementation.
Defining Workforce Growth Needs
Effective workforce growth planning hinges on accurately defining future needs. This involves understanding the factors influencing future workforce demands, forecasting skill gaps, and assessing current workforce capabilities. A robust understanding of these three areas forms the bedrock of a successful growth strategy.
Key Factors Influencing Future Workforce Demands
Several interconnected factors significantly impact future workforce demands. These include technological advancements, which necessitate new skills and potentially displace existing roles. Economic trends, such as growth in specific sectors or shifts in consumer demand, also heavily influence hiring needs. Demographic shifts, like aging populations or changes in the education pipeline, impact the availability of talent with specific skill sets. Finally, governmental regulations and industry-specific changes can create both opportunities and challenges for workforce planning. For example, the increasing emphasis on sustainability has led to a surge in demand for professionals with expertise in green technologies.
Forecasting Future Skill Gaps
Forecasting future skill gaps requires a multi-faceted approach. It begins with analyzing current workforce demographics and skills inventories to understand the existing talent pool. This analysis should then be combined with projections of future business needs, taking into account planned expansion, new product launches, or shifts in strategic direction. By comparing the projected future needs with the existing capabilities, organizations can identify potential skill gaps. Advanced techniques like trend analysis, examining historical data to predict future needs, can also be used. For instance, if a company has historically needed one software engineer for every 10 employees and plans to increase its workforce by 20%, they can estimate a need for two additional software engineers.
Assessing Current Workforce Capabilities
Assessing current workforce capabilities involves a thorough evaluation of the existing workforce’s skills, experience, and potential. This often involves using tools like skills assessments, performance reviews, and employee surveys. Analyzing current job descriptions and comparing them to the projected future needs helps pinpoint where skill gaps may exist. Furthermore, identifying high-potential employees and their career aspirations allows for proactive talent development and succession planning. A robust assessment may involve a combination of quantitative data, such as performance metrics, and qualitative data, from employee feedback and manager evaluations. For example, a company might use a combination of skills tests and manager assessments to determine the proficiency of its data analysts in using specific software.
Comparison of Forecasting Techniques
The selection of appropriate forecasting techniques depends on factors such as data availability, resources, and the complexity of the situation. Below is a comparison of some common methods:
| Forecasting Technique | Description | Advantages | Disadvantages |
|---|---|---|---|
| Regression Analysis | Statistical method using historical data to predict future trends. | Objective, data-driven; provides quantitative results. | Requires sufficient historical data; assumes linear relationships. |
| Delphi Method | Expert panel provides iterative feedback to reach consensus on future predictions. | Incorporates expert knowledge; useful for uncertain futures. | Subjective; time-consuming; relies on expert availability. |
| Scenario Planning | Develops multiple possible future scenarios based on different assumptions. | Considers uncertainty and multiple possibilities; promotes flexibility. | Can be complex and resource-intensive; may lead to analysis paralysis. |
| Trend Analysis | Analyzing historical data to identify patterns and extrapolate them into the future. | Simple and easy to understand; requires minimal data. | Assumes that past trends will continue; ignores potential disruptions. |
Strategic Workforce Planning
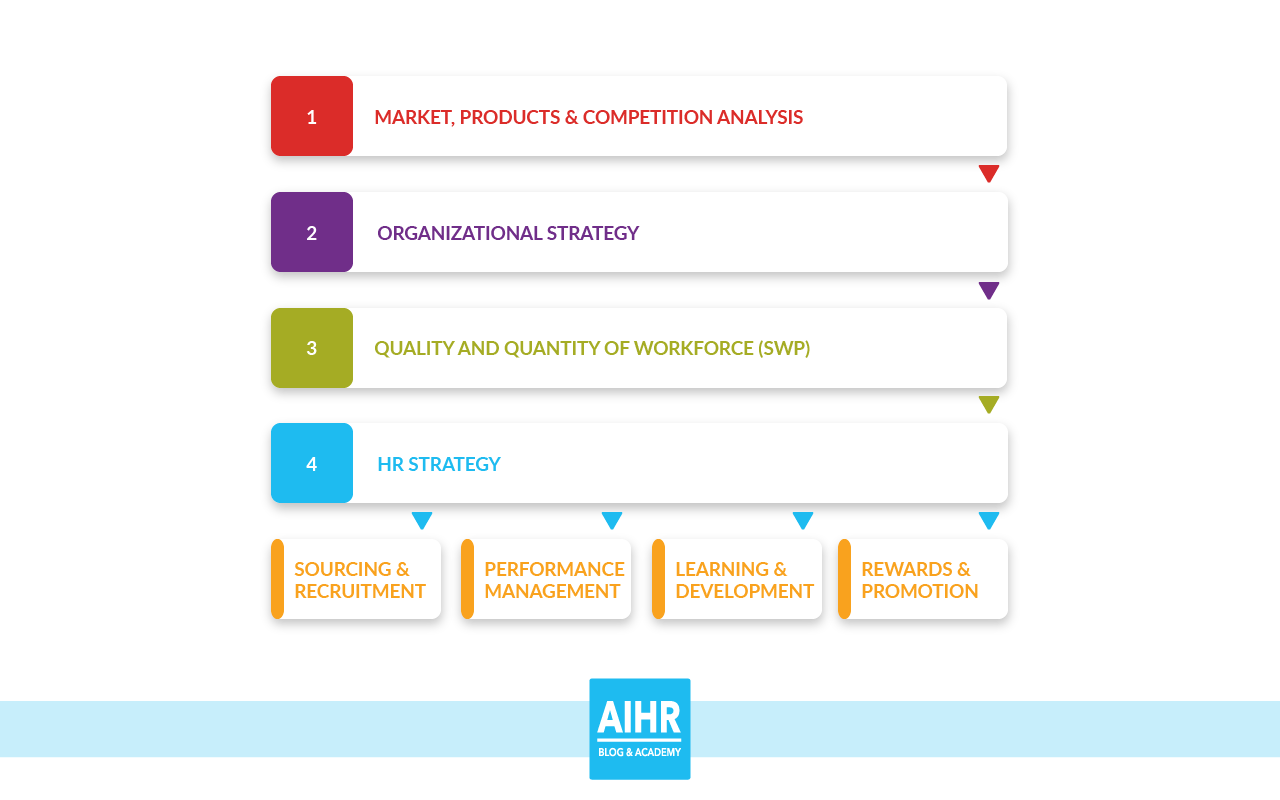
Developing a robust strategic workforce plan is crucial for successfully addressing identified workforce needs and achieving organizational goals. This plan acts as a roadmap, guiding talent acquisition, retention, and engagement strategies to ensure the organization has the right people with the right skills at the right time. It’s a dynamic process, requiring regular review and adaptation to changing business needs and market conditions.
A strategic workforce plan integrates workforce needs with overall business objectives. It’s not simply about filling vacancies; it’s about proactively shaping the workforce to drive future success. This involves analyzing current capabilities, anticipating future skill gaps, and developing strategies to bridge those gaps effectively. The plan should be clearly communicated to all stakeholders, fostering buy-in and collaboration across departments.
Effective workforce growth planning requires anticipating future needs. This includes considering technological advancements that impact staffing requirements; for instance, the rise of innovative retail solutions like virtual fitting rooms may reduce the need for traditional fitting room staff, while increasing demand for tech-savvy personnel to manage and maintain the systems. Therefore, a robust plan must account for these evolving technological roles to ensure a well-balanced and adaptable workforce.
Talent Acquisition Strategy
A well-defined talent acquisition strategy is essential for attracting and securing the talent needed to support organizational growth. This strategy should align directly with the overall workforce plan, identifying specific roles and skill sets required. It should also consider various recruitment channels, including internal promotions, external hiring, and partnerships with educational institutions. Effective strategies also involve competitive compensation and benefits packages, a strong employer brand, and a streamlined hiring process to minimize time-to-hire.
Employee Retention and Engagement Strategies
Retaining and engaging current employees is as important as acquiring new talent. High employee turnover can be costly and disruptive. A strategic workforce plan should incorporate strategies to improve employee retention and engagement, such as creating a positive work environment, providing opportunities for professional development and growth, offering competitive compensation and benefits, and fostering a strong sense of company culture. Regular employee feedback mechanisms are crucial to identify areas for improvement and address concerns proactively.
Examples of Successful Workforce Planning Initiatives
Effective workforce planning requires a proactive and strategic approach. Here are examples of successful initiatives from various sectors:
- Technology Company X: Implemented a comprehensive skills gap analysis, identifying a shortage of data scientists. They partnered with local universities to develop tailored training programs and created a robust internship program to cultivate future talent. This proactive approach ensured they had a pipeline of qualified candidates.
- Healthcare Provider Y: Faced with an aging workforce, they developed a succession planning program to identify and develop high-potential employees to fill leadership roles. This initiative ensured a smooth transition of knowledge and expertise, mitigating the risk of losing institutional memory.
- Manufacturing Company Z: Recognized the need for upskilling their workforce to adopt new technologies. They invested in employee training programs, focusing on automation and digital skills. This initiative enhanced employee capabilities and improved productivity, leading to increased competitiveness.
Skill Development and Training
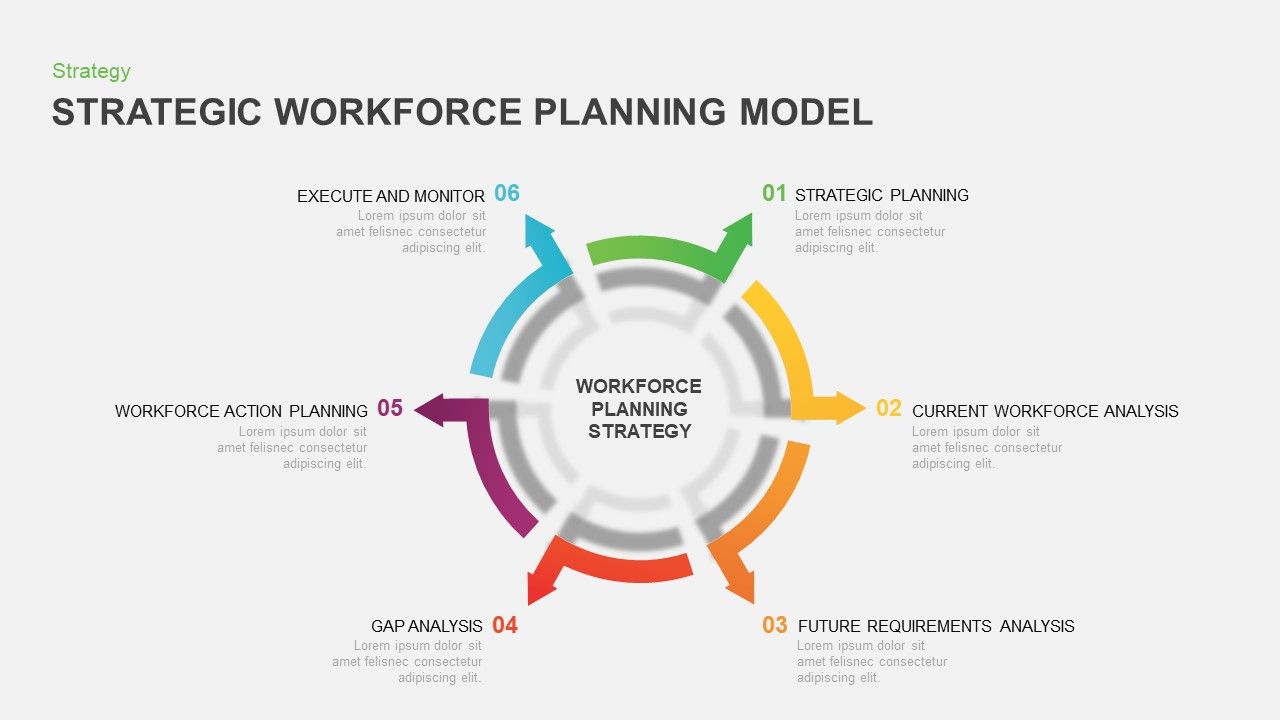
Investing in employee skill development is crucial for sustained workforce growth. A well-structured training program not only equips employees with the skills needed for current roles but also prepares them for future challenges and advancements within the organization. This proactive approach fosters employee engagement, improves productivity, and reduces the risk of skill gaps hindering future success.
A comprehensive skill development strategy requires a thorough understanding of current and future skill needs. This involves analyzing job descriptions, identifying emerging technologies, and considering industry trends. By proactively addressing these needs, organizations can ensure a competitive advantage and a workforce ready to meet evolving demands.
Key Skills for Future Roles
Identifying key skills involves a detailed analysis of current and projected roles within the organization. This analysis should consider both hard skills (technical abilities) and soft skills (interpersonal and communication skills). For example, if the company is moving towards a more data-driven approach, skills like data analysis, programming (Python, R), and data visualization will be crucial. Similarly, strong communication and teamwork skills will always be in high demand. This analysis can be facilitated through surveys, interviews with employees and managers, and a review of industry best practices. The results should be compiled into a skills inventory, highlighting both current skill levels and future requirements.
Comprehensive Training and Development Program Design
The training program should be modular, allowing for flexibility and customization to meet individual employee needs and organizational priorities. The program should incorporate a blend of learning methods, such as online courses, workshops, on-the-job training, and mentoring. A robust learning management system (LMS) can help track progress, manage training materials, and provide analytics on program effectiveness. The program should also incorporate regular assessments to evaluate employee learning and identify areas for improvement. The effectiveness of the program should be continuously monitored and adjusted based on feedback and performance data.
Mentorship Program for Skill Development
A well-structured mentorship program pairs experienced employees with those seeking to develop specific skills. Mentors provide guidance, support, and feedback, fostering a learning environment where mentees can apply their knowledge and develop professionally. The program should carefully match mentors and mentees based on skill sets, career goals, and personality compatibility. Regular check-ins and structured activities, such as project collaborations or shadowing opportunities, will ensure the program’s effectiveness. Mentors should receive training on effective mentoring techniques to maximize the impact of the program. This structured approach fosters a culture of knowledge sharing and accelerates employee development.
Training Program Modules
A well-structured training program should be divided into distinct modules to facilitate learning and tracking progress. The following Artikels a sample structure:
- Module 1: Introduction to Data Analysis: This module will cover fundamental statistical concepts and introduce data analysis tools such as Excel and Tableau. Delivery method: Online course with interactive exercises and quizzes.
- Module 2: Advanced Data Analysis Techniques: This module will delve into more advanced techniques, such as regression analysis and hypothesis testing. Delivery method: Workshop with hands-on activities and group projects.
- Module 3: Data Visualization and Communication: This module will focus on effectively communicating data insights through visualizations and presentations. Delivery method: On-the-job training and mentorship.
- Module 4: Project Management Fundamentals: This module will cover the basics of project management, including planning, execution, and monitoring. Delivery method: Online course with case studies and simulations.
- Module 5: Leadership and Communication Skills: This module will focus on developing effective leadership and communication skills. Delivery method: Workshop with role-playing exercises and group discussions.
Succession Planning and Talent Management
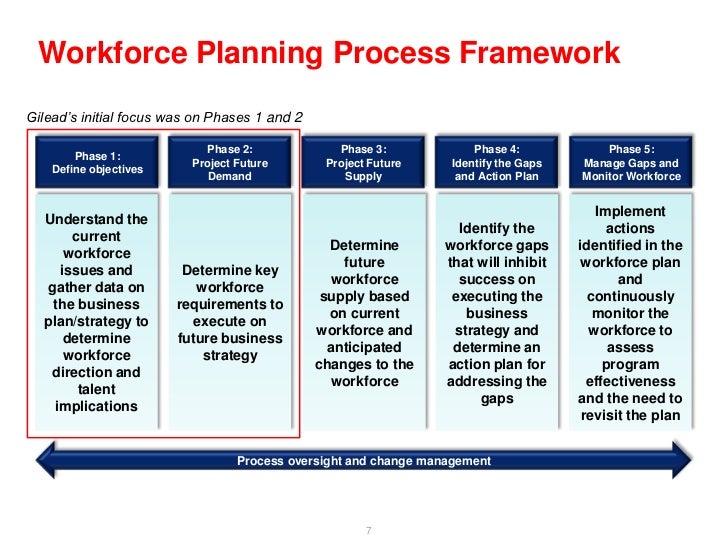
A robust succession plan and a well-structured talent management system are crucial for organizational growth and stability. These initiatives ensure a smooth transition of leadership and expertise, minimizing disruption and maximizing the potential of existing employees. By proactively identifying and developing high-potential individuals, organizations can build a strong pipeline of future leaders and maintain a competitive edge.
Effective succession planning and talent management are intertwined processes. Succession planning focuses on identifying and developing replacements for key roles, while talent management encompasses the broader strategy of attracting, developing, and retaining top talent. Both are essential for ensuring the long-term success of the organization.
Effective workforce growth planning requires a multi-faceted approach. Attracting top talent often involves strategic collaborations, and understanding successful partnership marketing tactics can significantly boost your recruitment efforts. By leveraging these partnerships, you can expand your reach and build a strong employer brand, ultimately contributing to a more robust and sustainable workforce.
Developing a Robust Succession Planning Process
A successful succession planning process begins with identifying critical roles within the organization – those roles whose absence would significantly impact operations. For each critical role, a pool of potential successors should be identified and evaluated based on their skills, experience, and potential. Development plans should then be created for each successor, outlining the specific training, experience, and mentoring opportunities needed to prepare them for the role. Regular reviews and updates to these plans are vital to ensure they remain relevant and effective. This proactive approach minimizes the risk of leadership gaps and ensures a smooth transition when key personnel depart.
Identifying and Developing High-Potential Employees
Identifying high-potential employees requires a multi-faceted approach. Performance reviews, 360-degree feedback, and assessments can provide valuable insights into an employee’s capabilities and potential. Looking beyond just current performance, organizations should also consider factors such as adaptability, learning agility, and leadership potential. Once identified, high-potential employees should be provided with challenging assignments, mentorship opportunities, and specialized training to accelerate their development. This investment in high-potential employees not only benefits the individuals but also strengthens the overall organization. Examples of development programs include fast-track management programs, leadership training workshops, and international assignments.
Creating a Talent Management System
A comprehensive talent management system provides a centralized repository for employee data, including skills, experience, performance reviews, and development plans. This system enables organizations to track employee progress, identify skill gaps, and make informed decisions regarding promotions, transfers, and training. The system should also facilitate communication between employees and managers, fostering a culture of continuous development and feedback. A well-designed system allows for efficient identification of suitable candidates for succession planning and enables proactive talent management decisions. This could involve using software platforms with features such as performance tracking, skills mapping, and learning management systems.
Using Performance Reviews to Identify Training Needs and Career Paths
Performance reviews offer a valuable opportunity to identify training needs and discuss career paths with employees. By analyzing performance data and feedback, managers can pinpoint areas where employees excel and areas requiring improvement. This information can then be used to develop targeted training programs and create individualized career development plans. The process fosters open communication and collaboration between managers and employees, resulting in a more engaged and motivated workforce.
| Employee Name | Performance Review Rating | Identified Skill Gaps | Recommended Training/Development |
|---|---|---|---|
| John Smith | Exceeds Expectations | None identified | Leadership training program |
| Jane Doe | Meets Expectations | Project management skills | Project management workshop |
| David Lee | Needs Improvement | Communication skills, technical expertise | Communication skills training, technical certification course |
| Sarah Jones | Exceeds Expectations | Strategic planning | Mentorship program with senior executive |
Budgeting and Resource Allocation: Workforce Growth Planning
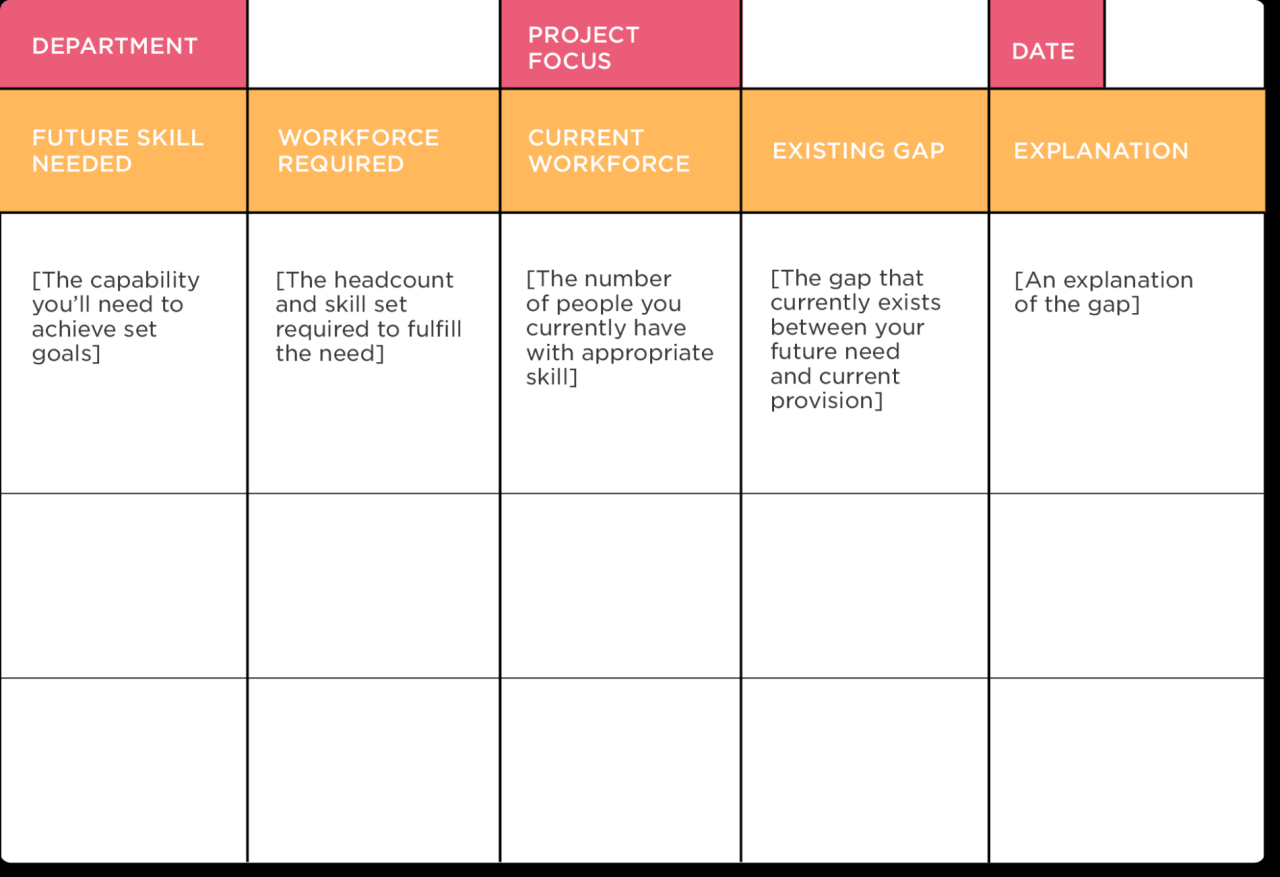
Effective budgeting and resource allocation are crucial for successful workforce growth. A well-defined budget ensures that sufficient funds are available to support initiatives aimed at attracting, developing, and retaining talent, ultimately contributing to the organization’s overall strategic goals. Without a clear financial plan, workforce growth strategies risk becoming unsustainable and failing to deliver the desired results.
A detailed budget for workforce growth should encompass all anticipated costs associated with recruitment, training, development, and retention. This includes expenses related to advertising job openings, conducting interviews, onboarding new hires, providing training programs, implementing performance management systems, and offering competitive compensation and benefits packages to retain existing employees. Careful consideration should be given to both direct and indirect costs.
Developing a Detailed Budget for Workforce Growth Initiatives
Budget development involves a thorough assessment of current resource levels, projected workforce needs, and the costs associated with meeting those needs. This requires detailed forecasting of recruitment costs (advertising, agency fees, relocation expenses), training costs (course fees, instructor salaries, materials), technology investments (learning management systems, performance management software), and compensation adjustments (salary increases, bonus programs). The budget should be broken down into specific categories, with clear allocation for each initiative. For example, a company anticipating a 10% increase in its sales team might allocate X% of the budget to recruitment, Y% to sales training, and Z% to performance-based incentives. Contingency funds should also be included to accommodate unforeseen expenses.
Effective Resource Allocation to Support Training, Recruitment, and Retention Efforts
Resource allocation involves strategically distributing the available budget across various workforce growth initiatives. Prioritization is key; resources should be directed towards initiatives with the highest potential return on investment (ROI). For instance, investing in leadership development programs for high-potential employees may yield greater returns than simply increasing the number of entry-level hires. A balanced approach, however, is crucial, ensuring that both recruitment and retention efforts receive adequate funding. Regular monitoring and adjustments to resource allocation are essential to ensure that funds are used effectively and efficiently.
Methods for Tracking and Measuring the ROI of Workforce Investments
Measuring the ROI of workforce investments is essential for demonstrating the value of these initiatives to stakeholders. Key performance indicators (KPIs) should be established to track the effectiveness of various programs. These KPIs might include employee turnover rates, employee satisfaction scores, productivity levels, and the return on training investment (ROTI). For example, a reduction in employee turnover following the implementation of a new retention program can be quantified and linked directly to cost savings. Similarly, improved productivity following a training program can be measured and correlated to increased revenue. Data analysis is crucial for understanding the impact of workforce investments and making data-driven decisions about future resource allocation.
Comparison of Different Budgeting Models for Workforce Planning
Different budgeting models offer various approaches to resource allocation. Choosing the right model depends on the organization’s specific needs and circumstances.
- Zero-Based Budgeting: This approach requires justifying every expense from scratch each year, regardless of prior spending levels. This method promotes efficiency by encouraging careful consideration of each expenditure. However, it can be time-consuming and resource-intensive.
- Incremental Budgeting: This is a more traditional method that uses the previous year’s budget as a baseline, adjusting it based on projected changes in needs and costs. It is simpler and less time-consuming than zero-based budgeting, but it may not be as effective in identifying areas for cost savings or innovation.
Measuring and Evaluating Success
Effective workforce growth planning isn’t just about implementing strategies; it’s about measuring their impact and making necessary adjustments. This involves establishing clear metrics, consistently monitoring progress, and gathering feedback to ensure the initiatives align with overall business objectives and employee needs. A robust evaluation process provides valuable insights for future planning cycles, optimizing resource allocation and maximizing the return on investment.
Successful workforce planning requires a systematic approach to measuring and evaluating the effectiveness of implemented initiatives. This involves defining key performance indicators (KPIs), monitoring progress against those KPIs, gathering employee feedback, and reporting progress to relevant stakeholders. By implementing this process, organizations can ensure their workforce strategies are achieving their intended outcomes and are adaptable to changing circumstances.
Key Performance Indicators (KPIs) for Workforce Growth
Defining appropriate KPIs is crucial for tracking progress towards workforce goals. These metrics should be specific, measurable, achievable, relevant, and time-bound (SMART). Examples of relevant KPIs include employee turnover rate, employee satisfaction scores, time-to-fill for open positions, cost per hire, and the number of employees with required skills. The selection of KPIs will depend on the specific goals of the workforce planning initiative. For instance, if a key goal is to reduce employee turnover, the turnover rate becomes a critical KPI to monitor closely. Similarly, if the focus is on improving employee skill sets, the number of employees completing relevant training programs would be a key indicator.
Monitoring and Evaluating Workforce Initiatives
Monitoring and evaluating the effectiveness of workforce initiatives involves a continuous process of data collection and analysis. This includes regularly reviewing the KPIs defined earlier, comparing actual performance against targets, and identifying any deviations. Regular progress reports, perhaps monthly or quarterly, should be generated to track performance against goals. Data analysis techniques, such as trend analysis and variance analysis, can be used to identify areas for improvement. For example, if the time-to-fill for a particular role consistently exceeds the target, this may indicate a need for adjustments to the recruitment process.
Gathering Employee Feedback on Workforce Planning Programs
Employee feedback is essential for evaluating the effectiveness of workforce planning programs and ensuring they meet employee needs. Various methods can be employed to gather this feedback, including employee surveys, focus groups, one-on-one interviews, and suggestion boxes. Surveys can provide quantitative data on employee satisfaction and perceptions of the programs. Focus groups and interviews can provide richer qualitative insights into the experiences and perspectives of employees. The choice of method will depend on the specific information needed and the resources available. For example, a short online survey could be used to gauge overall satisfaction, while focus groups could provide deeper understanding of specific aspects of a training program.
Reporting Progress to Stakeholders, Workforce growth planning
Communicating progress to stakeholders is crucial for maintaining transparency and securing buy-in for workforce planning initiatives. Reporting methods should be tailored to the audience and the information being conveyed. Examples of reporting methods include:
- Executive summaries: Concise reports highlighting key findings and recommendations for senior management.
- Detailed reports: Comprehensive reports providing in-depth analysis of data and progress towards goals.
- Dashboards: Interactive visual representations of key KPIs and performance trends.
- Presentations: Engaging presentations summarizing key findings and recommendations for stakeholders.
The frequency of reporting will depend on the nature of the initiative and the needs of stakeholders. Regular updates, perhaps monthly or quarterly, can help to maintain momentum and address any emerging issues proactively. For instance, a quarterly report might include an overview of progress on key initiatives, along with an analysis of variances from planned targets and any corrective actions taken.
Addressing Potential Challenges

Effective workforce growth planning requires anticipating and mitigating potential obstacles. Failure to do so can lead to significant disruptions in achieving organizational goals, impacting productivity, and hindering overall success. This section will explore common challenges and offer proactive mitigation strategies.
Workforce growth planning is inherently complex, influenced by internal and external factors beyond simple projections. Unforeseen circumstances can easily derail even the most meticulously crafted plans. Therefore, a robust approach demands a proactive identification of potential pitfalls and the development of contingency plans to address them.
Challenges in Workforce Growth Planning
Several key challenges can impede successful workforce growth planning. These include difficulties in accurately forecasting future needs, securing and retaining talent in a competitive market, managing the costs associated with expansion, and adapting to rapid technological change. Addressing these challenges requires a multifaceted approach that integrates strategic planning with flexible operational strategies.
Mitigation Strategies for Workforce Growth Challenges
Proactive mitigation strategies are crucial for navigating the complexities of workforce growth. These strategies should focus on building organizational resilience and adaptability. This involves developing robust forecasting models that account for uncertainty, implementing competitive compensation and benefits packages to attract and retain talent, and creating a culture of continuous learning and development. Furthermore, exploring flexible work arrangements and leveraging technology to streamline processes can contribute to efficient resource allocation and cost management.
Technological Advancements and Workforce Planning
Technological advancements significantly impact workforce planning. Automation, artificial intelligence, and data analytics are reshaping job roles and skill requirements. This necessitates a continuous assessment of current and future skill gaps, and the implementation of training programs to equip employees with the necessary competencies. For example, the rise of AI-powered tools requires upskilling or reskilling employees to manage and utilize these technologies effectively. Failure to adapt to these technological shifts can result in a skills mismatch and hinder organizational competitiveness. A proactive approach involves investing in employee training and development, embracing new technologies, and fostering a culture of continuous learning.
Adapting to Changes in the Labor Market
The labor market is dynamic and subject to constant shifts in supply and demand, influenced by economic conditions, technological advancements, and demographic trends. Adapting to these changes requires a flexible and agile approach to workforce planning.
Successful adaptation requires a multi-pronged strategy.
- Strengthening Employer Branding: Attracting top talent requires a compelling employer brand that showcases the organization’s culture, values, and opportunities for growth.
- Diversifying Recruitment Strategies: Exploring diverse recruitment channels, such as online platforms, professional networking events, and partnerships with educational institutions, can broaden the talent pool.
- Investing in Employee Retention: Creating a positive work environment, offering competitive compensation and benefits, and providing opportunities for career advancement can significantly reduce employee turnover.
- Developing Flexible Work Arrangements: Offering flexible work options, such as remote work or flexible hours, can attract and retain talent in a competitive market.
- Building a Culture of Continuous Learning: Investing in employee training and development programs ensures that the workforce possesses the skills and knowledge needed to adapt to changing market demands. This includes providing opportunities for upskilling, reskilling, and cross-training.
Epilogue
Successfully navigating the complexities of workforce growth requires a multifaceted approach that integrates strategic planning, talent development, and resource allocation. By proactively addressing future workforce needs, organizations can mitigate potential risks, foster a highly engaged workforce, and achieve sustainable growth. This guide provides a framework for building a comprehensive workforce growth plan, emphasizing the importance of continuous monitoring, evaluation, and adaptation to ensure alignment with evolving business needs and market dynamics. Remember, a well-executed plan is an investment in the future success of your organization.