Team growth strategies are crucial for organizational success. This guide explores multifaceted approaches to cultivate high-performing teams, focusing on goal setting, skill development, communication enhancement, fostering positive team culture, performance management, delegation, and progress tracking. We delve into practical strategies and tools to help teams achieve their full potential, fostering a collaborative and productive work environment.
By implementing these strategies, organizations can not only improve team performance but also boost employee morale and engagement. We will examine various methods for identifying and addressing skill gaps, improving communication flow, and creating a supportive environment that encourages collaboration and innovation. The ultimate goal is to build resilient and adaptable teams capable of navigating challenges and achieving ambitious objectives.
Defining Team Goals and Objectives
Establishing clear, measurable, and achievable goals is fundamental to successful team growth. Without defined objectives, team efforts can become fragmented and unproductive, hindering overall progress. A well-defined goal-setting process ensures everyone is working towards a common purpose, fostering collaboration and boosting morale.
Setting SMART goals is a crucial step in this process. SMART stands for Specific, Measurable, Achievable, Relevant, and Time-bound. These characteristics ensure that goals are not only ambitious but also realistic and trackable.
SMART Goals for Team Growth
Three examples of SMART goals designed to measurably improve team performance are:
- Increase team project completion rate by 15% within the next quarter, measured by the number of successfully completed projects against the total number of assigned projects. This will be achieved through improved task management and enhanced communication protocols.
- Reduce average project completion time by 10% in the next six months, measured by tracking the time elapsed from project initiation to final delivery. This improvement will be facilitated by implementing agile methodologies and streamlining workflows.
- Improve team member satisfaction scores by 20% by the end of the year, measured through anonymous employee surveys. This increase will be fostered by implementing regular feedback sessions, team-building activities, and addressing individual concerns promptly.
Aligning Individual Goals with Team Objectives
To ensure individual contributions directly support overall team objectives, a structured alignment process is necessary. This process fosters a sense of shared purpose and maximizes individual impact.
Effective team growth strategies often involve leveraging diverse communication channels to reach potential team members. For instance, consider promoting open positions through targeted podcast advertising; exploring avenues like those detailed in this helpful resource on Podcast marketing ideas can significantly broaden your reach. Ultimately, a multi-faceted approach to recruitment enhances your chances of attracting top talent and fostering a thriving team environment.
Aligning individual goals with team objectives involves a collaborative discussion between team members and their managers. Each team member should identify their key performance areas and propose individual goals that directly contribute to the achievement of the overall team objectives. These goals should be documented and regularly reviewed. For example, if the team objective is to improve customer satisfaction scores, an individual goal might be to reduce average customer response time by 10%.
Regular Review and Adjustment of Team Goals
Regular review and adjustment of team goals are critical for maintaining focus and ensuring progress aligns with changing circumstances. Performance data should be analyzed to identify areas of success and areas needing improvement.
Regular reviews, perhaps monthly or quarterly, should involve analyzing key performance indicators (KPIs) linked to the team’s SMART goals. If performance is lagging behind expectations, the team should collaboratively analyze the reasons and adjust the goals or strategies accordingly. For instance, if the team is failing to meet a deadline, it might require re-allocating resources or revisiting the project plan. Conversely, if a goal is exceeded, the team might consider setting a more ambitious target for the future.
Effective team growth strategies often involve fostering collaboration and friendly competition. A fun way to achieve this could be incorporating team-building activities, such as trying out a virtual table tennis game like the one found at Permainan tenis meja virtual. This lighthearted approach can boost morale and improve communication skills, ultimately contributing to a more cohesive and productive team environment.
Skill Development and Training
Investing in your team’s skill development is crucial for sustained growth and improved performance. A well-structured training program not only enhances individual capabilities but also strengthens the team’s overall effectiveness, leading to increased productivity and innovation. This section Artikels a strategic approach to identifying skill gaps, implementing targeted training, and tracking progress.
Identifying Skill Gaps within the Team
To effectively address skill gaps, a systematic approach is necessary. This involves a multi-faceted assessment process, combining individual self-assessments with manager evaluations and performance reviews. Team members should be encouraged to honestly evaluate their current skill levels and identify areas needing improvement. Managers, through observation and performance data, can provide additional insights, highlighting areas where team performance could be enhanced through targeted training. Regular performance reviews offer a structured platform to discuss skill gaps and collaboratively create development plans. Furthermore, 360-degree feedback mechanisms can offer a holistic view of an employee’s strengths and weaknesses, contributing to a more comprehensive skill gap analysis.
Training Programs to Address Skill Gaps
Addressing identified skill gaps requires a diverse range of training programs tailored to specific needs. Internal resources, such as mentorship programs, brown bag sessions, and internal knowledge bases, offer cost-effective solutions for common skill development needs. Mentorship programs pair experienced team members with those needing guidance, facilitating knowledge transfer and skill development through personalized coaching. Brown bag sessions, informal knowledge-sharing sessions, allow for the exchange of expertise and best practices. Internal knowledge bases, accessible online repositories, centralize relevant information, making it readily available to all team members. External resources, including online courses (Coursera, Udemy, LinkedIn Learning), workshops, and conferences, provide access to specialized expertise and broader perspectives. Online courses offer flexibility and scalability, while workshops provide hands-on learning experiences. Conferences facilitate networking and exposure to industry best practices. The choice of training method should be based on the specific skill gap, budget, and time constraints.
Tracking Individual and Team Progress in Skill Development
Effective tracking of individual and team progress is vital to measure the impact of training initiatives. A structured system should be implemented, combining qualitative and quantitative measures. Qualitative measures, such as feedback from managers, peers, and self-assessments, provide insights into the impact of training on performance. Quantitative measures, such as pre- and post-training assessments, demonstrate improvements in skill levels. Regular progress reviews, incorporating both qualitative and quantitative data, provide opportunities for feedback, adjustments, and reinforcement. A dedicated platform, such as a learning management system (LMS), can centralize training materials, track progress, and facilitate communication. The data collected can inform future training initiatives, ensuring continuous improvement and alignment with evolving team needs.
Comparison of Training Methods
| Training Method | Cost | Time Commitment | Effectiveness |
|---|---|---|---|
| Online Courses (e.g., Coursera, Udemy) | Variable, from free to several hundred dollars per course. | Flexible, self-paced learning; can range from a few hours to several weeks. | Highly effective for self-directed learners; effectiveness depends on course quality and learner engagement. |
| Workshops | Moderate to high, depending on the instructor and location. | Typically a few days to a week. | Highly effective for hands-on learning and networking; can be expensive. |
| Mentorship | Low (primarily time commitment from mentor). | Ongoing, flexible schedule. | Highly effective for personalized learning and skill development; requires commitment from both mentor and mentee. |
| Internal Training Programs | Low to moderate (primarily internal resources). | Variable, depending on the program. | Effectiveness depends on program design and content relevance. |
Enhancing Communication and Collaboration

Effective communication and collaboration are cornerstones of a high-performing team. Without them, even the most well-defined goals and skilled individuals will struggle to achieve their full potential. This section explores strategies to improve team communication and foster a collaborative environment, ultimately boosting productivity and team morale.
Strategies for Improving Team Communication
Improving team communication involves a multifaceted approach encompassing both technological solutions and behavioral changes. Clear communication channels, regular feedback mechanisms, and a commitment to active listening are crucial. The use of technology can significantly enhance communication efficiency and accessibility, while established best practices ensure the message is conveyed effectively and understood accurately. For instance, implementing a project management software that facilitates task assignment, progress tracking, and real-time updates can greatly improve transparency and reduce misunderstandings. Similarly, scheduling regular team meetings, utilizing video conferencing for remote teams, and encouraging open dialogue during these meetings can strengthen relationships and enhance communication flow.
Fostering a Culture of Collaboration and Open Communication
Creating a collaborative and open communication culture requires a deliberate and sustained effort. This involves establishing a psychologically safe environment where team members feel comfortable sharing ideas, expressing concerns, and offering constructive criticism without fear of retribution. Leaders play a critical role in modeling this behavior, actively encouraging open dialogue, and actively listening to team members’ perspectives. Team-building activities, both formal and informal, can help build trust and rapport, strengthening the bonds between team members and facilitating more open communication. Furthermore, implementing regular feedback sessions, both formal performance reviews and informal check-ins, allows for open communication regarding progress, challenges, and areas for improvement.
Addressing Communication Barriers and Providing Solutions, Team growth strategies
Several barriers can hinder effective communication within a team. These can include differences in communication styles, language barriers, geographical distance, lack of clarity in roles and responsibilities, and personality clashes. To overcome these barriers, teams can adopt strategies such as cross-cultural communication training, the use of translation tools, regular virtual meetings for geographically dispersed teams, clearly defined roles and responsibilities Artikeld in a project charter, and conflict resolution training. Promoting empathy and understanding amongst team members can also help bridge the gaps caused by personality differences. Establishing clear communication protocols, such as using specific channels for different types of communication, can also help prevent confusion and streamline information flow.
Communication Tools and Their Best Use Cases
Effective communication relies heavily on choosing the right tools for the job. Different tools serve different purposes, and selecting the appropriate one can significantly improve team efficiency and collaboration.
- Project Management Software (e.g., Asana, Trello, Monday.com): Ideal for task assignment, progress tracking, deadline management, and centralizing communication related to specific projects.
- Instant Messaging Platforms (e.g., Slack, Microsoft Teams): Excellent for quick communication, real-time collaboration, and informal discussions among team members.
- Video Conferencing Tools (e.g., Zoom, Google Meet, Microsoft Teams): Best for meetings, presentations, and collaborative work sessions, particularly for remote or geographically dispersed teams.
- Email: Suitable for formal communication, sharing documents, and asynchronous communication when immediate responses are not required.
- Shared Document Platforms (e.g., Google Docs, Microsoft SharePoint): Facilitates collaborative document creation, editing, and version control.
Fostering a Positive Team Culture

A positive team culture is the cornerstone of high performance. It’s more than just pleasant interactions; it’s a shared understanding of values, goals, and behaviors that foster trust, respect, and collaboration. Cultivating this environment requires proactive effort and a commitment from every team member.
Building a positive team culture involves several key strategies, all working in concert to create a supportive and productive workspace. These strategies are not independent but rather interconnected, reinforcing each other to achieve a synergistic effect.
Building Trust and Respect
Trust and respect are fundamental to any successful team. Building these elements requires consistent effort and demonstration. Open communication, where team members feel comfortable sharing their ideas and concerns without fear of judgment, is paramount. Active listening, acknowledging contributions, and providing constructive feedback are crucial steps in fostering a culture of mutual respect. Celebrating successes, both individual and team-wide, also strengthens bonds and reinforces positive interactions. Furthermore, demonstrating fairness and equity in decision-making and resource allocation is essential to building trust. Inconsistency erodes trust, whereas consistent, fair actions build it.
Promoting a Positive and Inclusive Team Environment
A positive and inclusive environment ensures that every team member feels valued, respected, and empowered to contribute their unique skills and perspectives. This includes actively promoting diversity and inclusion, creating opportunities for all members to participate, and fostering a culture of psychological safety where individuals feel comfortable taking risks and expressing themselves without fear of negative consequences. Regular team-building activities, focusing on shared experiences and collaborative problem-solving, can help to build camaraderie and strengthen relationships. Providing opportunities for mentorship and skill-sharing further strengthens team cohesion and creates a supportive learning environment. Regular feedback mechanisms, allowing team members to voice their opinions and suggestions, are also crucial for fostering an inclusive culture.
Addressing Conflicts and Disagreements Constructively
Conflicts are inevitable in any team, but how they are handled determines their impact. Establishing clear communication channels and protocols for conflict resolution is crucial. This might involve implementing a structured process for addressing disagreements, such as mediation or facilitated discussions. Emphasizing active listening and focusing on finding solutions rather than assigning blame are vital components of constructive conflict resolution. Training team members in conflict resolution techniques can significantly improve their ability to navigate disagreements effectively. Furthermore, fostering a culture of open dialogue and respectful debate allows for healthy conflict that can lead to innovation and improved decision-making. It’s important to remember that disagreements aren’t inherently negative; they can be opportunities for growth and improvement if managed properly.
Scenario Illustrating Positive Team Culture and Increased Productivity
Imagine a software development team working on a complex project with a tight deadline. This team, characterized by a strong positive team culture, proactively addresses challenges. Open communication allows for early identification and resolution of roadblocks. Trust and respect enable team members to readily seek help from colleagues, leading to efficient knowledge sharing. When conflicts arise, they’re addressed constructively through facilitated discussions, resulting in innovative solutions rather than stagnation. This collaborative approach, fueled by a positive and supportive environment, leads to increased productivity, higher quality code, and improved team morale. The project is completed not only on time but also exceeds expectations, demonstrating the direct link between a positive team culture and enhanced performance. This success further reinforces the positive culture, creating a self-perpetuating cycle of high performance and engagement.
Performance Management and Feedback
Effective performance management is crucial for team growth. A well-structured system ensures individual contributions align with team goals, fosters continuous improvement, and boosts overall team performance. This involves regular feedback, meaningful performance reviews, and appropriate recognition of achievements.
A robust performance management system relies on consistent and constructive feedback. This should be a two-way process, encouraging open communication and mutual understanding. Feedback should be specific, focusing on both strengths and areas for development, tied to observable behaviors and quantifiable results whenever possible. Regular check-ins, perhaps weekly or bi-weekly, allow for timely addressing of concerns and celebrating successes.
Regular Feedback Mechanisms
Implementing a structured approach to feedback delivery is essential. This could involve regular one-on-one meetings, utilizing a feedback form for consistent tracking, or incorporating peer feedback sessions. These methods should be tailored to the team’s size and working style, aiming for consistency and transparency.
Effective Performance Reviews
Performance reviews should be more than an annual appraisal; they should be a collaborative discussion focused on achievements, challenges, and future goals. Individual contributions are assessed against pre-defined key performance indicators (KPIs) and team goals. The review should delve into both quantitative data (e.g., sales figures, project completion rates) and qualitative assessments (e.g., teamwork, problem-solving skills, communication effectiveness). This holistic approach provides a comprehensive understanding of an individual’s performance within the team context.
Recognizing and Rewarding Team Achievements
Recognizing and rewarding team achievements fosters a positive and motivating work environment. This could involve public acknowledgement during team meetings, awarding bonuses or gift certificates, or offering opportunities for professional development. The recognition should be specific, highlighting the team’s contribution and the impact of their collective effort. This strengthens team cohesion and encourages future success.
Using Performance Data to Inform Future Team Growth Strategies
Performance data provides valuable insights for refining team growth strategies. By analyzing individual and team performance metrics, areas of strength and weakness can be identified. This data can then inform decisions about skill development initiatives, resource allocation, and team restructuring.
For example, let’s say a sales team consistently underperforms on a specific product line. Analyzing sales data might reveal a lack of product knowledge among team members. This insight could lead to targeted training on that product line, improving sales performance in the future. Similarly, if performance reviews consistently highlight poor communication as a recurring issue, implementing communication workshops could be a beneficial investment.
Delegation and Empowerment: Team Growth Strategies
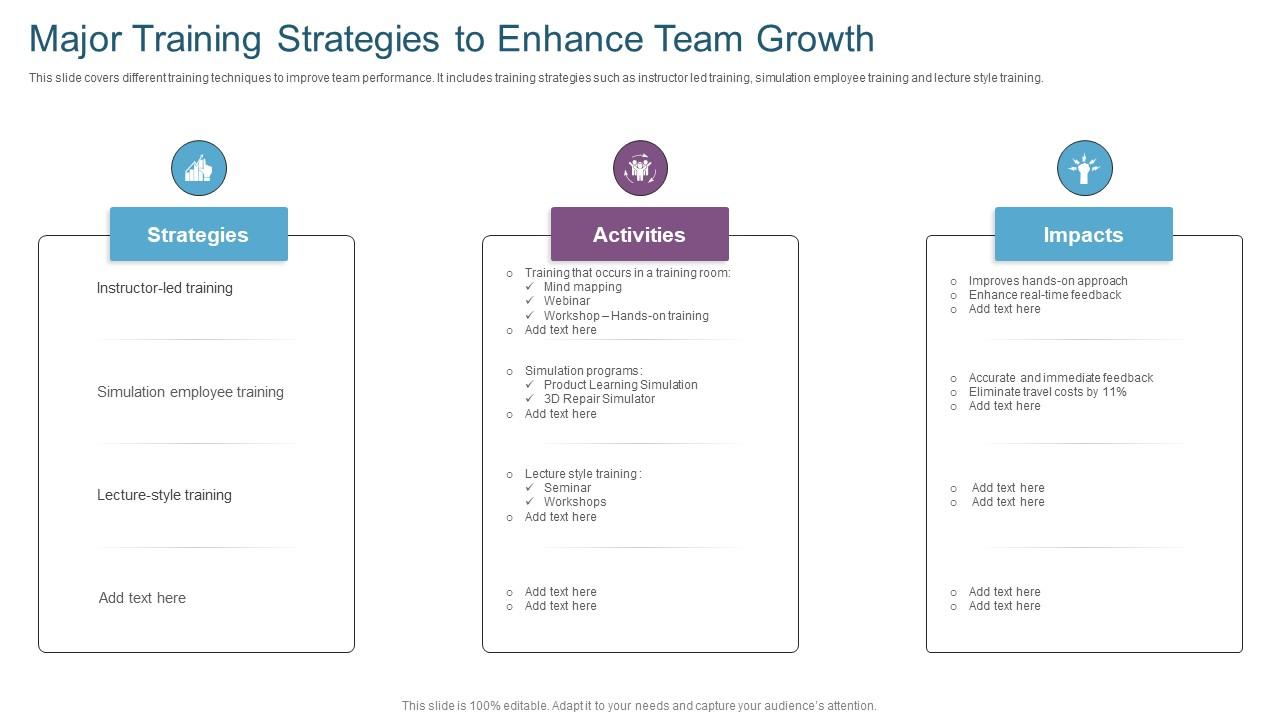
Effective delegation and empowerment are crucial for team growth. By entrusting tasks and fostering autonomy, leaders cultivate a more engaged and productive workforce, ultimately boosting overall team performance and individual skill development. This section explores practical techniques for delegation, strategies for empowering team members, and the resulting benefits for both individuals and the team.
Effective Delegation Techniques involve carefully considering the task, the individual’s skills and experience, and providing clear expectations and support. It’s not simply about offloading work, but about strategically assigning responsibilities to maximize individual and team potential.
Effective Delegation Techniques
Successful delegation hinges on a structured approach. First, clearly define the task, including desired outcomes, deadlines, and available resources. Second, select the appropriate team member based on their skills and capacity. Consider their strengths, weaknesses, and current workload. Third, provide clear instructions and necessary training or support. Fourth, establish regular check-ins to monitor progress and offer guidance without micromanaging. Finally, provide constructive feedback upon completion, focusing on both achievements and areas for improvement. For example, delegating a project to a team member with strong analytical skills, providing them with the necessary data and resources, and setting clear milestones with regular check-ins, fosters ownership and builds their confidence. Conversely, assigning a complex task to a junior team member without sufficient support would likely lead to frustration and poor results.
Empowering Team Members to Take Ownership
Empowerment involves providing team members with the authority, responsibility, and resources to manage their work independently. This includes granting decision-making power within their area of responsibility, encouraging initiative, and providing opportunities for professional growth. Open communication, trust, and a supportive environment are crucial for fostering ownership. For instance, allowing a team member to independently manage a client relationship, including decision-making on minor issues, demonstrates trust and encourages initiative. Regular feedback sessions, focusing on both successes and areas for improvement, further reinforce this empowerment and encourage continued ownership.
Benefits of Delegation and Empowerment
Delegation and empowerment offer numerous benefits. For individuals, it leads to increased skill development, enhanced confidence, and greater job satisfaction. For the team, it fosters collaboration, improves efficiency, and promotes a more positive and productive work environment. Increased efficiency results from better task allocation and reduced workload for the manager. Improved morale and motivation are direct consequences of increased autonomy and trust. For example, a team where members are empowered to make decisions related to their projects often shows increased productivity and a greater sense of collective responsibility. Conversely, a team lacking empowerment often experiences decreased morale and slower progress.
Comparison of Delegation Styles
Different delegation styles exist, each impacting team dynamics differently. A telling style provides detailed instructions with minimal input from the team member. A selling style involves explaining the task and its importance, encouraging questions and collaboration. A participating style involves shared decision-making and ongoing collaboration. A delegating style provides the team member with complete autonomy and responsibility. The optimal style depends on the task’s complexity, the team member’s experience, and the overall team culture. For instance, a telling style might be appropriate for a simple, well-defined task for a new team member, while a delegating style would be suitable for a complex project assigned to an experienced and highly skilled individual. The participating style is often most effective for fostering collaboration and shared learning within the team.
Measuring and Tracking Progress
Effective measurement is crucial for understanding the impact of team growth strategies. Without a system for tracking key metrics, it’s impossible to know whether initiatives are successful or to identify areas needing attention. This section Artikels a framework for monitoring progress and using data to drive continuous improvement.
A robust system for tracking team growth should encompass a range of quantitative and qualitative data points. Quantitative data provides objective measures of performance, while qualitative data offers valuable insights into team dynamics and employee experiences. Combining both types of data paints a more complete picture of team progress.
Key Metrics and Data Collection Methods
Tracking team growth requires a strategic selection of key performance indicators (KPIs). These metrics should align directly with the team’s goals and objectives. For instance, if a team’s objective is to improve project completion rates, then metrics such as “on-time project delivery percentage” and “number of projects completed per quarter” become critical. Similarly, if employee satisfaction is a key goal, regular surveys and feedback sessions provide valuable qualitative data. Data collection methods should be chosen based on the specific metrics being tracked, ensuring reliability and consistency. Examples include project management software for tracking project timelines and completion rates, employee satisfaction surveys, and regular team meetings dedicated to feedback and progress reviews.
Data Analysis and Interpretation
Once data is collected, the next step is to analyze and interpret the findings. This involves identifying trends, patterns, and outliers in the data. For example, a consistent decline in project completion rates might indicate a need for improved resource allocation or training. Conversely, a significant increase in employee satisfaction scores could suggest the success of initiatives aimed at fostering a positive team culture. Data analysis should be ongoing, allowing for adjustments to strategies as needed. Regular reporting, ideally on a monthly or quarterly basis, helps keep the team informed of progress and allows for timely intervention when necessary. This regular review process ensures that the team remains focused on its objectives and allows for proactive adjustments to improve performance.
Visual Representations of Team Progress
Visual representations are essential for effectively communicating team progress to stakeholders. They provide a clear and concise overview of key metrics, making it easier to understand trends and identify areas for improvement.
Examples of Visual Representations
1. Progress Bar Charts: These charts visually represent the progress towards a specific goal. For example, a progress bar could show the percentage of projects completed, the number of training sessions completed, or the overall employee satisfaction score. Each bar could be color-coded to indicate different levels of progress (e.g., green for on-track, yellow for caution, red for behind schedule).
2. Line Graphs: Line graphs are effective for illustrating trends over time. They can show the evolution of key metrics such as project completion rates, employee turnover rates, or customer satisfaction scores. By plotting these metrics against time, it is possible to easily identify upward or downward trends and pinpoint specific periods where performance improved or declined.
3. Radar Charts: Radar charts are useful for comparing performance across multiple metrics simultaneously. Each axis represents a different KPI, and the data points are connected to create a polygon. This allows for a quick visual comparison of performance across various areas. For example, a radar chart could show the team’s performance on metrics such as productivity, efficiency, communication, and collaboration.
4. Heatmaps: Heatmaps use color gradients to represent the magnitude of data. They are particularly useful for identifying patterns and correlations within large datasets. For instance, a heatmap could visualize employee feedback on different aspects of the team culture, highlighting areas that require attention.
Final Review
Ultimately, successful team growth hinges on a holistic approach that encompasses clear goal setting, continuous skill development, robust communication, a positive team culture, effective performance management, empowered delegation, and consistent progress tracking. By implementing the strategies Artikeld in this guide, organizations can cultivate high-performing teams that are not only productive but also engaged, motivated, and resilient. The journey to team excellence requires ongoing commitment, adaptation, and a focus on continuous improvement.