Product catalog management is the backbone of any successful e-commerce operation. Effective catalog management isn’t just about listing products; it’s about creating a seamless and engaging customer experience that drives sales. This involves careful planning, data organization, compelling content creation, and strategic distribution across multiple channels. From choosing the right PIM software to optimizing search functionality and ensuring data security, we’ll explore the multifaceted aspects of building and maintaining a high-performing product catalog.
This guide delves into the core components of a robust product catalog management system, covering everything from defining your product data structure and creating engaging content to optimizing search functionality and ensuring data security and compliance. We’ll examine both manual and automated approaches, compare various PIM solutions, and provide practical strategies for maximizing the effectiveness of your product catalog across various sales channels.
Defining Product Catalog Management

Product catalog management is the process of creating, maintaining, and optimizing a comprehensive and accurate digital representation of a company’s product offerings. It encompasses all aspects of managing product data, from initial creation and enrichment to ongoing updates and distribution across various sales channels. Effective catalog management is crucial for enhancing customer experience, streamlining operations, and ultimately driving sales.
Product catalog management systems play a pivotal role in organizing and presenting product information. A robust system goes beyond simply listing products; it provides a centralized hub for managing all associated data, ensuring consistency and accuracy across all platforms.
Core Components of a Robust Product Catalog Management System
A successful product catalog management system relies on several key components working in harmony. These include a centralized database to store product information, tools for data entry and updates, functionalities for managing product images and multimedia, and features for automating tasks such as data validation and synchronization across different channels (e.g., website, mobile app, marketplaces). Furthermore, robust search and filtering capabilities, reporting and analytics dashboards, and integration with other business systems (e.g., ERP, CRM) are essential for maximizing efficiency and gaining valuable insights. Without these integrated components, the system would be fragmented and inefficient.
Manual vs. Automated Catalog Management
Manual catalog management relies heavily on human intervention for every step of the process, from data entry to updates and distribution. This approach is often slow, error-prone, and lacks scalability. Automated catalog management, on the other hand, leverages software and technology to automate many of these tasks, reducing manual effort, minimizing errors, and improving efficiency. Automated systems typically feature features like automated data imports, updates, and validation, as well as automated workflows for tasks such as product creation and approval. The key difference lies in the level of human intervention required: manual systems require significant manual work, while automated systems minimize human involvement and maximize efficiency.
Comparison of PIM Software Solutions
Various Product Information Management (PIM) software solutions exist, each offering a unique set of features and capabilities. Some solutions focus on ease of use and affordability, while others offer advanced features such as complex data mapping, workflow automation, and multi-channel distribution capabilities. For example, a small business might opt for a simpler, cloud-based PIM solution, while a large enterprise might require a more robust, on-premise solution with advanced integration capabilities. The choice depends heavily on the specific needs and resources of the business. Factors to consider include scalability, integration capabilities, cost, user-friendliness, and the specific features offered.
Workflow for Efficient Product Data Entry and Updates
An efficient workflow for product data entry and updates is crucial for maintaining data accuracy and consistency. A well-defined workflow should incorporate several key steps: First, data collection from various sources (e.g., suppliers, manufacturers, internal teams). Second, data validation and standardization to ensure consistency and accuracy. Third, data enrichment to add context and detail to product information. Fourth, data approval and publishing across various sales channels. Finally, ongoing monitoring and updates to reflect changes in product information or market conditions. This structured approach minimizes errors, reduces manual effort, and ensures the timely dissemination of accurate product information.
Data Organization and Structure
Effective product catalog management hinges on a well-organized and structured data foundation. A robust system ensures data accuracy, consistency, and efficient retrieval, ultimately leading to improved search functionality, streamlined operations, and enhanced customer experience. Proper data organization facilitates scalability and simplifies updates as the catalog grows.
Efficient product data organization relies on a clearly defined structure. This involves establishing a hierarchical system, using consistent naming conventions, and employing a standardized attribute schema. This approach ensures data integrity and facilitates seamless integration with other systems, such as e-commerce platforms or ERP systems.
Hierarchical Product Data Structure
A hierarchical structure organizes products into logical categories and subcategories, mirroring the natural way customers might browse for products. This improves navigation and search, making it easier for users to find what they need. For example, a clothing retailer might organize their catalog by category (Men’s, Women’s, Children’s), then by subcategories (Shirts, Pants, Dresses), and finally by individual products. This structure can be represented visually using a tree diagram, where each branch represents a category or subcategory. The following table provides a simplified example of a product catalog using a hierarchical structure:
| Product ID | Name | Description | Price |
|---|---|---|---|
| SKU12345 | Men’s T-Shirt | 100% cotton, short sleeve, classic fit | $19.99 |
| SKU67890 | Women’s Dress | Floral print, knee-length, A-line | $49.99 |
| SKU13579 | Children’s Hoodie | Soft fleece, kangaroo pocket, various colors | $24.99 |
| SKU24680 | Men’s Jeans | Regular fit, dark wash, durable denim | $59.99 |
Product Attribute Schema
A well-defined schema is crucial for managing product attributes, including variations and options. This schema acts as a blueprint, specifying the types of data to be collected for each product. It should include fields for essential information like product name, description, price, weight, dimensions, and SKU. Additionally, it should accommodate variations such as size, color, and material. For example, a single product, like a shirt, might have variations for size (S, M, L, XL) and color (red, blue, green). The schema ensures consistency in data entry and prevents data inconsistencies across the catalog. This allows for efficient filtering and sorting options, improving the user experience.
Data Standardization and Consistency
Maintaining data standardization and consistency is paramount. Inconsistencies, such as using multiple names for the same product or using different units of measurement, can lead to errors, confusion, and difficulty in managing the catalog. Standardization involves establishing clear guidelines for data entry and ensuring that all data conforms to these guidelines. This includes using consistent units of measurement (e.g., kilograms, centimeters), formatting (e.g., date formats), and terminology. Consistent data improves data quality, reduces errors, and enhances the overall efficiency of the catalog management process.
Best Practices for Managing Product Images and Multimedia Content
High-quality product images and multimedia content are essential for engaging customers. Best practices include using high-resolution images with consistent backgrounds and lighting. Images should be optimized for web use to ensure fast loading times. Providing multiple images from different angles can help customers visualize the product better. Furthermore, videos and 360° views can provide an even more immersive experience. Consistent naming conventions for images and multimedia files (e.g., using product IDs) are crucial for organization and easy retrieval. Properly tagging and categorizing images with relevant s also facilitates search and retrieval.
Catalog Content Creation and Enrichment
Creating a compelling product catalog goes beyond simply listing items; it’s about crafting a shopping experience that converts browsers into buyers. Effective catalog content leverages high-quality visuals, persuasive descriptions, and social proof to build trust and drive sales. This section details strategies for creating and enriching your product catalog to maximize its impact.
Compelling Product Descriptions
Creating compelling product descriptions requires a blend of creativity and strategic thinking. Instead of simply listing features, focus on highlighting the benefits those features provide to the customer. Use strong action verbs and evocative language to paint a picture of how the product will improve the customer’s life. Consider incorporating storytelling elements to connect with the reader on an emotional level. For example, instead of “This blender has a powerful motor,” try “Experience effortless blending with our powerful motor – say goodbye to chunky smoothies and hello to perfectly pureed ingredients.” Remember to optimize descriptions for search engines by incorporating relevant s naturally within the text. A well-written description should be concise, informative, and persuasive, encouraging the reader to add the product to their cart.
High-Quality Images and Videos
Visuals are crucial for showcasing products effectively. High-resolution images should be used to display products from multiple angles, highlighting key features and details. Lifestyle images, showcasing the product in use, can be particularly effective in demonstrating its value and appeal. For example, an image of a family enjoying a meal prepared with a specific cookware set adds emotional context and encourages purchase. Videos can further enhance the shopping experience by allowing customers to see the product in action. Product demos, customer testimonials, and even short, engaging animations can be incorporated to increase engagement and provide a more immersive experience. Consider using 360° product views to allow customers to examine the product from every angle. Professional-quality photography and videography are essential to make a positive first impression and build customer confidence.
Customer Reviews and Ratings
Incorporating customer reviews and ratings into your product catalog provides invaluable social proof. Positive reviews build trust and credibility, influencing purchasing decisions. Displaying a star rating prominently next to each product provides a quick visual cue of its overall customer satisfaction. Negative reviews, while potentially concerning, offer opportunities for improvement and demonstrate transparency. Responding to both positive and negative reviews shows customers that you value their feedback and are committed to providing a positive shopping experience. Consider highlighting particularly insightful or helpful reviews to showcase customer experiences. This social proof significantly boosts consumer confidence and encourages conversions. Amazon’s product review system is a prime example of the power of user-generated content.
Managing Translations and Localization
For businesses targeting multiple markets, translating and localizing product information is critical. A poorly translated catalog can alienate potential customers and damage brand reputation. A robust system for managing translations should be implemented, involving professional translators familiar with the nuances of each target language. This system should encompass not just product descriptions but also all other relevant text within the catalog, including titles, headings, and marketing materials. Localization goes beyond simple translation; it involves adapting the content to reflect cultural norms and preferences of the target market. This might involve adjustments to pricing, units of measurement, and even the overall tone and style of the descriptions. Consider using translation management software to streamline the process and ensure consistency across all languages. Companies like Netflix effectively localize their content to resonate with diverse global audiences.
Catalog Publishing and Distribution: Product Catalog Management
Getting your meticulously crafted product catalog into the hands (or screens) of your customers is the final, crucial step. Effective publishing and distribution strategies are vital for maximizing reach and driving sales. This section explores the various methods available and the best practices for ensuring your catalog remains current and accessible across multiple channels.
Successful product catalog publishing and distribution requires a multifaceted approach, encompassing diverse channels and seamless integration with existing systems. This allows businesses to reach a broader audience and present their products effectively, regardless of customer preference for accessing information.
Efficient product catalog management is crucial for any business, ensuring accurate and up-to-date information for customers. Consider the meticulous detail required, much like creating a comprehensive recipe collection; for instance, a detailed guide like this one on traditional Indonesian cakes, Panduan memasak kue tradisional , showcases the level of precision needed. Similarly, a well-organized product catalog provides a positive customer experience and boosts sales.
Website Integration
Integrating your product catalog with your website is paramount. This usually involves using an e-commerce platform or a dedicated catalog management system that allows for dynamic updates and seamless navigation. A well-integrated catalog offers customers a user-friendly experience, allowing them to easily search, filter, and browse products. Imagine a clean, intuitive interface with high-quality product images, detailed descriptions, and customer reviews, all easily accessible via search or category browsing. This creates a positive shopping experience, encouraging engagement and purchases. Features like advanced search filters (e.g., by price, brand, color) and personalized recommendations further enhance the user experience.
Mobile App Integration
A dedicated mobile app provides a highly personalized and convenient shopping experience. The app should mirror the website’s functionality but optimize for the smaller screen size and touch-based interface. Push notifications for sales, new product launches, or personalized recommendations can also drive engagement. For example, a clothing retailer might use push notifications to alert users about new arrivals in their preferred style or size. This direct engagement can significantly boost sales and customer loyalty.
Print Catalog Distribution
While digital channels dominate, print catalogs still hold value, particularly for businesses targeting specific demographics or emphasizing a premium brand image. Effective print catalog distribution might involve targeted mail campaigns, partnerships with relevant businesses, or placement in high-traffic locations. A well-designed print catalog can convey a sense of quality and prestige that digital formats sometimes lack. Consider a high-end watchmaker using beautifully printed catalogs distributed to luxury hotels and exclusive events. The tangible nature of the catalog reinforces the perceived value of the products.
E-commerce Platform Integration
Seamless integration with your e-commerce platform is critical for a streamlined shopping experience. This means real-time updates of product information (pricing, availability, descriptions) between your catalog management system and the online store. Any changes made in one system should automatically reflect in the other, eliminating inconsistencies and preventing errors. This minimizes manual data entry, reduces the risk of human error, and ensures consistent product information across all channels. A successful integration might involve using APIs or dedicated connectors to synchronize data between systems.
Managing Catalog Updates and Revisions
Effective strategies for managing updates and revisions are crucial for maintaining data accuracy and consistency. A robust system for managing product information changes is essential. This typically involves a workflow process for approving changes, assigning responsibilities, and tracking updates. Version control is vital to track changes and allow for rollbacks if necessary. For instance, a system might allow for multiple users to edit product information, but all changes are reviewed and approved by a manager before being published live. This ensures quality control and prevents accidental errors from being published.
Version Control and Rollback Capabilities
Version control allows you to track changes made to your product catalog over time. This is crucial for identifying the source of errors, reverting to previous versions if necessary, and ensuring data integrity. A well-implemented version control system allows for easy rollback to previous versions in case of errors or unexpected issues. For example, if a pricing error is discovered after a catalog update, the system should allow a quick rollback to the previous version, minimizing the negative impact on sales and customer trust. This functionality is essential for maintaining data integrity and preventing costly mistakes.
Catalog Maintenance and Optimization
Maintaining a product catalog requires ongoing effort to ensure accuracy, completeness, and relevance. A poorly maintained catalog can lead to lost sales, frustrated customers, and decreased operational efficiency. Effective strategies for maintenance and optimization are crucial for maximizing the value of a product catalog.
Common Challenges in Maintaining Product Catalog Accuracy
Keeping a product catalog accurate and up-to-date presents several recurring challenges. Inconsistent data entry, human error, and the sheer volume of products to manage all contribute to inaccuracies. Furthermore, integrating data from multiple sources (e.g., ERP, CRM, supplier systems) can create discrepancies and inconsistencies. Delayed updates to product information, such as price changes or stock levels, can lead to customer dissatisfaction and lost sales. Finally, managing product variations and options (sizes, colors, etc.) adds complexity to the maintenance process.
Strategies for Handling Product Discontinuation and Updates
Effective strategies for managing product discontinuation and updates are essential for maintaining catalog integrity. A clear process for identifying and removing discontinued products is crucial. This should include automated alerts and workflows to ensure timely removal from the catalog and potentially, notification to customers with existing orders. For product updates, a version control system helps track changes and revert to previous versions if needed. Regular reviews of product information, ideally scheduled, ensures that details are current and consistent. Clear communication channels between different teams (e.g., marketing, sales, procurement) are necessary for coordinated updates and to avoid conflicting information.
Optimizing Product Catalog Search Functionality, Product catalog management
Optimizing product catalog search functionality is vital for a positive user experience. Implementing robust search algorithms, such as those using natural language processing, allows for more flexible and accurate searches. Providing comprehensive search filters based on various product attributes (e.g., price, brand, category, features) empowers users to easily narrow down their search results. Using auto-suggest and predictive search features enhances the search experience and helps users find what they’re looking for quickly. Regular testing and user feedback are crucial for refining search functionality and addressing usability issues. Synonym management and the use of stemming or lemmatization can improve search accuracy by accounting for variations in how users might search for a product.
Using Analytics to Track Catalog Performance
Analyzing catalog performance data offers valuable insights for improvement. Key metrics to track include search query analysis, conversion rates, bounce rates, and product view rates. This data can reveal popular products, areas needing improvement in search functionality, and issues with product descriptions or images. By analyzing user behavior, it is possible to identify poorly performing products, understand search patterns, and optimize catalog organization. A/B testing different catalog layouts, search algorithms, and product descriptions helps to refine the catalog based on real user data. Regular reporting and analysis of these metrics provide a data-driven approach to catalog optimization.
Integration with Other Systems
Effective product catalog management hinges on seamless integration with other crucial business systems. A well-integrated catalog ensures data consistency, reduces manual effort, and streamlines various business processes, ultimately improving operational efficiency and customer experience. This section details the key integrations and their benefits.
Integration with Inventory Management Systems
Integrating the product catalog with an inventory management system (IMS) provides real-time visibility into stock levels. This prevents overselling and ensures accurate product availability information is displayed to customers. The system automatically updates catalog information, such as stock levels and product availability, reflecting the actual inventory status. This eliminates discrepancies between what’s shown online and what’s physically available, leading to improved customer satisfaction and reduced order fulfillment issues. For example, if an IMS indicates that a particular shirt in size medium is out of stock, the catalog will immediately reflect this, preventing customers from ordering an unavailable item.
Integration with CRM and ERP Systems
Connecting the product catalog to Customer Relationship Management (CRM) and Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) systems unlocks a wealth of data and functionality. CRM integration allows for personalized product recommendations and targeted marketing campaigns based on customer preferences and purchase history. ERP integration provides access to comprehensive product data, including pricing, costs, and manufacturing information, facilitating efficient order processing and financial reporting. This holistic view streamlines operations and enhances decision-making. For instance, sales data from the CRM can be used to identify high-demand products, enabling the ERP system to optimize production and inventory levels accordingly, reflected in real-time updates to the product catalog.
API Integrations for Seamless Data Exchange
Application Programming Interfaces (APIs) are the backbone of seamless data exchange between the product catalog and other systems. APIs enable automated data synchronization, eliminating manual data entry and reducing the risk of errors. Real-time updates ensure data consistency across all platforms. Different API types, such as RESTful APIs, can be employed depending on the specific requirements and architecture of the systems involved. A robust API strategy ensures a flexible and scalable system capable of adapting to future integrations and technological advancements. For example, a REST API could be used to automatically update product prices in the catalog whenever a price change is made in the ERP system.
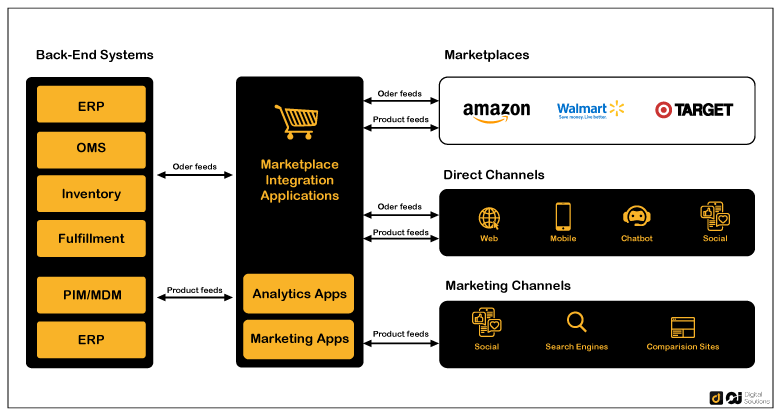
Information Flow Diagram
Imagine a diagram showing four interconnected boxes representing the Product Catalog Management system, the Inventory Management System (IMS), the Customer Relationship Management (CRM) system, and the Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) system. Arrows connect these boxes, illustrating the data flow. An arrow from the IMS to the Product Catalog shows inventory updates flowing into the catalog. Arrows from the ERP system to the Product Catalog show price and product information updates. Arrows from the Product Catalog to the CRM show product information and customer purchase history being shared. Finally, arrows from the CRM back to the Product Catalog represent customer preferences influencing product recommendations and displays within the catalog. This visual representation clearly demonstrates the interconnectedness and the dynamic exchange of data among these vital business systems.
Security and Compliance
Maintaining a secure and compliant product catalog is crucial for protecting sensitive business information and ensuring adherence to relevant regulations. Data breaches can lead to significant financial losses, reputational damage, and legal penalties. Furthermore, failing to comply with regulations like GDPR and CCPA can result in hefty fines. This section details potential security risks, best practices for data protection, and compliance requirements.
Potential Security Risks in Product Catalog Management
Product catalog management systems, if not properly secured, are vulnerable to various threats. These include unauthorized access to sensitive product data, data breaches resulting from vulnerabilities in the system or its integration points, and malicious activities such as data manipulation or deletion. Poorly configured access controls, lack of data encryption, and inadequate security monitoring can all significantly increase the risk of compromise. For instance, a weakness in the authentication system could allow malicious actors to gain access to the catalog and modify product pricing or descriptions, potentially leading to financial losses.
Best Practices for Securing Product Data
Robust security measures are paramount for protecting product data. This includes implementing strong access controls, using multi-factor authentication (MFA) to verify user identities, and encrypting sensitive data both in transit and at rest. Regular security audits and penetration testing are vital to identify and address vulnerabilities before they can be exploited. Data loss prevention (DLP) tools can monitor and prevent sensitive data from leaving the organization’s control. Furthermore, employee training on security best practices is essential to minimize the risk of human error. A well-defined incident response plan should be in place to effectively manage and mitigate the impact of any security incidents.
Compliance Requirements for Product Information
Organizations must comply with various regulations regarding the handling of product information, particularly those concerning consumer data privacy. The General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) in Europe and the California Consumer Privacy Act (CCPA) in the United States are prominent examples. These regulations mandate specific requirements for data collection, storage, processing, and sharing. Compliance requires organizations to implement robust data governance procedures, provide consumers with transparency regarding data usage, and ensure the right to data access, correction, and deletion. Failure to comply can result in significant financial penalties and reputational harm.
Security Protocol for Protecting Sensitive Product Information
A comprehensive security protocol should encompass several key elements. This includes a robust authentication and authorization system, utilizing strong passwords, MFA, and role-based access control (RBAC) to limit access to sensitive data based on user roles and responsibilities. Data encryption, both at rest and in transit, is crucial to protect against unauthorized access even if a breach occurs. Regular security assessments, including vulnerability scanning and penetration testing, should be conducted to proactively identify and mitigate potential weaknesses. A comprehensive incident response plan should Artikel procedures for handling security incidents, including data breaches, to minimize their impact. Finally, employee training and awareness programs are essential to ensure that all personnel understand and adhere to security policies and procedures.
Closure
Mastering product catalog management is crucial for thriving in today’s competitive e-commerce landscape. By implementing the strategies and best practices Artikeld in this guide, businesses can create a dynamic and engaging product catalog that not only showcases their offerings effectively but also drives sales and fosters customer loyalty. From streamlining data entry and updates to leveraging analytics for performance tracking and optimization, a well-managed catalog is a key ingredient for online success. Remember that continuous improvement and adaptation are essential to staying ahead in the ever-evolving world of e-commerce.
Efficient product catalog management is crucial for any business, ensuring accurate and up-to-date information for customers. Consider, for instance, how a sporting goods retailer might manage its inventory; they might need to list detailed specifications for equipment like beach volleyballs, perhaps even linking to resources like this article on the intricacies of the game itself: Permainan bola voli pantai.
Returning to catalog management, this level of detail enhances the customer experience and drives sales.