Product Bundling to Boost Sales sets the stage for exploring how strategically combining products can significantly increase revenue. This exploration delves into various bundling strategies, optimal product selection, effective pricing models, and impactful marketing techniques to maximize sales. We will examine successful examples and provide a framework for implementing and optimizing your own product bundles.
The process involves careful consideration of several key factors. Understanding different bundling types (pure, mixed, add-on) and their respective advantages and disadvantages is crucial. Equally important is identifying products that complement each other, aligning with customer needs and preferences. Effective pricing strategies, from simple discounts to value-based pricing, will be analyzed, along with the creation of compelling marketing campaigns to drive sales. Finally, we’ll discuss how to track and optimize bundle performance using key metrics to ensure continuous improvement.
Defining Product Bundling Strategies
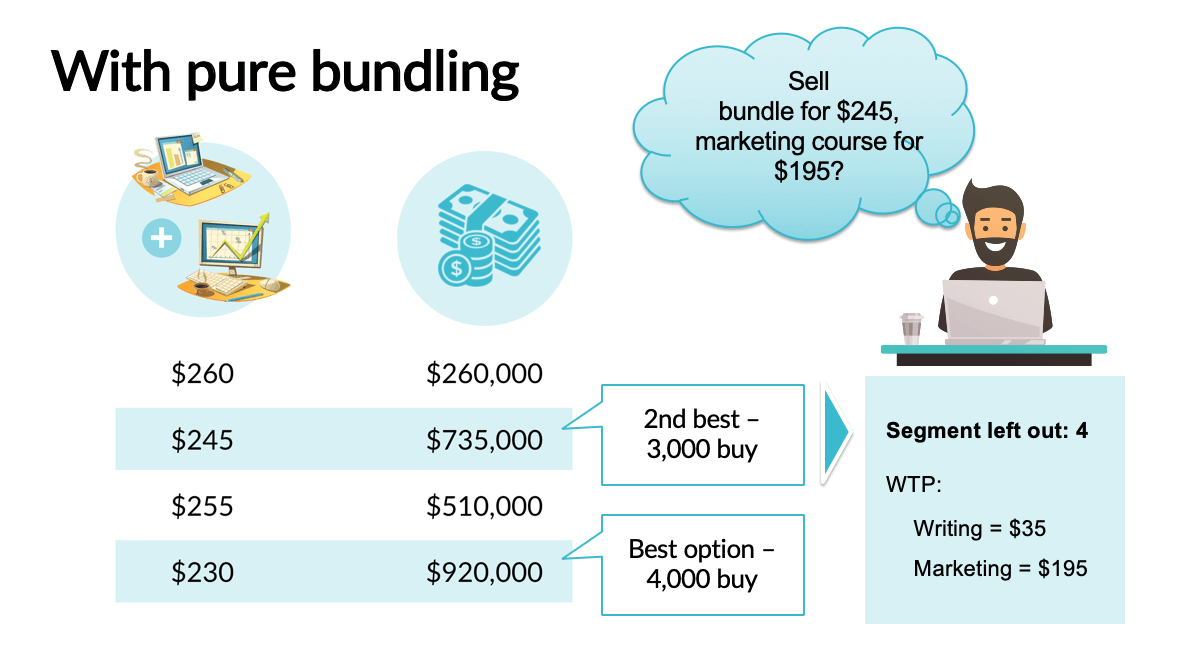
Product bundling is a powerful sales strategy that involves offering multiple products together at a discounted price compared to buying them individually. This approach can significantly boost sales by incentivizing customers to purchase more items and increasing the average order value. Understanding the various types of bundling strategies and their respective advantages and disadvantages is crucial for successful implementation.
Types of Product Bundles
Several distinct types of product bundles exist, each designed to cater to specific customer needs and marketing objectives. Choosing the right strategy depends on factors like product complementarity, target audience, and overall business goals.
Pure Bundles
Pure bundles consist of products that are typically purchased together and offer significant value when combined. These products often complement each other functionally or are closely related in terms of use or application. The advantage lies in the synergistic effect; the combined value exceeds the sum of the individual parts. A disadvantage is that it might not appeal to customers who only need one of the bundled products.
Mixed Bundles, Product Bundling to Boost Sales
Mixed bundles combine products that are not necessarily related but appeal to a similar customer segment or address a common need. This approach broadens the appeal to a wider audience compared to pure bundles. The advantage lies in its flexibility and potential to attract new customers. A disadvantage is that the perceived value might be lower if the products are not closely related, potentially leading to less compelling discounts.
Add-on Bundles
Add-on bundles involve offering complementary products alongside a primary purchase. These are often low-cost items that enhance the primary product’s functionality or usability. This strategy effectively increases the average order value without significantly impacting the customer’s initial purchase decision. The advantage lies in its simplicity and ability to generate incremental revenue. A disadvantage is that the add-ons might not always be desired by the customer, potentially leading to lower conversion rates if not carefully selected.
Examples of Successful Product Bundles
Numerous successful examples of product bundling exist across various industries. For instance, fast-food restaurants frequently offer “meal deals” combining a burger, fries, and a drink. Software companies often bundle their software with complementary applications or services. Subscription boxes, a popular e-commerce model, curate related products delivered periodically. These examples highlight the versatility and effectiveness of product bundling across different business models.
Comparison of Bundling Strategies
| Strategy Type | Description | Advantages | Disadvantages |
|---|---|---|---|
| Pure Bundle | Products frequently purchased together. | High perceived value, increased sales, synergistic effect. | May not appeal to customers needing only one product. |
| Mixed Bundle | Products appealing to a similar customer segment. | Broader appeal, increased average order value. | Lower perceived value if products are unrelated. |
| Add-on Bundle | Complementary products offered alongside a primary purchase. | Increased average order value, simple implementation. | Add-ons may not always be desired by the customer. |
Identifying Ideal Products for Bundling
Product bundling’s success hinges on selecting the right items. Effective bundling isn’t about randomly grouping products; it’s a strategic process aimed at increasing customer value and driving sales. Careful consideration of various factors ensures bundles resonate with your target audience and contribute positively to your bottom line.
Identifying products suitable for bundling requires a methodical approach. Several criteria must be met to create bundles that are both appealing to customers and profitable for the business. This involves understanding the relationship between products, their individual value propositions, and their overall contribution to the bundled offering.
Criteria for Selecting Products Suitable for Bundling
The selection process should prioritize products that complement each other, share a target audience, or address related customer needs. Analyzing sales data, customer feedback, and market trends provides valuable insights into which products are likely to perform well together. Products should also be priced strategically to ensure the bundle offers a perceived value greater than the sum of its parts. Finally, logistical considerations, such as storage and shipping, must be factored into the decision-making process.
Examples of Complementary and Non-Complementary Products
Complementary products naturally enhance each other’s value. For example, a coffee maker bundled with coffee beans and filters creates a complete coffee-making experience. Similarly, a shaving kit bundled with aftershave balm caters to a customer’s complete grooming needs. In contrast, bundling unrelated products, such as a toaster and a garden gnome, would likely confuse customers and fail to drive sales. The lack of synergy between these items renders the bundle unappealing and diminishes the overall perceived value. Another example of a poor bundle might be combining high-end headphones with inexpensive earbuds; the discrepancy in quality would undermine the appeal of the bundle.
The Importance of Considering Customer Needs and Preferences
Understanding customer needs and preferences is paramount. Market research, customer surveys, and sales data analysis reveal valuable insights into customer behavior and purchasing patterns. By identifying common purchasing patterns and related product interests, businesses can craft bundles that cater directly to specific customer segments. For instance, a bundle focused on home baking might include flour, sugar, yeast, and baking pans, targeting customers interested in baking. Ignoring customer preferences can lead to bundles that lack appeal and fail to resonate with the target market, resulting in reduced sales.
Flowchart for Selecting Products for Bundling
The following flowchart illustrates the systematic process of selecting products for bundling:
[Imagine a flowchart here. The flowchart would begin with a “Start” box, followed by a decision box asking “Do products share a target audience?”. If yes, proceed to a box asking “Do products complement each other?”. If yes, proceed to a box asking “Does the bundle offer increased perceived value?”. If yes, proceed to a box labeled “Create Bundle”. If no at any point, return to the beginning to select different products. The flowchart ends with an “End” box.]
The flowchart visualizes the decision-making process, emphasizing the importance of considering customer needs, product synergy, and perceived value before creating a product bundle. This systematic approach maximizes the chances of creating successful and profitable bundles.
Pricing Strategies for Bundles
Pricing product bundles effectively is crucial for maximizing profitability and attracting customers. A well-structured pricing strategy can significantly impact the perceived value and ultimately, the success of your bundled offerings. Choosing the right approach depends on your business goals, target audience, and the specific products included in the bundle.
Several pricing models exist, each with its own advantages and disadvantages. Understanding these models and their implications is key to optimizing your bundle pricing strategy.
Product bundling is a powerful sales strategy, offering customers added value and increasing average order value. To ensure its effectiveness, however, it’s crucial to monitor key performance indicators; understanding which metrics truly matter is essential, and you can learn more about this by checking out this helpful resource on Key Metrics to Track Success. By tracking these metrics, you can fine-tune your bundles and maximize their impact on boosting sales for your products.
Discount Bundles
Discount bundles offer a price reduction compared to buying the products individually. This straightforward approach is often highly effective in driving sales, particularly when targeting price-sensitive customers. The discount percentage should be substantial enough to incentivize purchase but not so large that it severely impacts profit margins. For example, offering a 15% discount on a bundle of three complementary skincare products (cleanser, toner, moisturizer) is more appealing than a smaller 5% discount. A poorly executed discount bundle, however, might offer too small a discount, failing to entice customers who would prefer to purchase items individually. Conversely, an excessively large discount could significantly erode profit margins.
Value-Based Pricing
Value-based pricing focuses on the perceived value of the bundle as a whole. This strategy is less about offering a direct discount and more about emphasizing the overall benefit and convenience the bundle provides. Instead of highlighting a percentage discount, the marketing emphasizes the total value received—for instance, “Get $100 worth of products for only $75!” This approach is particularly effective when bundling products that are complementary or frequently purchased together. An example of ineffective value-based pricing would be bundling unrelated products with inflated individual prices, creating a false sense of value.
Competitive Pricing
Competitive pricing involves analyzing the pricing strategies of competitors who offer similar bundles. This approach helps to ensure that your pricing is competitive within the market. It’s important to not only consider the price but also the value proposition offered by competitors. A company might offer a seemingly cheaper bundle, but if the quality of the included products is significantly lower, the perceived value may be less.
Factors to Consider When Setting Bundle Prices
Understanding the factors influencing pricing decisions is crucial for developing a successful strategy. Ignoring these can lead to underselling or losing potential profits.
The following factors should be carefully considered when determining the price of a product bundle:
- Cost of Goods Sold (COGS): This is the direct cost of producing or acquiring the products in the bundle. Pricing should always cover these costs to ensure profitability.
- Desired Profit Margin: Determine the target profit margin for the bundle, considering both the COGS and the desired return on investment.
- Customer Perception of Value: Research customer perceptions of the individual products and the bundle as a whole to understand their willingness to pay.
- Competitor Pricing: Analyze the pricing of similar bundles offered by competitors to remain competitive in the market.
- Market Demand: Assess the overall market demand for the products included in the bundle and adjust pricing accordingly.
- Promotional Objectives: Consider whether the bundle is intended to drive sales of specific products or to attract new customers.
Marketing and Promotion of Bundles
Effectively marketing product bundles requires a multi-faceted approach that highlights the increased value and convenience offered to customers. Successful campaigns leverage compelling messaging, strategic channel selection, and a deep understanding of the target audience. By focusing on the perceived savings and enhanced utility, businesses can significantly boost sales and customer satisfaction.
Effective marketing strategies for promoting product bundles hinge on clearly communicating the value proposition. This goes beyond simply stating the discount; it involves demonstrating how the bundled products complement each other and address customer needs more comprehensively. Visual aids, such as infographics showing individual product prices versus the bundle price, can significantly enhance this message.
Effective Marketing Strategies
Highlighting the convenience and time savings associated with purchasing a bundle is crucial. Busy consumers often appreciate the ease of acquiring multiple related products at once. Emphasizing the curated nature of the bundle—the thoughtfulness in selecting products that work well together—can also resonate strongly. This approach moves beyond a simple discount to offering a solution that simplifies the purchasing process. For example, a “Back to School” bundle might include a backpack, lunchbox, and stationery set, emphasizing convenience for parents.
Marketing Copy Example
Consider this marketing copy for a “Coffee Lover’s Bundle”: “Indulge your senses with our Coffee Lover’s Bundle! Enjoy a rich, aromatic blend of our signature dark roast coffee (1lb bag), a delectable pack of gourmet biscotti (6 pieces), and a stylish, reusable coffee mug—all for just $25! That’s a saving of $10 compared to buying each item separately! Start your day the perfect way with this irresistible combination.” This copy highlights the value, convenience, and the specific products included.
Examples of Successful Bundling Campaigns
Many companies have successfully used bundling to boost sales. For instance, software companies often bundle their flagship product with complementary apps or services, providing increased value for the customer. Similarly, fast-food restaurants frequently offer combo meals at a discounted price, making it more attractive than buying individual items. The success of these campaigns stems from a clear understanding of customer needs and the ability to offer a compelling value proposition. A notable example is Microsoft Office, which bundles Word, Excel, PowerPoint, and other applications, making it a more attractive purchase than buying each application separately.
Promotional Campaign for a Hypothetical Bundle
Let’s imagine a “Relaxation Bundle” containing aromatherapy candles, a calming essential oil diffuser, and a soothing eye mask.
Social Media Posts:
* Instagram: A visually appealing image showcasing the bundle, with text: “Unwind and de-stress with our Relaxation Bundle! Aromatherapy candles, essential oil diffuser, and a luxurious eye mask – all designed to help you relax and recharge. Link in bio!”
* Facebook: A post with a carousel of images showing each product individually and then together in the bundle, highlighting the individual product values and the overall bundle discount. The post could also include customer testimonials.
* Twitter: Short, engaging tweets focusing on individual benefits: “Escape the everyday with our soothing aromatherapy candles! Part of our new Relaxation Bundle – perfect for self-care.”
Email Marketing:
An email campaign could start with a subject line like “Unwind and Recharge: Introducing Our New Relaxation Bundle!” The email body would feature high-quality images of the bundle, a detailed description of each product, a clear price comparison, and a compelling call to action: “Treat yourself – shop now and enjoy [discount percentage] off!” The email could also include a countdown timer to create a sense of urgency.
Analyzing Product Bundling to Boost Sales Performance and Optimization
Understanding Product Bundling to Boost Sales bundles perform is crucial for maximizing their profitability and refining your bundling strategy. Effective tracking and analysis allow you to identify what’s working, what’s not, and where adjustments are needed to boost sales and overall revenue. This involves monitoring key metrics, analyzing sales data, and implementing A/B testing to optimize bundle configurations.
Tracking bundle performance requires a multifaceted approach that integrates various data points to gain a holistic understanding of your bundles’ success. This allows for informed decisions to improve profitability and customer satisfaction.
Methods for Tracking Product Bundling to Boost Sales Performance
Several methods can be employed to track the performance of product bundles. These methods should be integrated into your existing analytics system for a comprehensive view. Effective tracking ensures you can identify profitable bundles and areas for improvement.
- Sales Data Analysis: This involves examining the number of bundles sold, the revenue generated from each bundle, and the overall contribution of bundles to your total sales. This data can be segmented by various factors such as demographics, marketing channel, and time period.
- Website Analytics: Tools like Google Analytics can track bundle views, add-to-cart rates, and conversion rates. This provides insights into customer behavior and identifies bottlenecks in the sales funnel. For example, a low conversion rate might indicate a problem with the bundle’s description or pricing.
- Customer Feedback: Gathering customer feedback through surveys, reviews, or social media monitoring can provide valuable qualitative data on customer satisfaction with the bundles. This helps identify areas for improvement in bundle composition or marketing messaging.
- CRM Data Integration: Integrating your bundle sales data with your Customer Relationship Management (CRM) system allows for a more detailed analysis of customer behavior and purchase patterns related to bundles. This can reveal which customer segments are most responsive to specific bundles.
Key Metrics for Measuring Bundle Success
Several key metrics are essential for evaluating the effectiveness of your bundling strategy. These metrics provide quantifiable data to assess the overall success and profitability of your bundles.
- Conversion Rate: The percentage of customers who view a bundle and proceed to purchase it. A high conversion rate indicates an effective bundle offering and compelling marketing message.
- Average Order Value (AOV): The average amount spent per order that includes a bundle. A higher AOV suggests that bundles are successfully increasing the value of each transaction.
- Bundle Sales Revenue: The total revenue generated from bundle sales. This is a direct measure of the financial success of your bundling strategy.
- Bundle Contribution Margin: The difference between the revenue generated from bundle sales and the cost of goods sold (COGS) for the products included in the bundle. This metric reveals the profitability of each bundle.
- Customer Lifetime Value (CLTV): Analyzing the CLTV of customers who purchase bundles can reveal if bundles are driving customer loyalty and repeat purchases.
Analyzing Sales Data to Identify Areas for Improvement
Analyzing sales data is crucial for pinpointing areas where your bundle strategy can be improved. This analysis should be iterative, allowing for ongoing adjustments and optimization.
Product Bundling to Boost Sales For example, if data reveals that a particular bundle has a low conversion rate despite high views, this suggests a problem with the bundle’s pricing, description, or visual presentation. Conversely, a high conversion rate but low AOV might indicate a need to add higher-priced items to the bundle or offer upsells. By segmenting data by customer demographics or marketing channels, you can identify which customer segments are most receptive to specific bundles and tailor your strategies accordingly.
A/B Testing Different Bundle Configurations
A/B testing allows you to systematically compare different bundle configurations to determine which performs best. This data-driven approach minimizes guesswork and ensures that changes are based on empirical evidence.
A well-structured A/B test might compare two different bundles: one with a focus on value (e.g., a discount bundle) and another with a focus on premium items. By tracking key metrics like conversion rate and AOV for each bundle, you can identify the most effective configuration. It is important to ensure that the tests are run for a sufficient duration and with a large enough sample size to yield statistically significant results. For instance, you might A/B test different bundle descriptions, images, or pricing models. The results will guide you toward the optimal bundle configuration that maximizes sales and profitability.
Illustrative Examples of Successful Bundles: Product Bundling To Boost Sales

Product Bundling to Boost Sales, when done effectively, can significantly boost sales and enhance customer value. Successful bundles are strategically crafted, combining products that complement each other and offer customers a compelling reason to purchase the package over individual items. The following examples showcase the diverse applications and successes of this marketing strategy.
Microsoft Office Suite
Microsoft Office, a quintessential example of successful product bundling, combines several applications—Word, Excel, PowerPoint, Outlook, and others—into a single package. The success of this bundle stems from its synergistic nature; the applications complement each other, catering to a wide range of user needs, from document creation and data analysis to presentations and communication. The pricing strategy involves tiered subscriptions and one-time purchases, offering flexibility to suit different user budgets and needs. Marketing focuses on the overall productivity gains and ease of use offered by the suite, emphasizing the value of having all necessary applications in one place, rather than purchasing each individually. This integrated approach resonates strongly with both individual users and businesses.
McDonald’s Value Meals
McDonald’s Value Meals represent a highly successful example of product bundling in the fast-food industry. These bundles typically include a burger or sandwich, fries, and a drink, often at a price lower than purchasing the items individually. The pricing strategy leverages economies of scale and aims for increased sales volume. The marketing is straightforward, emphasizing value and convenience. The bundles are prominently displayed on menus and advertising materials, highlighting the savings and ease of ordering a complete meal. The success lies in its appeal to customers seeking affordability and convenience, streamlining the ordering process and encouraging higher spending per visit.
Starbucks Coffee and Pastry Bundles
Starbucks frequently offers bundles combining a coffee beverage with a pastry. These bundles are designed to enhance the overall customer experience by providing a complete and satisfying treat. The pricing strategy is often a slight discount compared to purchasing each item separately, creating a sense of value without significantly impacting profitability. The marketing emphasizes the pairing of complementary products, highlighting the enjoyment of savoring coffee with a delicious pastry. The presentation often involves aesthetically pleasing packaging or tray displays showcasing the bundle, further enhancing the appeal and creating a more premium experience.
Visual Representation: Starbucks Coffee and Pastry Bundle
Imagine a sleek, white cardboard sleeve holding a tall cup of coffee and a perfectly sized pastry. The sleeve is subtly branded with the Starbucks logo. The pastry, perhaps a croissant or muffin, is nestled in a separate compartment, keeping it warm and fresh. A small, elegant sticker on the sleeve indicates the bundle’s name, such as “Morning Treat Bundle” or “Afternoon Delight.” The overall presentation is clean, modern, and conveys a sense of premium quality and convenience, enhancing the perceived value of the bundle.
Ultimately, mastering the art of product bundling is about creating value for the customer while simultaneously boosting your bottom line. By carefully selecting products, employing strategic pricing, and crafting compelling marketing campaigns, businesses can leverage the power of bundling to achieve significant sales growth. The key is a data-driven approach, constantly monitoring performance and adapting strategies based on results to maximize the return on investment.
Product Bundling to Boost Sales is a powerful sales strategy; offering related products together often increases the average order value. To truly maximize your return, however, you need to effectively allocate resources, which is why understanding how to Optimize Your Marketing Budget is crucial. Strategic bundling, when combined with a well-optimized marketing plan, can significantly boost your overall sales performance and profitability.