New customer growth is the lifeblood of any successful business. Understanding the customer lifecycle, from initial acquisition to long-term retention, is crucial for sustainable growth. This exploration delves into key strategies, from optimizing marketing channels and analyzing customer acquisition costs (CAC) to leveraging customer segmentation and refining the onboarding process. We will examine how to effectively measure success, analyze customer feedback, and ultimately cultivate lasting customer relationships that drive continuous expansion.
This comprehensive guide provides actionable insights and practical examples to help businesses attract, convert, and retain new customers, leading to increased profitability and market share. We’ll cover various methods for analyzing data, identifying profitable customer segments, and optimizing marketing efforts to maximize return on investment. The information presented is designed to be both informative and applicable to a wide range of industries and business models.
Defining New Customer Acquisition
New customer acquisition is the process of attracting and converting new individuals or businesses into paying customers. It’s a crucial element of business growth, representing the lifeblood of any company striving for expansion and sustained success. Effective new customer acquisition strategies directly impact revenue, market share, and long-term profitability.
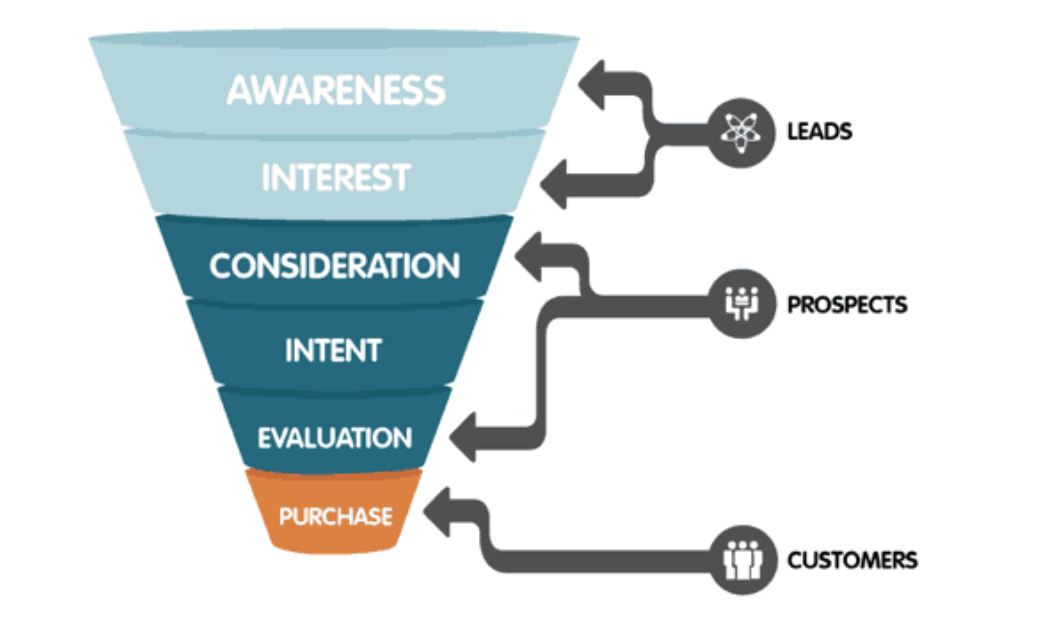
Stages of the Customer Lifecycle Relevant to New Customer Growth
Understanding the customer lifecycle is paramount for optimizing new customer acquisition. This lifecycle typically involves several key stages, each presenting opportunities to engage and convert prospects. Focusing efforts on each stage improves overall acquisition efficiency.
- Awareness: The potential customer becomes aware of your product or service, often through marketing or word-of-mouth.
- Interest: The potential customer shows interest, researching your offerings and comparing them to competitors.
- Decision: The potential customer decides whether or not to purchase your product or service.
- Action: The potential customer makes a purchase, becoming a new customer.
- Retention: The business focuses on retaining the new customer through excellent service and engagement.
Key Performance Indicators (KPIs) for New Customer Acquisition
Measuring the success of new customer acquisition requires tracking relevant KPIs. These metrics provide insights into campaign effectiveness and areas for improvement. Regular monitoring allows for data-driven decisions to optimize strategies.
- Cost Per Acquisition (CPA): The total cost of marketing and sales efforts divided by the number of new customers acquired. A lower CPA indicates greater efficiency.
- Customer Acquisition Cost (CAC): Similar to CPA, but encompasses all costs associated with acquiring a new customer, including salaries and operational expenses.
- Conversion Rate: The percentage of leads or website visitors who become paying customers. A higher conversion rate reflects a more effective sales funnel.
- Customer Lifetime Value (CLTV): The predicted revenue a customer will generate throughout their relationship with the business. A higher CLTV signifies more valuable customers.
- Return on Ad Spend (ROAS): Measures the effectiveness of advertising campaigns by comparing the revenue generated to the advertising spend. A ROAS greater than 1 indicates profitability.
Examples of Successful New Customer Acquisition Strategies
Successful new customer acquisition strategies vary across industries, but several common themes emerge. Adapting these strategies to your specific market and target audience is key to success.
- Content Marketing (B2B & B2C): Creating valuable, informative content (blog posts, ebooks, webinars) attracts potential customers organically and positions the business as a thought leader. Examples include HubSpot’s blog for inbound marketing or Neil Patel’s content on digital marketing.
- Paid Advertising (B2B & B2C): Utilizing platforms like Google Ads and social media advertising allows for targeted campaigns reaching specific demographics. Examples include highly targeted Facebook ads or Google Search campaigns for specific s.
- Social Media Marketing (B2B & B2C): Building a strong social media presence fosters brand awareness and engagement, leading to increased customer acquisition. Examples include engaging content on Instagram for a fashion brand or LinkedIn for a B2B SaaS company.
- Referral Programs (B2B & B2C): Incentivizing existing customers to refer new customers generates cost-effective acquisition. Examples include Dropbox’s early referral program or Airbnb’s referral bonuses.
- Email Marketing (B2B & B2C): Targeted email campaigns nurture leads and convert prospects into customers. Examples include automated email sequences for onboarding new subscribers or personalized email campaigns based on customer behavior.
Comparison of Customer Acquisition Channels
The following table compares various customer acquisition channels, highlighting their relative strengths and weaknesses. Understanding these differences informs strategic resource allocation.
| Channel | Cost Per Acquisition (CPA) | Conversion Rate | Customer Lifetime Value (CLTV) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Organic Search | Low | Moderate | High |
| Paid Advertising | Medium to High | Moderate to High | Medium to High |
| Social Media | Medium | Moderate | Medium |
| Referrals | Low | High | High |
| Email Marketing | Low to Medium | Moderate to High | Medium to High |
Analyzing Customer Acquisition Costs (CAC): New Customer Growth

Understanding Customer Acquisition Cost (CAC) is crucial for sustainable business growth. A well-managed CAC allows businesses to optimize marketing spend, ensuring profitability and a healthy return on investment. High CAC can quickly erode profits, while extremely low CAC might indicate a compromise on customer quality or long-term value. This section will delve into the factors influencing CAC, methods for its reduction, different calculation methods, and a sample cost breakdown.
Factors Influencing Customer Acquisition Cost
Several interconnected factors significantly impact CAC. Marketing channel efficiency plays a large role; some channels, like paid search advertising, tend to have higher costs per acquisition than organic content marketing. The target audience also matters; reaching a highly specialized niche often involves higher costs than targeting a broader market. The effectiveness of marketing campaigns, measured by conversion rates and engagement, directly influences CAC. Finally, the pricing strategy of the product or service affects CAC; higher-priced products can justify higher acquisition costs. For example, a luxury car manufacturer can afford a higher CAC than a budget clothing retailer because of the higher profit margin per sale.
Methods for Reducing CAC Without Compromising Customer Quality
Lowering CAC doesn’t necessitate sacrificing customer quality. Improving marketing campaign targeting through detailed audience segmentation and personalization can enhance conversion rates, reducing cost per acquisition. Optimizing marketing channels by focusing resources on high-performing channels and abandoning underperforming ones is crucial. A/B testing different marketing creatives and messaging allows for continuous improvement and optimization. Leveraging content marketing and building brand awareness through organic channels reduces reliance on expensive paid advertising. Finally, improving the sales process and streamlining the customer journey can reduce friction and increase conversion rates. For instance, a company might implement a more user-friendly website or a simplified checkout process.
Comparison of CAC Calculation Methods
Several methods exist for calculating CAC, each with its own strengths and weaknesses. The most common is the simple calculation of total marketing and sales costs divided by the number of new customers acquired within a specific period. This is a straightforward approach but might overlook indirect costs. A more comprehensive method includes all costs associated with acquiring a customer, such as customer service and onboarding costs, providing a more holistic view. Finally, some businesses calculate CAC based on a specific cohort of customers, allowing for a more nuanced understanding of acquisition costs across different customer segments. The choice of method depends on the level of detail required and the specific business context.
Hypothetical Cost Breakdown for a New Customer Acquisition Campaign
Let’s consider a hypothetical email marketing campaign targeting a new customer segment. The total budget is $10,000.
| Marketing Activity | Cost Allocation |
|---|---|
| Email List Acquisition | $2,000 |
| Email Design and Development | $1,000 |
| Email Marketing Platform Fees | $500 |
| Campaign Management and Optimization | $1,500 |
| Paid Advertising (Social Media) | $3,000 |
| Landing Page Development | $2,000 |
This breakdown illustrates how costs are distributed across different campaign elements. The allocation can be adjusted based on the specific campaign goals and expected ROI.
Understanding Customer Segmentation for Growth

Effective customer segmentation is crucial for maximizing new customer acquisition. By identifying distinct groups of customers with shared characteristics, businesses can tailor their marketing efforts for increased efficiency and higher conversion rates. This approach moves beyond generic advertising, allowing for personalized messaging that resonates more deeply with potential customers, ultimately driving stronger growth.
Understanding the nuances of your customer base allows for the creation of targeted marketing campaigns that speak directly to the specific needs and desires of each segment. This targeted approach leads to improved resource allocation, higher return on investment (ROI), and a more sustainable growth trajectory.
Identifying Key Customer Segments
Customer segmentation involves grouping customers based on shared characteristics. These characteristics can be broadly categorized into demographics (age, location, income), behavioral patterns (purchase history, website activity), and needs (product preferences, pain points). For example, a company selling fitness equipment might segment its customers based on age (young adults vs. older adults), activity level (beginner vs. advanced), and fitness goals (weight loss vs. muscle gain). Each segment would then receive marketing materials tailored to their specific needs and interests. This targeted approach maximizes the impact of marketing spend and increases the likelihood of conversion.
Tailoring Marketing Messages for Specific Segments
Once key customer segments have been identified, the next step is to craft marketing messages that resonate with each group’s unique characteristics. This involves understanding their motivations, pain points, and preferred communication channels. For example, a message emphasizing convenience and affordability might appeal to budget-conscious consumers, while a message highlighting premium features and exclusive benefits might resonate with high-value customers. Using different messaging for different segments prevents wasted ad spend on irrelevant audiences. A company selling software might use video tutorials for tech-savvy customers, while focusing on simple, step-by-step guides for less tech-proficient users.
Customer Segmentation Strategy
A well-defined customer segmentation strategy is essential for successful growth. The following bullet points Artikel a sample strategy:
- Segment 1: Budget-Conscious Consumers
- Targeting Criteria: Lower income, price-sensitive, value-driven purchases.
- Messaging Example: “Affordable solutions for your needs,” “Best value for your money,” highlighting discounts and promotions.
- Segment 2: Premium Customers
- Targeting Criteria: Higher income, willing to pay more for quality and convenience, appreciate exclusive benefits.
- Messaging Example: “Experience the ultimate in quality,” “Exclusive access and benefits,” highlighting premium features and personalized service.
- Segment 3: Tech-Savvy Users
- Targeting Criteria: Comfortable with technology, appreciate innovative features and advanced functionalities.
- Messaging Example: “Cutting-edge technology,” “Streamlined workflow,” focusing on advanced features and integration capabilities.
Improving Advertising Campaign Effectiveness with Segmentation Data
Using customer segmentation data allows for highly targeted advertising campaigns. By focusing advertising efforts on specific segments, businesses can increase the relevance of their ads, leading to higher click-through rates and conversion rates. For example, a company could use demographic data to target specific age groups on social media or use behavioral data to retarget website visitors who have shown interest in specific products. This precision targeting maximizes the return on investment for advertising spend, ensuring that marketing resources are used efficiently and effectively. Analyzing the performance of campaigns within each segment provides valuable insights for further optimization and refinement of the segmentation strategy.
Optimizing the Customer Onboarding Process
A smooth and efficient customer onboarding process is crucial for maximizing customer lifetime value and fostering long-term relationships. A well-designed onboarding experience transforms new customers into loyal advocates, significantly impacting overall business success. Failing to properly onboard customers can lead to high churn rates and wasted marketing spend.
Effective onboarding guides new users through the product or service, providing the necessary knowledge and support to achieve their goals. This proactive approach reduces frustration, increases engagement, and accelerates the time to value – the point at which a customer starts realizing the benefits of their purchase. This ultimately translates into improved customer satisfaction and increased retention.
Steps Involved in a Successful Customer Onboarding Process
A successful onboarding process involves a series of well-defined steps, each contributing to a positive initial customer experience. These steps should be carefully planned and executed to ensure a seamless transition from prospect to active user.
- Pre-boarding: This phase begins before the customer officially signs up. It involves setting clear expectations, confirming order details, and perhaps providing preparatory materials like welcome emails or setup guides.
- Initial Account Setup: This involves providing a simple and intuitive process for new customers to create their accounts and access the product or service. Clear instructions and helpful prompts are key.
- Product/Service Introduction: A clear and concise introduction to the product’s core features and functionality. This could involve interactive tutorials, video demos, or guided tours.
- Goal Setting and Achievement: Help customers define their goals and show them how the product can help them achieve those goals. This creates immediate value and engagement.
- Ongoing Support and Engagement: Providing ongoing support through various channels, such as email, chat, or knowledge bases, is essential for addressing any issues or questions. Regular communication and engagement maintain momentum and build rapport.
- Feedback Collection: Actively solicit feedback from new customers to identify areas for improvement in the onboarding process and the product itself. This iterative approach ensures continuous enhancement.
Examples of Effective Onboarding Strategies
Several strategies can significantly enhance customer onboarding and improve retention. These examples showcase practical applications of best practices.
- Personalized Onboarding: Tailoring the onboarding experience to individual customer needs and preferences. For example, a SaaS company might offer different onboarding paths for different user roles within a company.
- Interactive Tutorials and Product Tours: Engaging users with interactive tutorials and guided product tours that highlight key features and functionalities. This ensures users quickly understand how to use the product effectively.
- Gamification: Incorporating game-like elements, such as points, badges, and leaderboards, to motivate users and encourage engagement. This can be particularly effective for increasing product usage and driving adoption.
- Proactive Support and Communication: Providing proactive support through email, chat, or in-app messages to address common questions and issues before they arise. This demonstrates a commitment to customer success.
Measuring the Effectiveness of the Onboarding Process
Measuring the success of your onboarding process requires tracking relevant key performance indicators (KPIs). These metrics provide valuable insights into areas for improvement.
- Time to Value (TTV): The time it takes for a customer to achieve a significant benefit from using the product or service. A shorter TTV indicates a more effective onboarding process.
- Customer Activation Rate: The percentage of new customers who complete key actions within a defined timeframe, signifying successful adoption.
- Customer Churn Rate: The percentage of customers who cancel their subscription or stop using the product within a specific period. A lower churn rate suggests a positive onboarding experience.
- Customer Satisfaction (CSAT) Scores: Measuring customer satisfaction through surveys or feedback forms provides valuable insights into the overall onboarding experience.
- Net Promoter Score (NPS): This metric gauges customer loyalty and willingness to recommend the product or service to others. A high NPS suggests a positive onboarding experience that fosters loyalty.
Streamlined Customer Onboarding Process Flowchart
Imagine a flowchart with the following steps, represented visually with boxes and arrows indicating the flow:
* Start: New customer signs up.
* Account Creation: Customer completes account registration.
* Welcome Email: Automated welcome email with next steps.
* Product Introduction: Interactive tutorial or guided tour.
* Goal Setting: Customer sets up their goals within the product.
* First Success: Customer achieves a small win or milestone.
* Ongoing Support: Access to help articles, FAQs, or live chat.
* Feedback Request: Survey sent after a week of usage.
* End: Customer becomes an active user.
This visual representation would clearly Artikel the process, making it easy to understand and improve upon.
Leveraging Marketing Channels for New Customer Growth

Effective marketing is crucial for acquiring new customers and driving business growth. Understanding the strengths and weaknesses of various digital marketing channels, and crafting a cohesive multi-channel strategy, is essential for maximizing return on investment (ROI). This section will explore several key channels, highlighting their advantages, disadvantages, and optimization strategies.
Digital Marketing Channel Advantages and Disadvantages
A successful marketing strategy leverages a mix of channels to reach the widest possible audience. Each channel presents unique opportunities and challenges.
| Channel | Advantages | Disadvantages |
|---|---|---|
| Email Marketing | High personalization potential, direct communication, measurable ROI, cost-effective for targeted audiences. | Requires a robust email list, can be perceived as spam, inbox deliverability challenges, requires consistent content creation. |
| Social Media Marketing | Wide reach, highly engaging, excellent for brand building and community engagement, allows for real-time interaction. | Algorithm changes can impact reach, requires consistent content creation and community management, can be time-consuming, requires strong understanding of platform-specific best practices. |
| Content Marketing | Builds trust and credibility, attracts organic traffic, establishes thought leadership, generates leads over time. | Requires significant time and resources to create high-quality content, may not yield immediate results, requires optimization for visibility. |
| Search Engine Optimization () | Drives organic, qualified traffic, builds long-term brand visibility, cost-effective in the long run. | Requires ongoing optimization, results are not immediate, algorithm updates can impact rankings, competitive landscape. |
Examples of Successful Marketing Campaigns, New customer growth
Several brands have successfully leveraged digital marketing to drive significant new customer growth. For example, Dollar Shave Club’s viral YouTube video campaign disrupted the men’s grooming industry, generating massive brand awareness and attracting a large customer base quickly. Their success highlights the power of creative, engaging content marketing. Similarly, Airbnb’s strategic use of social media marketing, focusing on user-generated content and community building, has fostered strong brand loyalty and fueled significant growth. These examples demonstrate the potential of well-executed marketing campaigns to achieve remarkable results.
Optimizing Marketing Channels for Maximum Impact
Optimizing each channel requires a data-driven approach. For email marketing, A/B testing subject lines, content, and call-to-actions is vital. For social media, analyzing engagement metrics (likes, shares, comments) helps identify high-performing content and adjust strategies accordingly. Content marketing success hinges on creating high-quality, -optimized content that resonates with the target audience. Regular audits and research are crucial for maintaining strong search engine rankings. Continuous monitoring and adaptation based on performance data are key to success across all channels.
Multi-Channel Marketing Strategy for a Fitness App
Consider a fitness app aiming to attract new users. A multi-channel strategy might involve:
- Email Marketing: Targeted email campaigns promoting free trials, special offers, and fitness tips to a segmented audience (e.g., based on fitness goals, age, location).
- Social Media Marketing: Engaging content (videos, workout tips, user testimonials) on platforms like Instagram and TikTok, influencer marketing collaborations, running targeted ad campaigns.
- Content Marketing: Creating blog posts, articles, and infographics about fitness, nutrition, and healthy lifestyle, optimizing content for relevant s to improve search engine rankings.
- Search Engine Optimization (): Optimizing the app’s website and app store listing for relevant s to improve organic search visibility.
- Paid Advertising (PPC): Running targeted ads on Google and social media platforms to reach potential users actively searching for fitness apps.
Resource allocation would depend on the budget and the specific goals, but a balanced approach across these channels would likely yield the best results. For example, a larger budget might be allocated to paid advertising initially to drive rapid user acquisition, while simultaneously investing in and content marketing for long-term organic growth.
Measuring and Improving Customer Retention
Customer retention is crucial for sustainable business growth. It’s significantly more cost-effective to retain existing customers than to acquire new ones. Understanding the factors that contribute to customer churn and implementing strategies to improve retention are key to long-term success. This section will explore methods for measuring customer retention, identifying churn drivers, and implementing effective retention strategies.
Factors Contributing to High Customer Churn Rates
High customer churn often stems from a combination of factors. Poor customer service experiences, leading to dissatisfaction and negative word-of-mouth, are a primary driver. A lack of product-market fit, where the product or service doesn’t adequately meet customer needs or expectations, also contributes significantly. Furthermore, pricing issues, such as perceived high costs or a lack of value for money, can push customers to seek alternatives. Finally, a poor onboarding experience can leave customers feeling lost and unsupported, leading to early churn. Competitor actions, such as offering superior products or services at lower prices, can also influence churn rates.
Strategies for Improving Customer Retention and Loyalty
Improving customer retention involves proactive strategies focused on enhancing customer experience and building loyalty. Implementing a robust customer relationship management (CRM) system allows for personalized communication and targeted support. Proactive customer service, addressing potential issues before they escalate into complaints, is vital. Loyalty programs, offering rewards and exclusive benefits to returning customers, incentivize continued engagement. Regular feedback collection, through surveys and reviews, provides valuable insights into customer satisfaction and areas for improvement. Building a strong brand community fosters a sense of belonging and loyalty among customers. Finally, personalized communication and targeted offers can enhance the customer experience and increase loyalty.
Calculating Customer Churn Rate and Customer Lifetime Value (CLTV)
Understanding key metrics is essential for tracking retention efforts. The customer churn rate represents the percentage of customers lost over a specific period. It’s calculated as:
Churn Rate = (Number of Customers Lost / Number of Customers at the Beginning of the Period) x 100
For example, if a company started with 1000 customers and lost 100 in a month, the churn rate is (100/1000) x 100 = 10%.
Customer Lifetime Value (CLTV) predicts the total revenue a company expects to generate from a single customer throughout their relationship. Calculating CLTV can be complex, but a simplified version is:
CLTV = Average Purchase Value x Average Purchase Frequency x Average Customer Lifespan
For instance, if a customer spends an average of $100 per purchase, buys 4 times a year, and remains a customer for 5 years, the CLTV is $100 x 4 x 5 = $2000.
Customer Retention Strategies: Costs and Benefits
| Strategy | Cost | Benefits |
|---|---|---|
| Improved Customer Service | Training, software, increased staffing | Increased customer satisfaction, reduced churn, positive word-of-mouth |
| Loyalty Program | Rewards program development, marketing costs | Increased customer retention, repeat purchases, brand loyalty |
| Personalized Communication | Marketing automation software, data analysis | Enhanced customer experience, increased engagement, higher conversion rates |
| Proactive Customer Onboarding | Development of onboarding materials, training | Reduced early churn, faster customer adoption, improved customer satisfaction |
| Community Building | Social media management, community platform | Increased customer engagement, brand advocacy, valuable customer feedback |
Analyzing Customer Feedback for Improvement
Understanding and acting upon customer feedback is crucial for sustained growth. It allows businesses to identify areas for improvement, enhance the customer experience, and ultimately attract more customers through positive word-of-mouth and strong brand reputation. By systematically collecting, analyzing, and implementing changes based on feedback, companies can foster loyalty and drive significant business gains.
Customer feedback provides invaluable insights into various aspects of a business, from product design and functionality to customer service interactions and marketing effectiveness. This data allows companies to make data-driven decisions, ensuring resources are allocated to initiatives that yield the highest return on investment and ultimately contribute to improved customer satisfaction and increased revenue.
Methods for Collecting Customer Feedback
Several methods exist for gathering customer feedback, each offering unique advantages and disadvantages. Choosing the right approach depends on the specific goals and resources available.
- Surveys: Surveys, both online and offline, allow for structured data collection on specific aspects of the customer experience. They can range from short satisfaction surveys to longer, more detailed questionnaires probing specific features or services. For example, a Net Promoter Score (NPS) survey asks customers to rate their likelihood of recommending a company on a scale of 0 to 10, providing a quick metric for overall satisfaction. Another example is a post-purchase survey sent via email, inquiring about the ease of the buying process, product quality, and overall experience.
- Reviews: Online reviews on platforms like Google, Yelp, and Trustpilot provide valuable, often unfiltered feedback from customers. Analyzing the sentiment and common themes expressed in these reviews can pinpoint areas needing attention. For instance, consistently negative reviews about slow shipping times might indicate a need for improvements in the logistics process.
- Social Media Monitoring: Monitoring social media channels (Twitter, Facebook, Instagram, etc.) allows businesses to identify customer mentions, comments, and discussions about their brand, products, or services. This provides real-time insights into customer sentiment and emerging issues. Tracking mentions of specific hashtags or s can help focus the analysis on relevant conversations.
- Focus Groups and Interviews: Qualitative methods like focus groups and individual interviews allow for deeper exploration of customer needs and perceptions. These methods offer rich insights but are more resource-intensive than quantitative methods like surveys. A focus group might be conducted to understand customer reactions to a new product prototype before its official launch.
Analyzing Customer Feedback for Improvement
Once collected, customer feedback must be systematically analyzed to extract meaningful insights. This often involves identifying trends, patterns, and sentiment within the data.
- Sentiment Analysis: Sentiment analysis uses natural language processing (NLP) techniques to automatically determine the emotional tone (positive, negative, or neutral) of customer feedback. This allows for a quick overview of overall customer satisfaction and identification of areas with predominantly negative sentiment. A visual representation could be a bar chart showing the percentage of positive, negative, and neutral sentiment across different feedback channels.
- Customer Journey Mapping: Customer journey maps visually represent the steps a customer takes when interacting with a business. By overlaying customer feedback onto the map, companies can identify pain points and areas for improvement at each stage of the journey. For example, a customer journey map might highlight a drop-off rate during the checkout process, indicating a need for simplification or optimization.
- Topic Modeling: Topic modeling uses statistical techniques to identify recurring themes and topics within large amounts of text data. This can help to uncover underlying issues and prioritize areas for improvement. For example, topic modeling might reveal a recurring theme of dissatisfaction related to product packaging.
Examples of Companies Effectively Using Customer Feedback
Many companies have successfully leveraged customer feedback to drive improvements and growth. For example, Netflix uses A/B testing and data analysis to personalize recommendations and improve its user interface based on user preferences and viewing habits. Amazon continuously incorporates customer reviews and ratings into its product development and marketing strategies. Zappos has built a strong brand reputation based on exceptional customer service, partly fueled by actively seeking and responding to customer feedback.
Visual Representations of Customer Feedback
Imagine a bar chart showing the sentiment analysis of customer reviews for a new product launch. The chart displays the percentage of positive, negative, and neutral reviews. A higher percentage of positive reviews would indicate strong initial customer reception, while a significant number of negative reviews would highlight areas needing improvement. A second example would be a customer journey map depicting the customer’s interaction with a company’s website. The map could show the steps involved in purchasing a product, with annotations highlighting areas where customers reported difficulty or frustration. For instance, a bottleneck at the checkout stage could be visually represented, indicating a need for redesign or simplification of the checkout process.
Final Wrap-Up
Ultimately, achieving significant new customer growth requires a multifaceted approach that combines strategic planning, data-driven decision-making, and a deep understanding of the customer journey. By implementing the strategies Artikeld in this guide – from optimizing marketing channels and analyzing customer acquisition costs to leveraging customer segmentation and refining the onboarding process – businesses can effectively attract, convert, and retain new customers, driving sustainable growth and long-term success. Continuous monitoring, adaptation, and a commitment to customer satisfaction are essential for sustained progress in this dynamic landscape.
New customer growth is often driven by innovative solutions. For example, a key driver for our recent increase in users has been the successful launch of our new fitness tracking app, Aplikasi pemantau aktivitas fisik , which provides detailed insights and personalized fitness plans. This has significantly contributed to our overall new customer growth strategy and boosted user engagement.
Attracting new customers is crucial for business expansion, but equally important is nurturing those relationships to ensure longevity. A robust strategy for achieving sustainable growth involves understanding that acquiring new customers is only half the battle; retaining them is just as vital. For insights into effective techniques, consider exploring this helpful guide on Customer retention strategy which can significantly impact your new customer growth trajectory.
Ultimately, a balanced approach focusing on both acquisition and retention leads to more predictable and sustainable business success.