Marketing ROI calculation is crucial for business success. Understanding how to accurately measure the return on your marketing investments allows for data-driven decision-making, optimizing campaigns, and maximizing profits. This guide explores the methods, metrics, and challenges involved in calculating marketing ROI, providing a framework for businesses to improve their marketing strategies and achieve better results.
We’ll delve into various formulas, address common pitfalls, and offer actionable strategies for enhancing your ROI. From defining key metrics to visualizing your results, this comprehensive guide equips you with the knowledge to effectively track, analyze, and improve your marketing performance across different channels.
Defining Marketing ROI

Marketing return on investment (ROI) is a crucial metric that measures the effectiveness of marketing campaigns by comparing the net profit generated from a marketing initiative to the cost of that initiative. It provides a quantifiable assessment of how well marketing efforts contribute to the overall financial success of a business. Understanding and optimizing marketing ROI is vital for making informed decisions about resource allocation and ensuring that marketing budgets are spent efficiently and effectively.
A high marketing ROI indicates that marketing activities are generating a significant return on investment, while a low or negative ROI suggests that marketing strategies may need to be reevaluated or adjusted. This metric allows businesses to identify which campaigns are performing well and which ones are underperforming, enabling data-driven optimization and improved overall marketing performance.
Marketing ROI versus Other KPIs
Marketing ROI is distinct from other key performance indicators (KPIs), though it often works in conjunction with them. While marketing ROI focuses specifically on the financial return of marketing activities, other KPIs may measure different aspects of marketing success, such as brand awareness, customer engagement, or website traffic. For instance, website traffic (measured by unique visitors or page views) is a valuable KPI, but it doesn’t directly translate to revenue. Similarly, social media engagement (likes, shares, comments) is important for building brand presence, but doesn’t inherently reflect financial returns. Marketing ROI, however, directly ties marketing spend to revenue generation, providing a clear picture of profitability.
Examples of Successful Marketing ROI Calculations
Many businesses successfully leverage marketing ROI calculations to guide their strategies. For example, a retail company might track the ROI of an email marketing campaign by comparing the revenue generated from sales driven by that campaign to the cost of designing, sending, and managing the email campaign. If the revenue significantly exceeds the cost, the ROI is positive and indicates a successful campaign. Conversely, if the revenue is lower than the cost, the ROI is negative, highlighting areas for improvement in the campaign’s strategy or targeting. Another example could be a software company measuring the ROI of a paid advertising campaign on platforms like Google Ads or LinkedIn. By tracking the cost-per-acquisition (CPA) and the lifetime value (LTV) of customers acquired through these ads, they can determine the overall profitability of the campaign. A successful campaign would show a high LTV compared to the CPA, resulting in a positive ROI. These calculations allow businesses to refine their marketing approaches, focusing resources on high-performing channels and strategies while minimizing investment in underperforming areas.
Key Metrics for Calculating Marketing ROI
Accurately calculating marketing ROI requires a comprehensive understanding of key performance indicators (KPIs) and a robust system for data collection and analysis. This involves identifying the right metrics, gathering data from diverse sources, and employing appropriate analytical methods to determine the effectiveness of marketing campaigns. Ignoring crucial metrics can lead to inaccurate assessments and ultimately hinder informed decision-making.
The process of calculating marketing ROI necessitates a careful selection and measurement of relevant metrics. These metrics should align directly with the specific goals and objectives of the marketing campaign. The data gathered should be both quantitative and qualitative, providing a holistic view of campaign performance. The subsequent analysis will then illuminate the return on investment, informing future strategies and resource allocation.
Essential Metrics for Marketing ROI Calculation
Several key metrics are crucial for a comprehensive understanding of marketing ROI. These metrics fall into several categories, providing a multifaceted view of campaign success. A combination of these metrics offers a more complete picture than relying on a single indicator.
- Revenue Generated: This is the most direct measure of marketing success. It represents the total revenue directly attributable to the marketing campaign. This can be tracked through sales data, linked to specific marketing activities via unique identifiers (e.g., promotional codes).
- Cost of Goods Sold (COGS): This metric accounts for the direct costs associated with producing or delivering the goods or services sold as a result of the marketing campaign. Subtracting COGS from revenue provides gross profit.
- Marketing Expenses: This encompasses all costs associated with the marketing campaign, including advertising, content creation, personnel, and software. Accurate tracking of these expenses is essential for calculating the ROI accurately.
- Customer Acquisition Cost (CAC): This metric represents the total cost of acquiring a new customer. It’s calculated by dividing total marketing expenses by the number of new customers acquired. A lower CAC generally indicates a more efficient marketing strategy.
- Customer Lifetime Value (CLTV): This metric predicts the total revenue a customer will generate throughout their relationship with the company. Comparing CLTV to CAC helps assess the long-term profitability of customer acquisition efforts.
- Website Traffic and Engagement: Metrics such as website visits, bounce rate, time on site, and conversion rates provide insights into the effectiveness of online marketing efforts. These metrics can be tracked through analytics platforms like Google Analytics.
- Social Media Engagement: Metrics like likes, shares, comments, and follower growth indicate the reach and resonance of social media campaigns. These metrics, however, need to be correlated with other metrics to demonstrate a clear link to revenue generation.
Data Collection and Organization
Gathering and organizing data from various sources is a critical step in calculating marketing ROI. Data often resides in disparate systems, requiring a structured approach to integration and analysis. Inconsistent data can significantly impact the accuracy of ROI calculations.
Data can be collected from a variety of sources including CRM systems, marketing automation platforms, website analytics dashboards, social media analytics tools, and sales reports. Consolidating this data into a central repository, perhaps a data warehouse or a marketing analytics platform, is crucial for efficient analysis. This often involves using data integration tools and techniques to ensure data consistency and accuracy. For example, a company might use a marketing automation platform to track email campaigns, website analytics to track website traffic, and a CRM system to track sales conversions. All this data needs to be integrated to get a holistic view.
Methods for Measuring Marketing Campaign Effectiveness
Several methods exist for measuring marketing campaign effectiveness, each with its strengths and weaknesses. The choice of method depends on the specific campaign objectives and the available data.
- Attribution Modeling: This involves assigning credit for conversions to different marketing touchpoints. Different models exist (e.g., last-click, first-click, linear) each providing a different perspective on which marketing activities are most effective. Choosing the right model depends on the nature of the marketing campaign and the customer journey.
- A/B Testing: This involves comparing the performance of two versions of a marketing asset (e.g., website landing page, email subject line) to determine which performs better. A/B testing helps optimize marketing campaigns by identifying what resonates most effectively with the target audience.
- Marketing Mix Modeling (MMM): This statistical technique analyzes the impact of various marketing channels on sales, accounting for external factors like seasonality and economic conditions. MMM provides a more comprehensive view of the overall marketing effectiveness than individual campaign analysis.
Calculating Marketing ROI
Calculating marketing return on investment (ROI) is crucial for understanding the effectiveness of marketing strategies and optimizing resource allocation. Different methods exist, each with its own strengths and weaknesses, depending on the data available and the specific marketing objectives. Accurately attributing costs and revenue is paramount for obtaining meaningful results.
Marketing ROI Calculation Formulas
Several formulas can be used to calculate marketing ROI, each offering a slightly different perspective. The choice of formula depends on the specific needs and data availability.
Formula 1: (Revenue Generated – Marketing Expenses) / Marketing Expenses * 100%
This is the most common formula, providing a straightforward percentage return. It’s easy to understand and implement, but it may oversimplify the impact of marketing if other factors significantly influence revenue. It also assumes a direct causal link between marketing spend and revenue generation, which isn’t always the case.
Formula 2: (Net Profit Generated – Marketing Expenses) / Marketing Expenses * 100%
This formula incorporates net profit instead of revenue, offering a more comprehensive view by accounting for other costs involved in generating revenue. It provides a clearer picture of the actual profitability of marketing efforts. However, accurate calculation requires meticulous tracking of all relevant costs, which can be challenging.
Formula 3: (Attributed Revenue – Marketing Expenses) / Marketing Expenses * 100%
This approach focuses on attributing revenue directly to specific marketing campaigns. This offers the most accurate ROI calculation when possible. However, accurate attribution is often difficult, requiring sophisticated tracking and analytical tools. It’s particularly useful for digital marketing where tracking is more feasible.
Importance of Accurate Marketing Expense Attribution
Accurately attributing marketing expenses to specific campaigns is paramount for effective ROI calculation. Without accurate attribution, it’s impossible to determine which campaigns are performing well and which are underperforming. This prevents informed decision-making regarding resource allocation and optimization. For example, if a company runs multiple campaigns simultaneously, and the total revenue is high, but the attribution is poor, it’s impossible to determine which specific campaigns drove that revenue, hindering future strategy planning.
Hypothetical Marketing ROI Calculation
Let’s consider a hypothetical example of a new product launch campaign.
| Category | Cost ($) | Revenue ($) | Profit ($) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Marketing Campaign (Social Media Ads) | 5000 | 20000 | 15000 |
| Marketing Campaign (Email Marketing) | 2000 | 10000 | 8000 |
| Marketing Campaign (Content Marketing) | 3000 | 15000 | 12000 |
| Total | 10000 | 45000 | 35000 |
Using Formula 1: (45000 – 10000) / 10000 * 100% = 350% ROI.
Using Formula 2: (35000 – 10000) / 10000 * 100% = 250% ROI.
Using Formula 3 (assuming perfect attribution): The ROI for each campaign can be calculated individually using either Formula 1 or 2, based on the revenue and cost for each specific campaign.
Challenges in Marketing ROI Calculation
Accurately calculating marketing ROI can be surprisingly difficult, even with sophisticated analytics tools. Several factors contribute to the challenges, often leading to inaccurate or incomplete assessments of marketing effectiveness. Understanding these challenges is crucial for improving the reliability and usefulness of your ROI calculations.
Many pitfalls exist when attempting to quantify the return on marketing investments. These stem from limitations in data collection, the complexity of attributing conversions to specific marketing activities, and the inherent difficulty in assigning monetary value to certain marketing outcomes, such as brand awareness. Ignoring these challenges can lead to flawed decisions and ultimately, wasted resources.
Inaccurate Data and Attribution Issues
Inaccurate data is a major obstacle to calculating a true marketing ROI. Incomplete or flawed data sets, resulting from issues with data collection, tracking, and integration, can significantly skew results. For example, if website analytics are improperly configured, the number of conversions attributed to a specific campaign might be underestimated or overestimated. Similarly, inaccurate customer data can lead to misinterpretations of customer behavior and the effectiveness of targeted campaigns. Attribution is another significant hurdle; determining which marketing touchpoints contribute to a conversion can be extremely complex, especially in multi-channel marketing strategies. A customer might interact with several touchpoints (e.g., social media ad, email, and a blog post) before making a purchase. Determining the relative contribution of each touchpoint requires sophisticated attribution modeling, which itself can be subject to error. For instance, a last-click attribution model might overemphasize the final interaction, underestimating the influence of earlier touchpoints.
Overcoming Challenges and Improving Accuracy
Several strategies can mitigate the challenges associated with calculating marketing ROI. Firstly, investing in robust data infrastructure is essential. This includes implementing a comprehensive data collection system that integrates data from various sources (e.g., CRM, website analytics, social media platforms) and ensures data accuracy and consistency. Secondly, adopting a more sophisticated attribution model, such as multi-touch attribution, can provide a more nuanced understanding of the customer journey and the contribution of different marketing channels. This model distributes credit across all touchpoints involved in a conversion, offering a more realistic view of each channel’s impact. Thirdly, regularly auditing data quality and processes is crucial to identify and correct errors before they significantly affect ROI calculations. This includes validating data against other sources and reviewing data collection methods for potential biases or inaccuracies. Finally, focusing on clear marketing objectives and KPIs ensures that the right data is collected and analyzed. Defining specific, measurable, achievable, relevant, and time-bound (SMART) goals allows for more accurate measurement of marketing success and ROI. For example, instead of a vague goal like “increase brand awareness,” a SMART goal might be “increase website traffic by 20% within three months through targeted social media advertising.”
Improving Marketing ROI
Improving marketing ROI is not a one-time fix but an ongoing process of refinement and optimization. By systematically analyzing data and making informed adjustments, businesses can significantly enhance the return on their marketing investments. This involves a continuous feedback loop, where data informs strategy, strategy informs action, and results are measured and used to further refine the approach.
A data-driven approach to improving marketing ROI is crucial. This involves carefully tracking key metrics, analyzing the results, and using these insights to make strategic changes to marketing campaigns. This iterative process allows for continuous improvement and a higher overall return on investment.
Accurately calculating Marketing ROI is crucial for any business. Understanding which marketing efforts deliver the best return helps prioritize spending. To significantly boost your ROI, consider implementing effective expansion strategies, such as those detailed in this helpful guide on Expansion-driven growth tactics. By strategically expanding your market reach, you can increase your customer base and, ultimately, improve your overall marketing ROI.
A Step-by-Step Process for Improving Marketing ROI Based on Data Analysis
This process Artikels a structured approach to improving marketing ROI using data analysis as the guiding principle. Each step builds upon the previous one, creating a cyclical process of continuous improvement.
- Data Collection and Measurement: Begin by identifying and tracking the key metrics relevant to your marketing goals. This might include website traffic, conversion rates, customer acquisition cost (CAC), customer lifetime value (CLTV), and return on ad spend (ROAS). Use analytics tools to track these metrics accurately and consistently.
- Data Analysis and Interpretation: Once data is collected, analyze it to identify trends, patterns, and areas for improvement. What channels are performing best? Which campaigns are generating the highest ROI? What are the common characteristics of high-performing campaigns?
- Identify Key Areas for Improvement: Based on the data analysis, pinpoint specific areas where improvements can be made. This might involve optimizing specific channels, refining targeting strategies, or improving the quality of marketing materials.
- Implement Changes and Test: Implement the identified improvements and carefully track the results. A/B testing different approaches can help determine which changes are most effective. This ensures a data-driven approach to optimization.
- Monitor and Iterate: Continuously monitor the performance of your marketing campaigns and make adjustments as needed. The marketing landscape is constantly evolving, so regular monitoring and iterative improvements are crucial for maintaining a high ROI.
Actionable Strategies for Optimizing Marketing Campaigns
Effective strategies for enhancing marketing ROI require a multifaceted approach, encompassing budget allocation, channel optimization, and content improvement.
The following strategies, categorized for clarity, offer practical steps to optimize marketing efforts and boost ROI. Remember that the most effective strategy will depend on your specific business, target audience, and marketing goals.
Accurately calculating Marketing ROI requires a clear understanding of your campaign’s goals and metrics. This meticulous approach is similar to crafting a compelling film script; you need a strong narrative structure, just as you need a well-defined marketing strategy. Learning how to effectively structure a narrative can be beneficial, check out this helpful guide on Cara menulis skrip film to understand the importance of a strong framework.
Ultimately, a well-defined plan, whether it’s a film script or a marketing campaign, is key to achieving a positive ROI.
Budget Allocation Strategies
- Prioritize High-Performing Channels: Allocate a larger portion of your budget to the channels that consistently deliver the best results. This might involve shifting resources from underperforming channels to those that demonstrate a higher ROI.
- Diversify Budget Allocation: While prioritizing high-performing channels is important, avoid putting all your eggs in one basket. Diversifying your budget across multiple channels can mitigate risk and tap into different audience segments.
- Dynamic Budget Allocation: Implement a system that allows for dynamic budget allocation, adjusting spending based on real-time performance data. This ensures that resources are always directed towards the most effective channels and campaigns.
Channel Optimization Strategies
- Improve Targeting: Refine your targeting strategies to reach the most relevant audience segments. Utilize data and analytics to identify your ideal customer profile (ICP) and tailor your messaging accordingly.
- A/B Test Different Approaches: Experiment with different ad creatives, landing pages, and call-to-actions to identify what resonates best with your target audience. A/B testing allows for data-driven decision-making and continuous improvement.
- Optimize Landing Pages: Ensure your landing pages are optimized for conversions. This involves using clear and concise messaging, strong calls-to-action, and a user-friendly design.
Content Improvement Strategies
- Create High-Quality Content: Invest in creating valuable, engaging, and informative content that resonates with your target audience. This includes blog posts, videos, infographics, and other forms of media.
- Optimize Content for Search Engines (): Implement best practices to improve your website’s ranking in search engine results pages (SERPs). This increases organic traffic and reduces reliance on paid advertising.
- Personalize Content: Tailor your content to the specific needs and interests of your target audience. Personalized content is more engaging and leads to higher conversion rates.
Visualizing Marketing ROI
Data visualization is crucial for understanding and communicating marketing ROI. Effectively presented visuals transform complex numerical data into easily digestible insights, allowing for quicker identification of successful strategies and areas needing improvement. This facilitates better decision-making and resource allocation.
Effective visualization of marketing ROI requires choosing appropriate chart types to highlight key trends and relationships within the data. Different chart types excel at representing different aspects of the data, and the selection should align with the specific message being conveyed.
Chart Types for Visualizing Marketing ROI
Several chart types are well-suited for displaying marketing ROI data. Bar charts are excellent for comparing the ROI of different marketing campaigns or channels side-by-side. Line charts effectively illustrate ROI trends over time, showing growth or decline. Pie charts are useful for showing the proportional contribution of various marketing activities to the overall ROI. Finally, scatter plots can reveal correlations between marketing spend and resulting revenue.
Examples of Effective Visualizations
A bar chart could compare the ROI of email marketing (e.g., 25%), social media marketing (e.g., 15%), and paid search (e.g., 30%) campaigns. A line chart could track the monthly ROI of a specific campaign over a year, showing fluctuations and overall growth. A pie chart could illustrate the percentage contribution of each marketing channel to the total company revenue. A scatter plot could display the relationship between advertising expenditure and sales revenue, revealing if increased spending correlates with higher revenue.
Compelling Visual Representation of Marketing ROI Data
Consider a bar chart depicting the ROI of three distinct marketing campaigns (Campaign A, Campaign B, and Campaign C) over a six-month period. The x-axis would represent the months (January to June), and the y-axis would represent the ROI percentage. Each campaign would be represented by a different colored bar for each month. Data points would show the calculated ROI for each campaign in each month. For instance, Campaign A might show a steady increase from 10% in January to 25% in June, Campaign B a fluctuating performance, and Campaign C a consistent but lower ROI throughout the six months. A clear legend would identify each campaign, and the chart title would be “Marketing Campaign ROI – January to June.” This visual would quickly communicate the relative success of each campaign over time, enabling straightforward comparisons and informed strategic adjustments.
Marketing ROI and Different Marketing Channels
Understanding how marketing ROI varies across different channels is crucial for effective budget allocation and maximizing return on investment. Each channel presents unique challenges and opportunities, demanding a tailored approach to ROI calculation and optimization. This section will explore the nuances of calculating ROI for various marketing channels and strategies for effective budget distribution.
Social Media Marketing ROI, Marketing ROI calculation
Calculating social media ROI requires a multifaceted approach, going beyond simple likes and shares. Key metrics include website traffic driven from social media, lead generation from social campaigns, and ultimately, revenue attributed to social media activities. Attribution modeling plays a critical role here, as it’s often difficult to directly link a social media interaction to a final sale. For instance, a customer might engage with a brand on Instagram, then later make a purchase on the company website. Sophisticated tracking and analytics are needed to accurately attribute this conversion. The formula for calculating ROI remains consistent: (Revenue generated – Marketing spend) / Marketing spend * 100. However, accurately determining the “revenue generated” portion for social media necessitates robust tracking and analysis.
Email Marketing ROI
Email marketing boasts a relatively straightforward ROI calculation. Key metrics include open rates, click-through rates, conversion rates (e.g., purchases, sign-ups), and ultimately, revenue generated from email campaigns. Because email marketing often uses unique links and tracking codes, attributing revenue to specific email campaigns is often easier than with social media. For example, a company sending a promotional email with a unique discount code can easily track how many sales result from that specific email. This simplifies the ROI calculation, making it a highly measurable channel.
Search Engine Optimization () ROI
Calculating ROI is more challenging due to its long-term nature and the difficulty in directly attributing website traffic and conversions to specific activities. While tracking rankings and organic traffic is essential, linking these metrics directly to revenue requires careful analysis. For instance, an improvement in organic search ranking for a specific might lead to increased website traffic and eventually, more sales, but proving a direct causal link requires sophisticated analytics. Therefore, ROI often relies on a combination of qualitative and quantitative data, including website traffic, lead generation, and brand awareness metrics, in addition to revenue generated. The timeframe for assessing ROI is also considerably longer than for other channels, often spanning several months or even years.
Budget Allocation Based on ROI Analysis
Effective budget allocation across marketing channels requires a data-driven approach. By analyzing the ROI of each channel, businesses can strategically allocate resources to the channels that yield the highest returns. This involves comparing the ROI of each channel, considering factors such as the cost per acquisition (CPA), customer lifetime value (CLTV), and the overall marketing objectives. For example, if email marketing consistently demonstrates a higher ROI than social media, a company might choose to allocate a larger portion of its marketing budget to email marketing. This process should be iterative, regularly reviewed and adjusted based on performance data. A company might initially allocate budget equally across channels, then shift resources based on observed ROI differences.
Last Recap: Marketing ROI Calculation
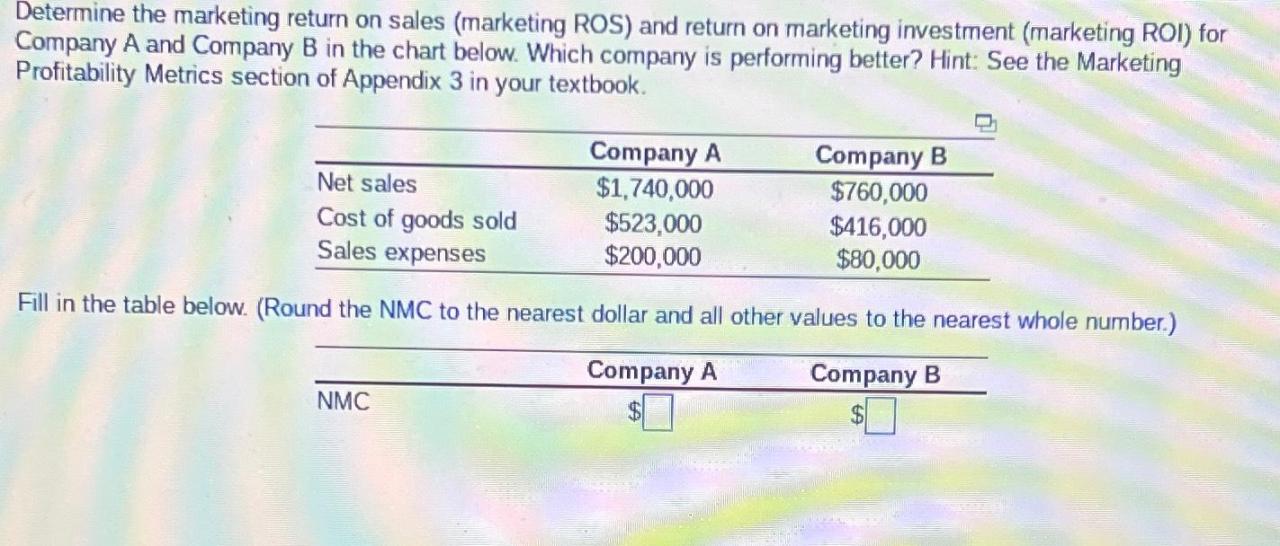
Mastering marketing ROI calculation is not merely about numbers; it’s about gaining a deeper understanding of your marketing effectiveness. By consistently tracking key metrics, analyzing data, and adapting your strategies, you can transform your marketing efforts from guesswork into a precise, profit-driving machine. Remember, the journey towards maximizing ROI is ongoing – continuous improvement and refinement are key to long-term success.