Growth-focused business models prioritize rapid expansion and market dominance. This approach necessitates a keen understanding of customer acquisition, efficient scaling, and continuous innovation. Successfully navigating this path requires a strategic blend of marketing acumen, operational efficiency, and a clear vision for future growth. Understanding the nuances of funding, competitive analysis, and data-driven decision-making is crucial for sustained success in this dynamic environment.
This exploration delves into the core principles of growth-focused business models, examining strategies for customer acquisition and retention, scaling operations, securing funding, fostering innovation, and navigating the competitive landscape. We will analyze key performance indicators (KPIs), discuss various funding options, and highlight the importance of adaptability in a constantly evolving market.
Defining Growth-Focused Business Models
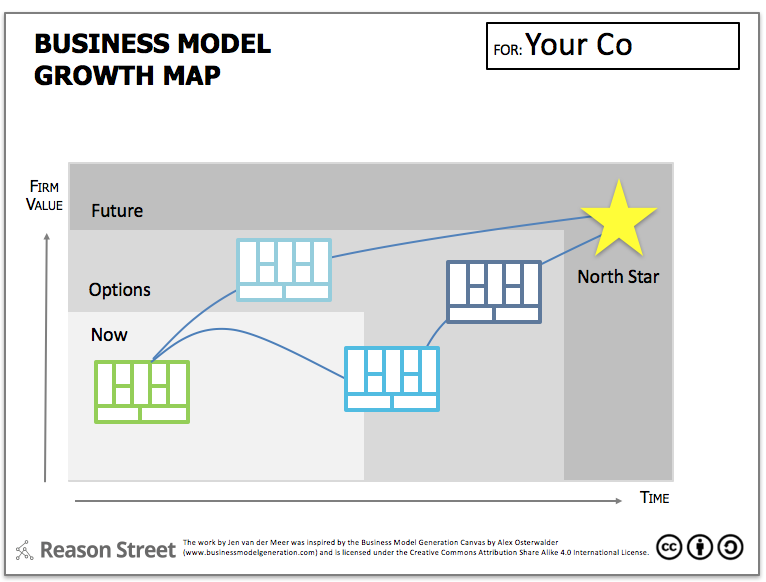
Growth-focused business models prioritize rapid expansion and market share acquisition above all else. These models often involve aggressive strategies to attract new customers, increase revenue streams, and scale operations quickly. While profitability is a factor, it’s often secondary to the overarching goal of achieving significant growth in a relatively short timeframe.
Growth-focused business models are characterized by several key features. They typically involve high investment in marketing and sales, a focus on rapid product development and iteration, and a willingness to accept higher levels of risk in pursuit of ambitious growth targets. Furthermore, they often leverage data-driven decision-making to optimize marketing campaigns, product development, and overall business strategy.
Core Characteristics of Growth-Focused Business Models
Several core characteristics define growth-focused business models. These include a relentless focus on customer acquisition, often through aggressive marketing strategies and innovative product offerings. Rapid scaling of operations is another key element, frequently requiring significant investment in infrastructure, personnel, and technology. Finally, a willingness to embrace experimentation and adapt quickly to market changes is crucial for success in this high-growth environment. Companies using these models often prioritize speed and efficiency over meticulous planning and risk aversion.
Examples of Industries Where Growth-Focused Models Are Prevalent
Growth-focused business models are particularly prevalent in industries characterized by rapid technological advancements and significant market opportunities. The technology sector, for example, with its fast-paced innovation cycles and the constant emergence of new platforms and applications, is a prime example. Similarly, the e-commerce industry, driven by the increasing adoption of online shopping and the expansion of global markets, frequently employs growth-focused strategies. Finally, the food delivery and ride-sharing industries also demonstrate a strong reliance on growth-focused models, prioritizing rapid expansion and market dominance. These industries often see intense competition, necessitating aggressive growth strategies to secure a leading position.
Comparison of Growth-Focused and Sustainability-Focused Models
Growth-focused and sustainability-focused business models represent distinct approaches to business strategy. While growth-focused models prioritize rapid expansion and market share, sustainability-focused models emphasize long-term viability and environmental and social responsibility. Growth-focused models often involve high levels of resource consumption and may prioritize short-term gains over long-term sustainability. In contrast, sustainability-focused models aim to minimize environmental impact and create positive social outcomes, even if it means slower growth. For example, a company focused on sustainable agriculture might prioritize environmentally friendly practices, even if it means lower yields compared to a company using intensive farming methods focused solely on maximizing production and profits. The choice between these models often depends on the company’s values, long-term vision, and the industry’s specific context.
Key Performance Indicators (KPIs) for Growth-Focused Businesses
Measuring success in growth-focused businesses requires a different set of KPIs than those used in more traditional, profitability-focused models. While profitability is still important, growth-focused businesses typically place a greater emphasis on metrics that reflect their expansion rate and market penetration. Key KPIs include customer acquisition cost (CAC), customer lifetime value (CLTV), monthly recurring revenue (MRR), and user growth rates. Tracking these metrics provides insights into the efficiency of growth strategies and helps identify areas for improvement. For example, a high CAC relative to CLTV indicates that the cost of acquiring customers is outweighing the revenue generated, signaling a need to optimize marketing and sales efforts. Monitoring MRR provides a clear picture of the business’s recurring revenue streams, crucial for projecting future growth. Finally, consistently tracking user growth is essential for understanding the rate of adoption and market penetration.
Acquisition and Retention Strategies

Growth-focused businesses require robust strategies for both acquiring new customers and retaining existing ones. A successful approach involves a well-defined plan that leverages various marketing and sales channels, tailored to the specific target audience and business model. The interplay between acquisition and retention is crucial; acquiring customers is costly, so retaining them is paramount for long-term profitability and sustainable growth.
Customer Acquisition Strategy for a Hypothetical Growth-Focused Business
Let’s consider a hypothetical subscription-based online learning platform, “SkillBoost.” SkillBoost’s customer acquisition strategy would focus on a multi-channel approach. Initially, a strong emphasis would be placed on content marketing, creating valuable and engaging content (blog posts, webinars, free courses) related to various skill development areas to attract organic traffic and establish thought leadership. Simultaneously, targeted paid advertising campaigns on platforms like Google Ads and social media (LinkedIn, Facebook) would be implemented to reach specific demographics interested in professional development. Furthermore, strategic partnerships with universities and corporations offering SkillBoost as an employee benefit would broaden reach and build credibility. Finally, influencer marketing collaborations with industry experts would leverage their established audiences to promote the platform. This multi-pronged approach aims to generate a steady stream of high-quality leads.
Examples of Successful Customer Retention Strategies
Several growth-focused companies excel at customer retention. Netflix, for example, leverages data-driven personalization to recommend relevant content, ensuring users continue to find value in their subscription. Companies like Adobe employ robust customer success programs, providing proactive support and resources to help users maximize their product’s potential. Subscription boxes like Birchbox utilize loyalty programs and exclusive offers to incentivize continued subscriptions. These strategies are based on understanding customer needs and preferences, providing ongoing value, and fostering a sense of community.
The Role of Marketing and Sales in Driving Growth
Marketing and sales are intertwined and crucial for driving growth. Marketing focuses on generating awareness, building brand recognition, and attracting potential customers through various channels. Sales, on the other hand, focuses on converting leads into paying customers through direct interaction and relationship building. In a growth-focused business, both functions must work in sync. Marketing provides the qualified leads, while sales nurtures those leads and closes deals. Effective communication and collaboration between marketing and sales teams are essential for maximizing conversion rates and achieving sustainable growth. Data analytics plays a crucial role in tracking performance, identifying areas for improvement, and optimizing both marketing and sales efforts.
Customer Acquisition Channel Comparison
| Channel | Cost | Reach | Effectiveness |
|---|---|---|---|
| Social Media Marketing | Moderate to High (depending on platform and targeting) | High (depending on targeting and campaign optimization) | High (when targeted effectively and content resonates with the audience) |
| Content Marketing | Low to Moderate (primarily time and resource investment) | Moderate to High (organic reach potential is high, but can take time to build) | High (builds trust and credibility over time, leading to organic lead generation) |
| Paid Advertising (Google Ads, etc.) | High (costs vary significantly depending on bidding and targeting) | High (potential for broad reach, but requires careful targeting) | Moderate to High (highly effective for immediate lead generation, but requires ongoing optimization) |
| Email Marketing | Low to Moderate (cost of email marketing platforms and email creation) | Moderate (limited by email list size, but highly targeted) | Moderate to High (effective for nurturing leads and driving conversions) |
Scaling Operations and Infrastructure

Rapid growth presents exhilarating opportunities, but also significant operational challenges. Successfully navigating this phase requires proactive planning and a flexible approach to scaling both your workforce and technological infrastructure. Failure to do so can lead to bottlenecks, decreased efficiency, and ultimately, hinder further growth. This section will explore strategies for managing this crucial stage of development.
Scaling operations for a rapidly growing business presents a unique set of hurdles. Maintaining quality and consistency while significantly increasing output is a constant balancing act. Hiring and training new employees quickly, while ensuring they are adequately integrated into the existing team, is a major challenge. Furthermore, maintaining company culture and values as the workforce expands can be difficult. Existing processes and workflows may become strained or even break down under the pressure of increased volume. Finally, managing cash flow and resource allocation efficiently becomes even more critical during periods of rapid growth.
Challenges of Scaling Operations
Rapid expansion often leads to a strain on existing resources. Increased demand may outpace the capacity of current systems, leading to delays, errors, and decreased customer satisfaction. For example, a rapidly growing e-commerce business might experience website crashes due to overwhelming traffic, or a software company might struggle to handle increased customer support requests. Another common challenge is maintaining the quality of products or services while scaling production. This requires careful monitoring of processes and potentially investing in new technologies or training programs. Finally, ensuring that all employees are aligned with the company’s vision and values as the team expands becomes paramount to maintain a cohesive and productive workforce.
Strategies for Managing Rapid Growth and Preventing Burnout
Effective strategies for managing rapid growth and preventing burnout involve a multi-pronged approach. Prioritizing automation of repetitive tasks is crucial to free up employee time and reduce the risk of errors. Implementing robust project management systems ensures tasks are clearly defined, assigned, and tracked effectively. Investing in employee training and development programs helps upskill the workforce and prepare them for increased responsibilities. Regular performance reviews and feedback sessions help identify areas for improvement and prevent employees from feeling overwhelmed. Furthermore, fostering a culture of open communication and collaboration encourages teamwork and reduces stress. Finally, offering flexible work arrangements and promoting work-life balance helps prevent employee burnout and maintain morale.
Scaling Technological Infrastructure
Scaling a business’s technological infrastructure to support increased demand requires careful planning and execution. This involves assessing current infrastructure capacity and identifying potential bottlenecks. Moving to cloud-based solutions offers scalability and flexibility, allowing businesses to easily adjust resources based on demand. Investing in robust and scalable database systems is essential to handle growing amounts of data. Furthermore, implementing monitoring and analytics tools helps identify performance issues and optimize resource allocation. For instance, a rapidly growing SaaS company might migrate its infrastructure to the cloud to handle a surge in user registrations and data storage needs. Regular security audits and updates are also crucial to protect sensitive data as the infrastructure expands.
Adapting Business Models to Different Growth Phases
A successful business model is adaptable and evolves alongside the company’s growth. In the early stages, a lean and agile approach might be optimal, focusing on rapid iteration and customer feedback. As the business scales, more structured processes and systems may be needed to ensure consistency and efficiency. For example, a startup might initially rely on word-of-mouth marketing, but as it grows, it might invest in more sophisticated marketing campaigns. The pricing strategy might also need to be adjusted based on the company’s scale and market position. For instance, a company might initially offer a low price to gain market share, but as it becomes more established, it might increase prices to reflect its higher value proposition. Continuously analyzing key performance indicators (KPIs) and adapting the business model accordingly is essential for sustained growth.
Funding and Investment Strategies
Securing funding is crucial for the growth of any business, particularly those focused on rapid expansion. The choice of funding strategy significantly impacts a company’s trajectory, influencing its operational flexibility, equity dilution, and overall long-term success. Understanding the various options and their implications is paramount for navigating this critical phase of business development.
Funding options for growth-focused businesses are diverse and each presents a unique set of advantages and disadvantages. The optimal choice depends heavily on the company’s stage of development, risk tolerance, and long-term goals.
Funding Options for Growth-Focused Businesses
Several avenues exist for securing capital. Bootstrapping, angel investors, venture capital, and debt financing represent some of the most common approaches. Each offers a distinct profile of risk and reward.
- Bootstrapping: This involves funding the business solely through the founders’ personal savings, revenue generated, and cost-cutting measures. It minimizes equity dilution but can severely limit growth potential due to constrained resources.
- Angel Investors: High-net-worth individuals invest their personal capital in exchange for equity. They offer not only funding but also mentorship and industry connections, although the investment amounts are typically smaller than those from venture capitalists.
- Venture Capital (VC): Venture capital firms invest in high-growth businesses with significant potential, usually in exchange for a substantial equity stake. They bring significant capital and expertise but demand high returns and often exert considerable influence on the company’s direction.
- Debt Financing: This involves borrowing money from banks, credit unions, or other lenders. It avoids equity dilution but requires regular interest payments and can burden the business with significant debt.
Comparison of Funding Sources, Growth-focused business models
A direct comparison highlights the trade-offs inherent in each funding option.
| Funding Source | Advantages | Disadvantages |
|---|---|---|
| Bootstrapping | No equity dilution, full control | Limited growth potential, slow scaling |
| Angel Investors | Mentorship, access to networks, less equity dilution than VC | Smaller investment amounts, potential for disagreements |
| Venture Capital | Significant capital injection, industry expertise | High equity dilution, potential loss of control, pressure for rapid growth |
| Debt Financing | No equity dilution, predictable repayment schedule | Interest payments, potential for financial distress if revenue falls short |
Creating a Compelling Pitch Deck
A well-structured pitch deck is essential for attracting investors. It should concisely communicate the business’s value proposition, market opportunity, team capabilities, and financial projections. A strong narrative is crucial, conveying passion and a clear vision for the future.
The deck should typically include:
- Problem & Solution: Clearly define the problem being addressed and the proposed solution.
- Market Opportunity: Demonstrate the market size, target audience, and competitive landscape.
- Business Model: Explain how the business generates revenue and achieves profitability.
- Team: Highlight the experience and expertise of the founding team.
- Financial Projections: Present realistic and well-supported financial forecasts.
- Ask: Clearly state the amount of funding being sought and its intended use.
Key Financial Metrics for Investors
Investors in growth-focused businesses scrutinize several key financial metrics to assess the company’s potential for return. These metrics provide insights into the business’s performance, efficiency, and growth trajectory.
Some key metrics include:
- Revenue Growth: Demonstrates the company’s ability to increase sales over time.
- Customer Acquisition Cost (CAC): Measures the cost of acquiring a new customer.
- Customer Lifetime Value (CLTV): Estimates the total revenue generated by a customer over their relationship with the company.
- Burn Rate: Indicates the rate at which the company is spending its cash reserves.
- Gross Margin: Shows the profitability of the company’s products or services.
Innovation and Adaptability: Growth-focused Business Models
Sustained growth in today’s dynamic business environment hinges on a commitment to continuous innovation and the ability to adapt swiftly to evolving market conditions. Businesses that fail to embrace change risk obsolescence, while those that proactively anticipate and respond to shifts in consumer preferences, technology, and competitive landscapes are more likely to thrive. This section will explore the importance of innovation, showcase successful adaptation strategies, identify potential risks of rapid growth, and Artikel methods for fostering a culture of innovation.
Continuous innovation is not merely about developing new products or services; it’s a fundamental shift in mindset that permeates all aspects of the business. It’s about constantly seeking better ways to operate, serve customers, and deliver value. This requires a proactive approach to identifying emerging trends, understanding customer needs, and exploring new technologies. A culture of experimentation and learning from failures is crucial to this process. Without continuous innovation, businesses risk becoming stagnant and losing their competitive edge.
Examples of Successful Adaptation to Changing Market Conditions
Several businesses have demonstrated remarkable adaptability in the face of significant market shifts. Netflix, initially a DVD rental service by mail, successfully transitioned to a streaming platform, anticipating the rise of broadband internet and changing consumer preferences for on-demand entertainment. Similarly, Blockbuster’s failure to adapt to the digital revolution stands in stark contrast to Netflix’s proactive approach. Another example is the transformation of Kodak, a once-dominant player in film photography, which failed to adapt to the rise of digital photography, ultimately leading to its bankruptcy. These examples highlight the critical importance of anticipating and responding to technological advancements and evolving customer needs.
Potential Risks Associated with Rapid Growth and Mitigation Strategies
Rapid growth, while desirable, presents several inherent risks. One key risk is the strain on infrastructure and resources. A sudden influx of customers or orders can overwhelm existing systems, leading to operational inefficiencies, delays, and ultimately, customer dissatisfaction. Another risk is the potential for a loss of quality control as businesses struggle to maintain standards during periods of rapid expansion. Furthermore, rapid growth can lead to cash flow problems if revenue generation doesn’t keep pace with expenses.
Mitigation strategies include proactive capacity planning, investing in scalable infrastructure, implementing robust quality control systems, and securing adequate funding to support expansion. Careful financial management and a focus on efficient operations are essential to navigate the challenges of rapid growth successfully. Regularly assessing the capacity of the organization to handle increased demand and implementing measures to improve efficiency can help to mitigate these risks.
Methods for Fostering a Culture of Innovation
Creating a culture of innovation requires a multifaceted approach. It’s not enough to simply encourage innovation; it requires a deliberate and sustained effort to cultivate the right environment.
- Encourage experimentation and risk-taking: Establish a safe space for employees to propose new ideas, experiment with different approaches, and learn from failures without fear of retribution.
- Invest in research and development: Allocate sufficient resources to explore new technologies, develop innovative products and services, and stay ahead of the competition.
- Embrace collaboration and knowledge sharing: Foster a collaborative environment where employees from different departments and backgrounds can share ideas and work together to solve problems.
- Provide training and development opportunities: Equip employees with the skills and knowledge they need to innovate and adapt to changing market conditions.
- Recognize and reward innovation: Celebrate successes and acknowledge the contributions of individuals and teams who have demonstrated innovative thinking.
- Embrace agile methodologies: Implement agile project management techniques to enable faster iteration and adaptation to changing requirements.
Competitive Analysis and Market Positioning
Understanding the competitive landscape and crafting a strong market position are crucial for any growth-focused business. A thorough competitive analysis reveals opportunities, while effective positioning differentiates your offering and secures a sustainable market share. This involves not only identifying competitors but also understanding their strengths, weaknesses, and strategies.
Competitive analysis provides a clear picture of the market dynamics, allowing businesses to identify underserved segments, potential partnerships, and areas for innovation. A well-defined market position, in turn, helps attract target customers, build brand loyalty, and command premium pricing. This section explores these concepts in detail, illustrating how a hypothetical business can leverage them for growth.
Competitive Landscape Analysis for a Hypothetical “Sustainable Snack” Business
Let’s consider a hypothetical business focused on producing and selling sustainable, healthy snacks. A competitive analysis would involve identifying direct competitors (other companies offering similar healthy snacks), indirect competitors (companies offering alternative healthy options like fresh fruit or meal replacement bars), and potential future competitors (startups entering the market with innovative sustainable snack products). The analysis would then assess each competitor’s market share, pricing strategies, product offerings, marketing efforts, and overall strengths and weaknesses. For instance, a competitor might excel in distribution, while another might have a strong brand reputation. By understanding these aspects, the sustainable snack business can identify gaps in the market and opportunities for differentiation.
Differentiating a Sustainable Snack Business from Competitors
Differentiation is key to success. Our hypothetical sustainable snack business could differentiate itself through several strategies. This could include focusing on unique ingredients (e.g., using locally sourced, organic ingredients), employing innovative packaging (e.g., compostable packaging), emphasizing ethical sourcing and production practices (e.g., fair-trade certification), or building a strong brand identity around sustainability and health. Another key differentiator could be offering a subscription service, providing convenience and building customer loyalty. The combination of multiple differentiation strategies creates a stronger overall competitive advantage. For example, a competitor might focus solely on organic ingredients, while our business combines organic ingredients with compostable packaging and a subscription model, offering a more comprehensive and appealing value proposition.
Market Positioning Strategy for a Sustainable Snack Business
Based on the competitive analysis, a clear market positioning strategy is developed. The sustainable snack business could position itself as the “premium, ethically sourced, and convenient healthy snack option”. This positioning statement targets health-conscious consumers who are also environmentally aware and value convenience. This positioning will inform all marketing and product development decisions, ensuring consistent messaging and brand perception. A supporting marketing campaign could highlight the unique ingredients, sustainable packaging, and convenient subscription model, further reinforcing the chosen positioning. For instance, marketing materials could showcase the local farmers supplying the ingredients, emphasizing the ethical and environmental benefits.
Using Market Research to Inform Growth Strategies
Market research is essential for validating assumptions and informing growth strategies. For the sustainable snack business, this might involve conducting surveys, focus groups, and analyzing sales data to understand consumer preferences, identify unmet needs, and test different marketing messages. For example, conducting consumer surveys could reveal preferred flavors, packaging types, and price points. Analyzing sales data could identify high-performing products and geographic regions, allowing for targeted marketing efforts and optimized product development. This data-driven approach ensures that growth strategies are aligned with actual market demand and consumer behavior. A/B testing different marketing materials could further optimize campaign effectiveness, ensuring maximum ROI on marketing investments.
Measuring and Analyzing Growth
Understanding and tracking growth is crucial for any business aiming for success. Effective measurement provides insights into performance, identifies areas for improvement, and guides strategic decision-making. Without accurate data, growth remains a vague aspiration rather than a measurable objective.
Growth Measurement Methods
Several methods exist for tracking and measuring business growth. These range from simple calculations to sophisticated analytical models, depending on the business’s size, complexity, and specific goals. Choosing the right method depends on the data available and the insights sought.
- Revenue Growth: This is a fundamental metric, calculated as the percentage change in revenue over a specific period. A simple formula is: [(Current Revenue – Previous Revenue) / Previous Revenue] * 100%. This provides a direct measure of the business’s top-line performance.
- Customer Growth: Tracking the number of new customers acquired over time is critical. This can be further broken down by customer segments to identify growth areas and pinpoint potential issues. Understanding customer acquisition cost (CAC) in relation to customer lifetime value (CLTV) is also essential.
- Market Share Growth: Measuring a company’s market share indicates its competitive position. This requires data on the overall market size and the company’s share of that market. Growth in market share suggests a successful strategy in gaining customer preference.
- Profitability Growth: While revenue growth is important, profit margins and overall profitability are ultimately key to long-term sustainability. Tracking metrics like gross profit margin, net profit margin, and return on investment (ROI) provides a holistic view of financial health.
Visual Representation of Growth
A typical growth curve for a successful business often resembles an S-curve. The curve starts slowly, representing the initial stages of development and market penetration (slow growth phase). It then enters a period of rapid, exponential growth as the business gains traction and scales its operations (high-growth phase). Finally, the curve begins to flatten as the business matures and approaches its market saturation point (maturity phase). The steepness of the curve’s slope reflects the speed of growth, while the overall shape illustrates the typical stages of a business lifecycle. For example, a company like Amazon experienced a relatively slow initial growth phase, followed by a period of extremely rapid growth as online shopping became mainstream, and is now experiencing a slower, though still positive, growth rate in its mature phase.
Key Metrics for Monitoring Growth
Several key metrics provide valuable insights into a business’s progress towards its growth goals. These metrics should be carefully selected based on the specific business model and strategic objectives.
- Website Traffic and Engagement: For businesses with a significant online presence, website traffic, bounce rate, time on site, and conversion rates are crucial indicators of marketing effectiveness and customer engagement.
- Customer Acquisition Cost (CAC): This metric measures the cost of acquiring a new customer, providing insights into the efficiency of marketing and sales efforts. A low CAC indicates cost-effective customer acquisition.
- Customer Lifetime Value (CLTV): This metric represents the total revenue expected from a customer over their entire relationship with the business. A high CLTV suggests strong customer loyalty and retention.
- Churn Rate: This measures the rate at which customers stop doing business with a company. A low churn rate signifies strong customer retention and satisfaction.
Data Interpretation and Utilization
Data analysis is crucial for translating raw metrics into actionable insights. This involves using various analytical techniques, including trend analysis, comparative analysis, and forecasting, to identify patterns, anomalies, and opportunities. For example, a consistently high churn rate might indicate a problem with customer service, prompting the company to invest in training or process improvements. Similarly, a decline in website traffic might signal the need for a marketing campaign refresh. By interpreting data accurately and systematically, businesses can make informed decisions that drive sustainable growth.
Summary

In conclusion, building a successful growth-focused business demands a proactive and multifaceted approach. From meticulously crafting acquisition and retention strategies to effectively scaling operations and securing appropriate funding, each element plays a crucial role in achieving sustainable growth. By embracing continuous innovation, leveraging data-driven insights, and maintaining a keen awareness of the competitive landscape, businesses can position themselves for long-term success in the ever-evolving marketplace. Ultimately, the journey towards sustained growth requires strategic planning, adaptability, and a relentless pursuit of excellence.
Growth-focused business models prioritize scaling operations and market reach. A successful strategy often involves identifying and capitalizing on niche markets; for example, consider the potential in reviving traditional recipes, perhaps using a resource like this excellent guide: Panduan memasak kue tradisional. This approach demonstrates how even seemingly small markets, when strategically targeted, can contribute significantly to overall growth within a larger business model.
Growth-focused business models prioritize rapid expansion and market share. A prime example of a business leveraging this strategy is the mobile gaming industry, where companies often release updates and new content frequently to maintain player engagement. Consider the intense competition within the market, exemplified by games like the incredibly fast-paced motorcycle racing game found at Game balap motor super cepat.
This rapid release cycle, a key component of growth-focused models, ensures consistent revenue streams and user retention.